Description
cnc router tables Safety Certifications
CNC router tables require strict adherence to safety certifications and guidelines to ensure operator safety, equipment protection, and high-quality outputs. Several key aspects encompass these safety measures:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators must wear safety glasses, hearing protection, and dust masks. Loose clothing and long hair should be secured to prevent entanglement with the machine.
2. Machine Inspection and Maintenance: Regular inspection of the CNC router for signs of wear or damage is essential. This includes checking cutting tools, ensuring proper material fixation, and verifying that workpieces are within the machine’s capacity. Maintenance should follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, including routine lubrication and calibration.
3. Workspace Setup: The workspace should be clean, well-ventilated, and sufficiently lit. Adequate space around the machine is crucial to prevent accidents, and dust extraction systems should be in place to manage airborne particles.
4. Operational Procedures: Proper machine setup involves homing and zeroing the machine before each job, setting correct spindle speeds and feed rates, and verifying toolpaths through simulation. Operators should never leave the machine unattended during critical phases of operation and should know how to use emergency stop mechanisms.
5. Training and Compliance: Comprehensive training on machine operation, safety protocols, and emergency procedures is mandatory for all operators. Compliance with industry-specific safety standards and regional regulations helps avoid legal issues and enhances operational safety.
6. Emergency Procedures: Clear emergency procedures and evacuation routes should be established. Operators must be familiar with the location and use of emergency stop buttons to quickly halt the machine in case of malfunction.
These safety practices not only protect operators and equipment but also ensure continuous, high-quality production. Adherence to these guidelines fosters a safer, more efficient working environment and aligns with legal and ethical responsibilities.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “cnc router tables”
CNC router tables are crucial tools in woodworking, metalworking, and other industries, offering precision cutting, engraving, and drilling. Here are the key technical parameters to consider:
1. Work Area:
– Size: Defines the maximum dimensions of the material that can be processed. Common sizes include 4’x4′, 4’x8′, and 5’x10′.
2. Spindle:
– Power: Measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW), typically ranging from 1.5 kW to 12 kW.
– Speed: RPM (Revolutions Per Minute), often between 8,000 and 24,000 RPM.
3. Drive System:
– Type: Rack and pinion, ball screw, or lead screw mechanisms, influencing precision and maintenance needs.
4. Control System:
– Controller: Types include Mach3, Mach4, NC Studio, and proprietary controllers from manufacturers like Fanuc or Siemens.
– Interface: User interfaces often include USB, Ethernet, and touch screen displays.
5. Accuracy and Repeatability:
– Precision: Typically measured in micrometers (µm) or thousandths of an inch (mil), with high-end machines offering accuracy within ±0.01 mm.
– Repeatability: Indicates the machine’s ability to return to a position consistently, often within ±0.05 mm.
6. Table Type:
– Material: Aluminum, steel, or cast iron, each affecting durability and vibration resistance.
– Vacuum or T-Slot: Vacuum tables offer fast setup and hold down of materials, while T-slot tables provide flexible clamping options.
7. Motor Type:
– Stepper vs. Servo Motors: Stepper motors are cost-effective with good precision, while servo motors offer higher speed, torque, and better precision control.
8. Software Compatibility:
– CAD/CAM Software: Compatibility with software such as VCarve, AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Fusion 360.
9. Machine Frame:
– Construction: Rigid construction materials like steel or aluminum to minimize vibrations and ensure stability.
10. Cutting Speed and Feed Rate:
– Speed: Maximum movement speed, typically up to 300 inches per minute (IPM) or higher.
– Feed Rate: The rate at which the tool moves through material, usually adjustable depending on material and cutting requirements.
These parameters help ensure the CNC router table is suitable for specific applications, balancing precision, speed, and durability.
List Product features of “cnc router tables”
CNC router tables are precision-driven machines used for cutting, engraving, and shaping various materials such as wood, plastic, and metal. Here are the key features:
1. Table Size and Work Area: Sizes vary, with work areas typically ranging from small desktop versions to large industrial models. The table size determines the maximum material dimensions the router can handle.
