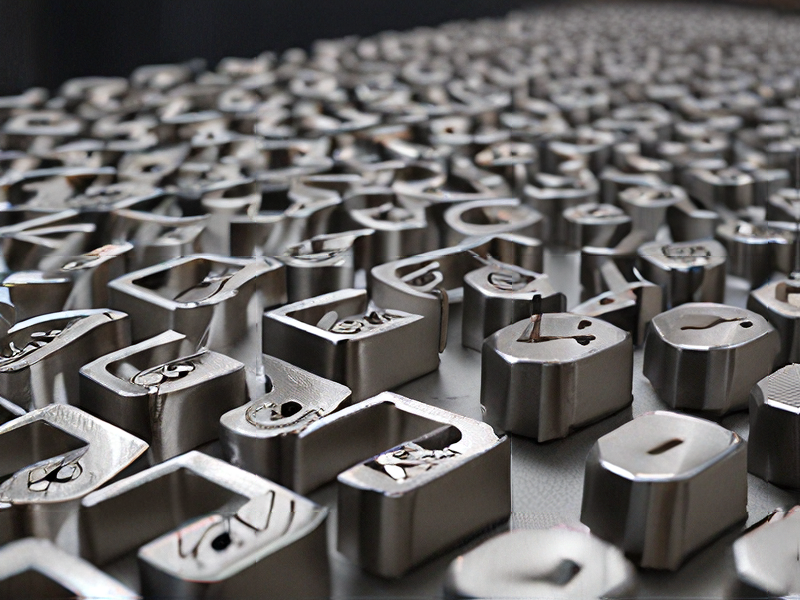
Technology and Applications of 3d print metal
3D printing of metal, also known as metal additive manufacturing, has revolutionized various industries by enabling the creation of complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods struggle to achieve. The technology primarily employs processes such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and Binder Jetting.
SLM utilizes a laser to fuse metal powder layer by layer, creating highly dense parts suitable for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications. EBM operates similarly but uses an electron beam in a vacuum, which is effective for high-temperature materials and provides excellent mechanical properties.
The applications of metal 3D printing are vast. In aerospace, it allows for lightweight components, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. The automotive industry benefits from rapid prototyping and the manufacture of complex parts that reduce assembly time. In the medical field, custom implants and tools can be produced to fit individual patient needs, improving treatment outcomes.
Metal 3D printing also allows for material optimization, reducing waste compared to subtractive methods. This capability promotes sustainable practices in manufacturing, as components are produced only as needed. Furthermore, the technology supports on-demand production, minimizing inventory costs and enabling localized manufacturing.
While metal 3D printing offers numerous advantages, challenges such as high equipment costs, surface finish quality, and material limitations still exist. However, ongoing advancements in technology are steadily overcoming these hurdles, making metal 3D printing an increasingly viable option for various sectors. As research continues to push the boundaries, the future of metal additive manufacturing looks promising, paving the way for innovative designs and applications.
Quality Testing Methods for 3d print metal and how to control quality
Quality testing in 3D printed metal components is critical to ensure mechanical integrity and performance. Key methods include:
1. Visual Inspection: Initial checks involve examining the surface for defects such as cracks, porosity, and incomplete fusion. This can be done using magnifying tools or automated vision systems.
2. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
– Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws.
– X-Ray or Computed Tomography (CT): Provides detailed 2D or 3D imaging to identify internal defects without damaging the part.
– Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT): Effective for detecting surface and near-surface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials.
3. Mechanical Testing:
– Tensile Testing: Determines the material’s strength, ductility, and elasticity by pulling a sample until it fractures.
– Hardness Testing: Measures resistance to deformation, often using methods such as Rockwell or Vickers hardness tests.
4. Microstructural Analysis: Employing optical or scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to investigate grain structure and distribution, which can affect mechanical properties.
Quality Control:
– Standardized Processes: Implement standards such as ISO and ASTM for 3D metal printing to ensure consistency across production.
– Process Monitoring: Continuously check parameters (temperature, laser power, build speed) during the printing process with sensors to detect deviations in real-time.
– Post-Processing Assessments: Conduct regular evaluations post-printing, including heat treatment or surface finishing checks to optimize material properties.
By combining these methods and controls, manufacturers can achieve high-quality outcomes in 3D metal printing, ensuring performance and reliability in final applications.
