Technology and Applications of 3d printers for metal
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has revolutionized the production of metal parts across various industries due to its ability to create complex geometries and enhance material efficiency. Using techniques like Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and direct energy deposition, metal 3D printers fuse metal powders layer by layer to form parts.
Applications:
1. Aerospace: Lightweight, intricate components like turbine blades and brackets are produced to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency. 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and customization for specific aircraft needs.
2. Automotive: Manufacturers leverage metal 3D printing for rapid prototyping and the production of low-volume parts, such as brackets and housings, allowing for more efficient design iterations and reductions in waste.
3. Medical: Customized implants and prosthetics are created to meet individual patient requirements. This ensures better fit and functionality, enhancing patient outcomes.
4. Tooling: Metal 3D printing allows for the rapid production of molds, dies, and other tooling methods that can be quickly iterated upon, reducing lead times significantly.
5. Oil and Gas: Components that withstand extreme environments, such as valves and pumps, are produced with high precision, supporting increased efficiency and reducing downtime.
Advantages:
Metal 3D printing reduces material waste, allows for complex designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing, and shortens production times. As technology evolves, advancements in metal alloys and printing techniques promise even greater applications and efficiencies, solidifying 3D printing’s position as a disruptive force in manufacturing.
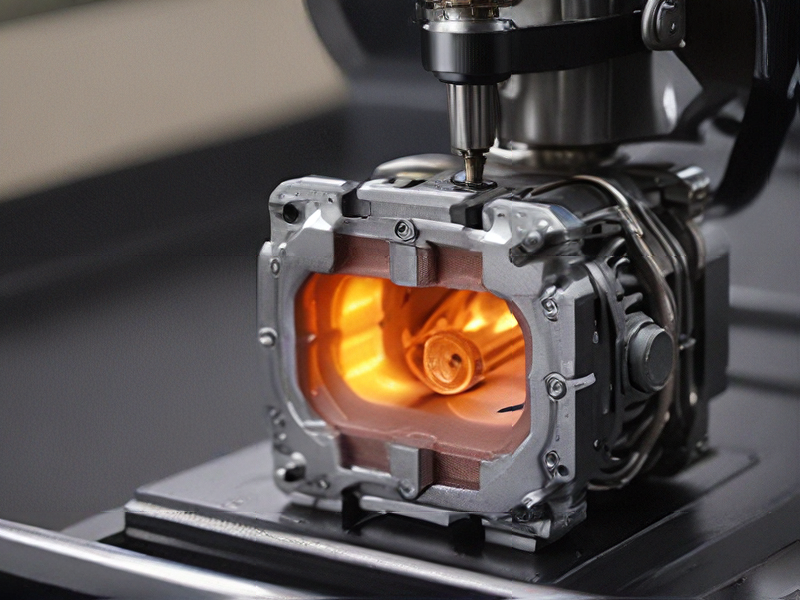

Quality Testing Methods for 3d printers for metal and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for 3D printers in metal include various techniques aimed at ensuring the integrity and performance of printed components. Key methods include:
1. Visual Inspection: Initially, inspect the printed parts for surface defects, irregular geometries, and inconsistencies. Employ optical systems or scanning technology for detailed analysis.
2. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing, X-ray computed tomography, and magnetic particle inspection can be useful to identify internal defects such as voids or cracks without damaging the component.
3. Mechanical Testing: Conduct tensile, compressive, and fatigue tests to determine the strength, ductility, and durability of the printed parts. These tests validate the material properties and performance under load.
4. Microstructural Analysis: Employ metallography to examine the grain structure and phase distribution in the material. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can provide insights into the material’s microstructure and reveal defects such as porosity.
5. Dimensional Accuracy Assessment: Utilize coordinate measurement machines (CMM) or laser scanning for precise dimensional verification against CAD specifications to ensure tolerances are met.
To control quality, implement a robust quality management system that includes:
– Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop clear protocols for every aspect of the printing process.
– Regular Calibration and Maintenance: Ensure that printers and measuring instruments are regularly calibrated to maintain precision.
– Data Acquisition and Monitoring: Use sensors to monitor process parameters like temperature and laser power in real-time, enabling immediate correction of deviations from desired parameters.
– Post-Processing Inspection: Establish a routine for testing parts after printing to identify any defects introduced during the manufacturing process.
By integrating these methods, manufacturers can maintain high standards of quality and reliability in metal 3D printing.

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from 3d printers for metal
When procuring metal 3D printers, it’s essential to consider several key factors to ensure you make an informed decision that aligns with your organization’s needs.
1. Application Requirements: Define the specific applications you plan to use the 3D printer for, whether prototyping, tooling, or final production parts. This will guide you in selecting the appropriate technology (e.g.,Selective Laser Melting, Electron Beam Melting).
2. Material Compatibility: Different 3D printers support various metals (e.g., titanium, stainless steel, aluminum). Ensure that the printer you select can work with the materials that meet your business’s quality and performance standards.
3. Build Volume and Size: Assess the maximum build volume required for your projects. A larger build area allows for bigger components or multiple parts to be produced simultaneously, optimizing production capabilities.
4. Print Speed and Efficiency: Evaluate the print speed based on your production needs. Faster printers may have higher upfront costs but can lead to significant time savings in the long run.
5. Post-Processing Requirements: Understand the post-processing steps involved, as these can affect production timelines and costs. Consider if the printer includes features that simplify post-processing.
6. User-Friendliness and Support: Opt for models that are user-friendly and come with reliable customer support. Training and maintenance services may be critical for effective usage.
7. Cost Considerations: Factor in not just the initial investment but also ongoing operational costs, including maintenance, material sourcing, and potential downtime.
By carefully considering these elements, you can make a strategic procurement decision that maximizes the return on investment for your metal 3D printing needs.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from 3d printers for metal in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from 3D Printers for Metal in China
1. What are the benefits of using 3D printing for metal parts in China?
3D printing offers design flexibility, reduced material waste, and the ability to create complex geometries that traditional methods struggle with. Additionally, China’s advanced manufacturing infrastructure can lead to cost-effective production.
2. What types of metals can be 3D printed in China?
Common metals include stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and cobalt-chrome. Specific processes may vary, so confirm material compatibility with your project needs.
3. How do I find a reliable manufacturer for metal 3D printing?
Research suppliers via online platforms, trade shows, and industry directories. Verify their credentials, read reviews, ask for past work samples, and request references from previous clients.
4. What is the typical lead time for 3D printed metal parts?
Lead times vary based on complexity, quantity, and manufacturer. Generally, you can expect a turnaround of 2 to 4 weeks for prototypes and longer for larger production runs.
5. Are there quality assurance processes in place?
Reputable manufacturers in China implement strict quality control measures, including material testing, dimensional inspections, and certifications like ISO. Clarify these processes during initial discussions.
6. What are the cost factors involved in metal 3D printing?
Costs are influenced by material choice, part complexity, production volume, and post-processing requirements. Request detailed quotes to compare.
7. How can I ensure intellectual property protection?
Sign Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and consider using reputable lawyers familiar with Chinese IP law to ensure your designs and technologies are safeguarded.
8. What post-processing options are available?
Common post-processing techniques include machining, polishing, heat treatment, and surface finishing to improve aesthetics and functionality.