2. Spindle Motor: The power and speed of the spindle motor, usually measured in horsepower (HP) and RPM, affect the cutting efficiency and the types of materials that can be processed.
3. Drive System: Common drive systems include rack and pinion, ball screw, and lead screw mechanisms. These systems influence precision, speed, and maintenance requirements.
4. Control System: CNC routers use computer numerical control (CNC) systems to automate and control movements. Advanced systems offer user-friendly interfaces, touchscreen controls, and compatibility with various design software.
5. Construction Material: Frames are often made from steel, aluminum, or a combination to ensure durability and stability during operation.
6. Cutting Tool Compatibility: CNC router tables support various cutting tools and bits, enhancing versatility in cutting, engraving, drilling, and shaping tasks.
7. Vacuum Table: Some models feature vacuum tables to hold materials securely in place during machining, reducing movement and improving precision.
8. Software Compatibility: Compatibility with CAD/CAM software is essential for designing and executing complex patterns and shapes.
9. Axis Configuration: Most routers operate on 3-axis (X, Y, Z), but advanced models may include additional axes (4-axis or 5-axis) for more complex machining.
10. Cooling System: Integrated cooling systems, such as air or liquid cooling, help maintain optimal operating temperatures and prolong the lifespan of the spindle and cutting tools.
11. Dust Collection: Built-in dust collection systems or ports for external vacuums help maintain a clean work environment and prevent material buildup on the machine.
12. Safety Features: Emergency stop buttons, protective covers, and safety interlocks ensure safe operation for users.
13. Ease of Use: Features like automatic tool changers (ATC), tool height setters, and user-friendly software interfaces enhance ease of use and efficiency.
These features collectively determine the performance, versatility, and user experience of CNC router tables, making them suitable for various industrial and hobbyist applications.
List Application of “cnc router tables”
CNC router tables are versatile tools with applications across various industries due to their precision, efficiency, and ability to handle complex designs. Here are some common applications:
1. Woodworking: CNC router tables are extensively used in woodworking for cutting, shaping, and carving intricate designs in wood. This includes creating furniture, cabinetry, decorative panels, and wooden signs. Their precision ensures consistent results and the ability to handle custom designs easily.
2. Sign Making: These machines are ideal for producing detailed signs, including 3D lettering and intricate graphics. They can work with various materials like wood, plastic, and metal, making them a favorite in the signage industry.
3. Prototyping: In product development, CNC router tables are used for rapid prototyping. They allow designers to quickly create and test models, making it easier to iterate and refine designs before mass production.
4. Arts and Crafts: Artists and craftsmen use CNC router tables to create detailed artwork, including sculptures, jewelry, and decorative items. The precision and versatility of these machines enable the production of complex patterns and fine details.
5. Automotive Industry: CNC routers are used to produce parts and components for vehicles. This includes custom dashboards, interior panels, and other intricate parts that require high precision and consistency.
6. Aerospace: In aerospace, CNC router tables are used to cut and shape lightweight materials like composites and aluminum for aircraft components. Their ability to produce parts with tight tolerances is critical in this industry.
7. Plastics and Composites: These machines are used to cut and shape various plastics and composite materials, which are common in industries like electronics, automotive, and aerospace.
8. Education: CNC router tables are used in educational settings to teach students about manufacturing processes, CAD/CAM software, and machine operation, preparing them for careers in engineering and manufacturing.
Overall, CNC router tables are essential tools in any field that requires precision cutting, shaping, and design, significantly enhancing productivity and enabling the creation of complex and customized products.
List Various Types of “cnc router tables”
CNC router tables come in various types, catering to different applications and user needs. Here are some of the main types:
1. Benchtop CNC Router Tables:
– Compact Size: Designed for small shops or hobbyists with limited space.
– Applications: Ideal for engraving, small part manufacturing, and detailed work on materials like wood, plastic, and soft metals.
– Features: Typically have a smaller work area and are more affordable.
2. Desktop CNC Router Tables:
– Moderate Size: Larger than benchtop models, suitable for small to medium-sized projects.
– Applications: Used for crafting, sign making, and educational purposes.