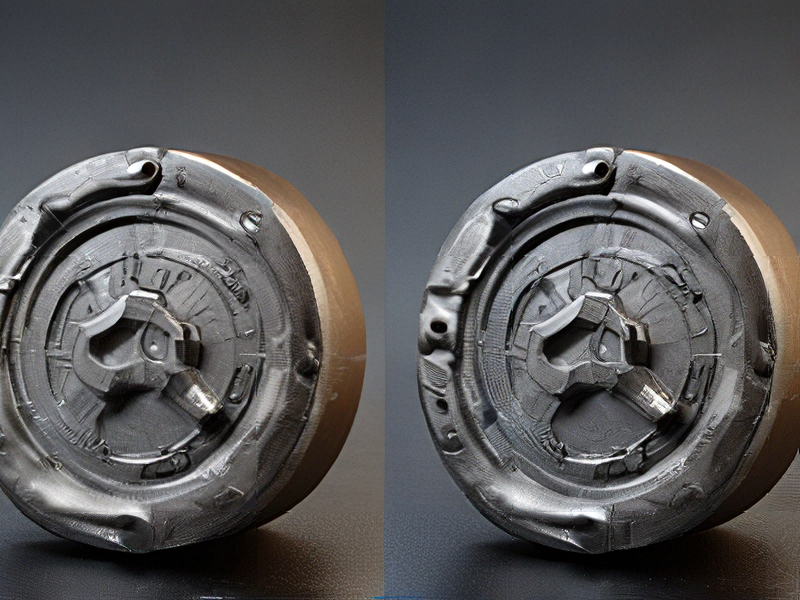

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from 3d print metal
When considering procurement of 3D-printed metal components, it’s essential to evaluate several key factors to ensure quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some tips and considerations:
1. Material Selection: Understand the different metal materials available for 3D printing, such as titanium, aluminum, stainless steel, and cobalt-chrome. Each has unique properties affecting strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and cost.
2. Technology and Process: Familiarize yourself with the various 3D printing technologies (e.g., Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), Electron Beam Melting (EBM)). Assess which technology aligns best with your requirements regarding precision, surface finish, and production volume.
3. Supplier Capability: Evaluate potential suppliers for their experience, certifications (like ISO 9001), and quality assurance processes. Request samples and assess their ability to meet your specifications consistently.
4. Design Considerations: Ensure that your designs are optimized for 3D printing. Consider factors like part geometry, complexity, and the orientation during printing, which can significantly impact strength and post-processing needs.
5. Cost Analysis: Analyze the total cost of ownership, including printing costs, post-processing, and potential rework. Compare these with traditional manufacturing methods to make informed decisions.
6. Lead Times: Understand the lead times for production, which can vary significantly between suppliers and processes. Align your procurement timeline with your production schedules.
7. Post-Processing Needs: Be aware of the necessary post-processing techniques (e.g., heat treatment, machining, surface finishing), which may add time and cost to your project.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make informed decisions that enhance the effectiveness of your procurement strategy for 3D-printed metal components.
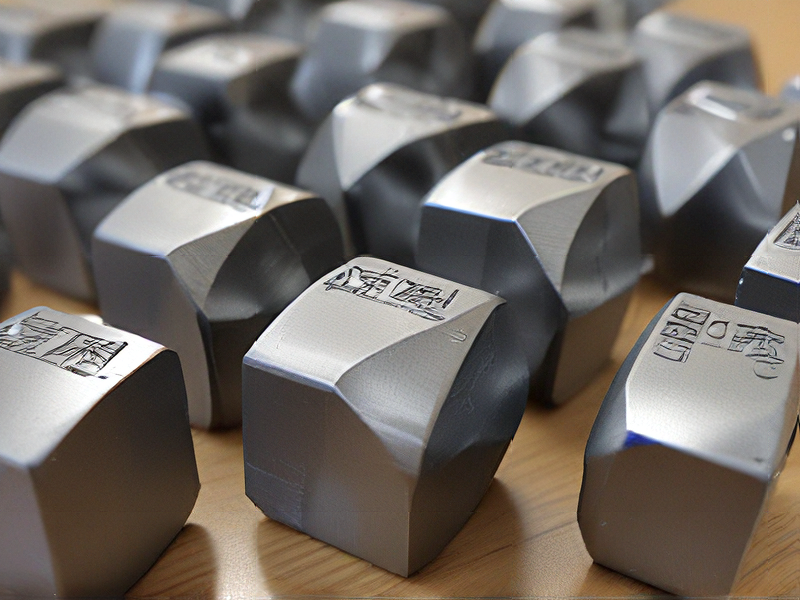

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from 3d print metal in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing 3D Printed Metal in China
1. What materials can be used for 3D printing metal in China?
Common materials include stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and nickel alloys. Each material has unique properties tailored for different applications.
2. What technologies are typically used for metal 3D printing?
The most prevalent technologies are Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM), both of which involve melting metal powders layer by layer.
3. How can I find reliable manufacturers?
Conduct extensive research using platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, or local trade shows. Verify through client testimonials, certifications, and factory visits if possible.
4. What are the typical lead times for production?
Lead times usually range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on complexity, material availability, and order volume.
5. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
MOQs vary between manufacturers. Some may accept small batches, while others may require higher volumes for cost-effectiveness.
6. Are there quality control standards to adhere to?
Yes, it’s essential to have clear agreements on quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Request samples and inspect them before full production.
7. How can I ensure intellectual property protection?
Sign Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and utilize legal protections available under Chinese law. Engaging local legal counsel is advisable.
8. What are the shipping options from China?
Shipping methods include air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Consider working with a freight forwarder to manage logistics.
9. How do I manage costs?
Factor in material costs, production complexity, shipping, and tariffs. Conduct thorough price comparisons and negotiate terms upfront.