– Features: Offer a balance between size, power, and cost, often portable.
3. Mid-Sized CNC Router Tables:
– Medium to Large Size: Fit for small businesses and professional workshops.
– Applications: Versatile for woodworking, cabinet making, and metalwork.
– Features: Provide a larger work area and more robust construction than benchtop and desktop models.
4. Full-Sized CNC Router Tables:
– Large Size: Designed for industrial applications.
– Applications: High-volume production, large-scale woodworking, and metal fabrication.
– Features: Heavy-duty construction, expansive work areas, and advanced capabilities.
5. 5-Axis CNC Router Tables:
– Advanced Design: Capable of moving the cutting tool in five different axes.
– Applications: Complex and precise work such as aerospace components, automotive parts, and intricate carvings.
– Features: Highly versatile and capable of producing intricate designs and shapes.
6. Multi-Head CNC Router Tables:
– Multiple Spindles: Feature multiple cutting heads to work on several parts simultaneously.
– Applications: Mass production and efficiency in repetitive tasks.
– Features: Increase productivity and reduce production time.
7. Vacuum CNC Router Tables:
– Vacuum Hold-Down: Use a vacuum system to secure materials to the table.
– Applications: Ensuring precision and stability in cutting operations.
– Features: Enhance material handling, especially for thin or lightweight materials.
8. Rotary Axis CNC Router Tables:
– Rotary Attachment: Include an additional rotary axis for cylindrical workpieces.
– Applications: 3D carving, producing rounded or multi-sided parts.
– Features: Expand the machine’s capabilities beyond flat surface work.
Each type of CNC router table is designed to meet specific needs, from hobbyists and small business operations to large industrial applications.
cnc router tables Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
CNC router tables are versatile tools used in woodworking, metalworking, and other material cutting applications. Enhancing their functionality through accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options can significantly improve performance and efficiency.
Accessories
1. Dust Collection Systems: Essential for maintaining a clean work environment and ensuring the longevity of the machine by preventing dust buildup.
2. Vacuum Tables: Help in securing materials during cutting, reducing movement and improving precision.
3. Spindle Upgrades: Higher RPM spindles can handle tougher materials and increase cutting speeds.
4. Tool Changers: Automatic tool changers (ATCs) enhance productivity by minimizing manual intervention during tool changes.
5. Clamping Systems: Provide a secure hold for various materials, ensuring precise cuts.
Upgrades
1. Software Enhancements: Advanced CAD/CAM software can provide better control, more features, and improved efficiency.
2. Linear Guides and Bearings: Upgrading to higher quality guides and bearings can improve accuracy and reduce wear.
3. Higher Power Motors: More powerful motors can handle tougher materials and provide faster cutting speeds.
4. Control Systems: Upgrading to more advanced control systems can offer better user interfaces, more precise controls, and additional features like remote monitoring.
5. Cooling Systems: Enhancements like misting or liquid cooling can help manage heat during intensive operations, protecting both the tool and material.
Custom Manufacturing Options
1. Table Size Adjustments: Customizing the size of the table to fit specific workshop spaces or material sizes can optimize workflow.
2. Material-Specific Modifications: Customizing the router to handle specific materials, such as adding specialized spindles for metal or stone cutting.
3. Additional Axis: Adding a fourth or fifth axis can greatly expand the capabilities of the router, allowing for more complex and detailed work.
4. Frame Customization: Reinforcing or customizing the frame for specific needs, such as heavy-duty operations or portability.
5. Safety Features: Custom safety features like enclosures or emergency stop systems tailored to specific operational environments.
By selecting the right combination of accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options, users can significantly enhance the capabilities and efficiency of their CNC router tables, tailoring them to meet specific needs and challenges.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “cnc router tables”
Quality Control in CNC Router Table Manufacturing:
1. Material Inspection:
– Raw materials, including metals and electronics, are inspected for defects.
– Suppliers are vetted, and materials come with certifications of compliance.
2. Dimensional Accuracy:
– Parts are measured using precision tools like calipers and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) to ensure they meet design specifications.
3. Component Testing:
– Motors, drives, and controllers are tested for performance.
– Electrical components undergo rigorous testing to ensure functionality.
4. Assembly Checks:
– Assembled units are inspected to ensure correct fit and function.
– Each step in the assembly process is documented and verified.
5. Functional Testing:
– Completed CNC router tables are tested under load to simulate real-world conditions.
– Precision tests include cutting tests on various materials to verify accuracy and repeatability.
6. Final Inspection:
– A thorough final inspection checks for visual defects, alignment, and operational functionality.
– Documentation is reviewed to ensure all QC steps have been completed.
7. Continuous Improvement:
– Feedback from customers is analyzed to identify recurring issues and improve processes.
– Regular audits and employee training help maintain high standards.
Manufacturing Process of CNC Router Tables:
1. Design and Engineering:
– CAD software is used to design the router table and its components.
– Prototypes are developed and tested.
2. Material Procurement:
– High-quality materials, such as aluminum, steel, and electronic components, are sourced.
– Suppliers are chosen based on reliability and quality.
3. Machining:
– CNC machining is used to produce precise parts.
– Processes include milling, turning, and grinding.
4. Assembly:
– The frame, gantry, and other components are assembled.
– Wiring and electronic components are installed.
5. Software Integration:
– Control software is installed and configured.
– Systems are calibrated for accuracy.
6. Testing and Calibration:
– Each unit undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets specifications.
– Adjustments are made as necessary to fine-tune performance.
7. Packaging and Shipping:
– Finished products are carefully packaged to prevent damage during transit.
– Products are shipped with detailed manuals and support documents.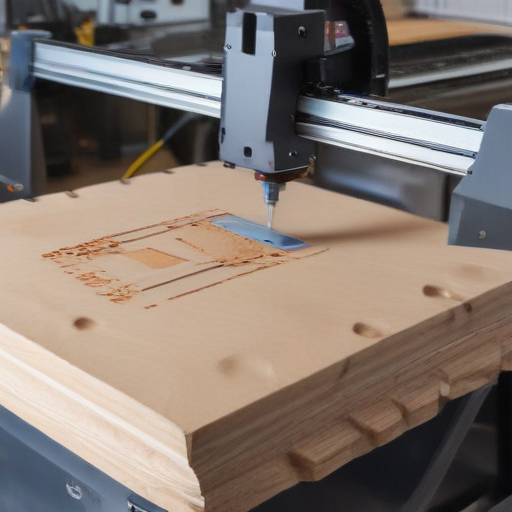
Materials of “cnc router tables”
CNC router tables are designed for precision machining and come in various materials, each chosen for specific properties that suit different applications. Here are the primary materials used:
1. Steel:
– Properties: High strength, durability, and rigidity.
– Advantages: Ideal for heavy-duty machining, capable of handling tough materials, and resistant to wear and deformation.
– Applications: Often used in industrial settings where high precision and durability are paramount.
2. Aluminum:
– Properties: Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent thermal conductivity.
– Advantages: Easier to transport and install, suitable for high-speed machining, and less prone to rust.
– Applications: Common in hobbyist and light industrial machines where portability and efficiency are important.
3. Cast Iron:
– Properties: Extremely rigid, high damping capacity, and excellent vibration absorption.
– Advantages: Reduces chatter and vibrations during machining, providing superior surface finishes.
– Applications: Used in high-precision CNC routers requiring minimal deflection and high stability.
4. Composite Materials:
– Properties: Vary widely but typically include a combination of resin and fiber (carbon or glass).
– Advantages: Lightweight, high stiffness, and corrosion-resistant.
– Applications: Ideal for custom or specialized CNC router tables where specific performance characteristics are needed.
5. MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard):
– Properties: Smooth, consistent surface, and affordable.
– Advantages: Easy to replace, good for prototyping, and suitable for soft materials like wood and plastics.
– Applications: Often used for spoilboards or in low-cost CNC routers aimed at woodworking and light-duty applications.
Each material offers unique benefits, making it essential to choose the right one based on the specific requirements of the machining tasks, the types of materials being worked on, and the desired precision and durability of the CNC router table.
“cnc router tables” Comparative Analysis
Comparative Analysis of CNC Router Tables in 2024
CNC router tables offer a range of features and capabilities that cater to both professional woodworkers and hobbyists. Here’s a comparative analysis of some of the top models available in 2024:
#### 1. Axiom Iconic Series
– Price: Starting at $4,000
– Work Area: Various sizes, up to 24” x 48”
– Materials: Wood, plastics, soft metals
– Features: User-friendly design, over 20 available accessories, intuitive DSP pendant controller, minimal dead space footprint.
– Pros: Ideal for beginners, extensive learning resources, good for small to medium projects.
– Cons: Expensive for entry-level users【5†source】【6†source】.
#### 2. BobsCNC KL744
– Price: Starting at $2,875
– Work Area: 48” x 48” x 5”
– Materials: Primarily wood
– Features: SG25U supported rail system, NEMA 23 Servo motor, drag chain wire management, dual 48 VDC power supply.
– Pros: Great for intricate designs, renowned customer support, energy efficient.
– Cons: Complex assembly process【5†source】.
#### 3. Laguna Swift 4×8 CNC Router
– Price: $14,495
– Work Area: 4×8 feet
– Materials: Various, including thick wood and metals
– Features: Rack and pinion drive system, high-speed cutting, MDF pads and T-slots, optional vacuum table.
– Pros: High accuracy and speed, durable, versatile.
– Cons: Expensive vacuum table upgrade, higher initial cost【8†source】.
#### 4. ShopBot PRSalpha Series
– Price: $20,344 (without spindle)
– Work Area: 4×8 feet
– Materials: Various, including metals
– Features: Industrial-grade spindle, robust construction, intuitive control software.
– Pros: High-speed cutting, excellent for large projects, robust accessories.
– Cons: Requires a computer to operate, not as rigid as some competitors【9†source】【8†source】.
#### 5. StyleCNC 4×8 CNC Router
– Price: $3,980
– Work Area: 4×8 feet
– Materials: Wood, soft metals
– Features: Cast iron frame, 3kW water-cooled spindle, vacuum table, DSP controller.
– Pros: Affordable, robust design, powerful spindle.
– Cons: Basic drive system, entry-level capabilities【8†source】.
#### 6. SainSmart Genmitsu CNC Router Machine
– Price: Varies by model
– Work Area: Various small-scale sizes
– Materials: Wood, plastics, soft metals
– Features: Pre-assembled, laser module upgrade, quiet operation.
– Pros: Easy to set up, versatile, affordable.
– Cons: Limited to smaller projects, not suitable for advanced users【6†source】.
Conclusion
Selecting the right CNC router table depends on your specific needs, whether it’s for professional, high-volume woodworking or smaller, detailed projects. Models like the Axiom Iconic Series and Laguna Swift are great for professional use, offering robust features and high precision, while options like the BobsCNC KL744 and SainSmart Genmitsu are better suited for hobbyists and small business projects due to their affordability and ease of use【5†source】【7†source】【9†source】.
“cnc router tables” Warranty and Support
When purchasing a CNC router table, understanding the warranty and support options is crucial for ensuring long-term reliability and productivity. Here’s a concise overview of what to look for:
Warranty
1. Duration: Warranties typically range from one to three years. Look for longer durations as they often indicate confidence in the product’s durability.
2. Coverage: Ensure the warranty covers critical components such as the spindle, control system, and mechanical parts. Some warranties might exclude consumables like bits and collets.
3. Conditions: Understand the terms and conditions. Some warranties might require regular maintenance by authorized technicians or adherence to specific operational guidelines to remain valid.
4. Exclusions: Be aware of what is not covered. Misuse, improper installation, or modifications might void the warranty.
Support
1. Technical Support: Opt for manufacturers that offer robust technical support. This includes phone support, email support, and live chat. Availability during your operational hours is beneficial.
2. Training: Comprehensive training programs can significantly reduce the learning curve. Look for companies that provide in-person or virtual training sessions.
3. Documentation: Ensure access to detailed manuals, troubleshooting guides, and instructional videos. These resources can be invaluable for both new and experienced users.
4. Service: Check if on-site service is available and understand the costs involved. Remote diagnostics and support can also be a cost-effective and time-saving option.
5. Community and Forums: A strong user community can provide peer support, share tips, and offer solutions based on real-world experiences.
Recommendations
– Research and Reviews: Investigate customer reviews and testimonials regarding warranty and support experiences.
– Vendor Reputation: Choose well-established vendors with a proven track record in customer service and support.
Prioritizing these factors will help you choose a CNC router table that not only meets your technical needs but also provides peace of mind through reliable warranty and support services.
List “cnc router tables” FAQ
CNC Router Tables FAQ
1. What is a CNC router table?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) router table is a machine used to cut, carve, and engrave materials such as wood, plastic, metal, and foam. It is controlled by a computer, which ensures precise and repeatable movements.
2. How does a CNC router table work?
A CNC router table operates by following a pre-programmed design, typically created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design is converted into G-code, which the machine’s controller interprets to move the router along X, Y, and Z axes.
3. What materials can be used with a CNC router table?
CNC router tables can work with various materials, including wood, MDF, plywood, plastic, aluminum, brass, and foam.
4. What are the benefits of using a CNC router table?
Benefits include high precision, repeatability, efficiency, and the ability to produce complex shapes. It also reduces human error and allows for mass production of parts.
5. What is the difference between a CNC router and a CNC mill?
CNC routers are typically used for cutting softer materials and are designed for high-speed operations. CNC mills are more robust and can handle harder materials like metals with higher precision but generally at slower speeds.
6. How do I choose the right CNC router table for my needs?
Consider factors such as the size of the work area, material compatibility, spindle power, precision requirements, software compatibility, and budget.
7. What maintenance does a CNC router table require?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning the table and components, lubricating moving parts, checking and tightening bolts, and ensuring the software and firmware are up to date.
8. Is training required to operate a CNC router table?
Yes, basic training is recommended to understand the software, machine operation, safety protocols, and maintenance procedures.
9. Can I upgrade my CNC router table?
Many CNC router tables offer upgrade options such as more powerful spindles, vacuum hold-down systems, and enhanced control software.
10. How much does a CNC router table cost?
Prices vary widely based on size, features, and capabilities. Entry-level models can start around $2,000, while industrial models can exceed $50,000.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about cnc router tables for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure! Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQs) with answers for buyers sourcing CNC router tables from China:
1. What should I consider when choosing a CNC router table?
– Consider the table size, spindle power, precision, speed, software compatibility, and the specific materials you plan to work with.
2. What are the common types of CNC router tables available?
– The common types include 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC routers, with variations for specific materials like wood, metal, and plastic.
3. What is the typical lead time for delivery?
– Lead times can vary but generally range from 30 to 60 days, depending on the manufacturer’s production schedule and your location.
4. What are the shipping options and costs?
– Shipping options include sea freight, air freight, and express courier services. Costs depend on the size and weight of the CNC router table and the shipping method chosen.
5. Are there any import duties or taxes?
– Yes, import duties and taxes vary by country. It’s essential to check your local regulations and factor these costs into your budget.
6. What warranty and after-sales support is provided?
– Most manufacturers offer a 1-2 year warranty on parts and components, with varying levels of after-sales support. Ensure you clarify this before purchase.
7. Can I customize the CNC router table to my specifications?
– Many Chinese manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific requirements. Discuss your needs with the supplier to confirm feasibility and costs.
8. What certifications should I look for?
– Look for certifications such as CE, ISO9001, and other relevant quality and safety standards applicable to your country.
9. How can I verify the credibility of a Chinese supplier?
– Verify through online reviews, third-party inspection services, factory visits, and checking business licenses and certifications.
10. What payment terms are typically accepted?
– Common payment terms include T/T (bank transfer), L/C (letter of credit), and sometimes PayPal for smaller orders. A typical structure might be 30% deposit and 70% before shipment.
These FAQs cover the essential aspects of sourcing CNC router tables from China, helping buyers make informed decisions.
