Description
aluminum metal casting Safety Certifications
Safety certifications are critical in aluminum metal casting to ensure workplace safety, environmental protection, and product quality. Here are key safety certifications relevant to aluminum metal casting:
1. ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems):
– This international standard specifies requirements for an occupational health and safety (OH&S) management system, aiming to improve employee safety, reduce workplace risks, and create better, safer working conditions.
2. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) Compliance:
– In the United States, OSHA sets and enforces standards to assure safe and healthful working conditions. Compliance with OSHA standards is crucial for preventing workplace injuries and illnesses in metal casting operations.
3. NFPA 484 (Combustible Metals Standard):
– This standard provides requirements for the safe processing, handling, and storage of combustible metals and their alloys, including aluminum. It addresses fire and explosion hazards unique to these materials.
4. EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) Regulations:
– Compliance with EPA regulations ensures that metal casting facilities manage pollutants and hazardous waste properly, thus protecting the environment and public health.
5. ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems):
– While primarily a quality management standard, ISO 9001 includes provisions that impact safety by ensuring consistent production processes and adherence to safety protocols.
6. ANSI Z10 (Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems):
– This American standard provides a framework for a comprehensive occupational health and safety management system, emphasizing continual improvement and proactive safety measures.
7. ASTM Standards:
– Various ASTM standards are applicable to aluminum casting, ensuring that safety, quality, and performance criteria are met during the casting process.
8. IATF 16949 (Automotive Quality Management System):
– This standard is particularly relevant for aluminum casting companies supplying the automotive industry. It includes stringent requirements for quality and safety in the manufacturing process.
These certifications and standards collectively ensure that aluminum metal casting operations adhere to rigorous safety, health, and environmental protocols, thereby safeguarding workers, the environment, and end-users.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “aluminum metal casting”
Aluminum Metal Casting Technical Parameters
1. Alloy Composition:
– Commonly used alloys: 356, 319, 6061, and 7075.
– Elements: Silicon, copper, magnesium, manganese, and zinc.
2. Melting Temperature:
– Pure aluminum: ~660.3°C (1220.54°F).
– Alloyed aluminum: 600-700°C (1112-1292°F).
3. Pouring Temperature:
– Typically 680-750°C (1256-1382°F) depending on the alloy and casting process.
4. Mold Materials:
– Sand, permanent mold (steel), ceramic, and investment (wax) molds.
5. Casting Processes:
– Sand casting, die casting, investment casting, and permanent mold casting.
6. Cooling Rate:
– Controlled cooling to avoid defects, such as porosity and shrinkage. Rapid cooling in die casting, slower in sand and permanent mold casting.
7. Solidification Time:
– Varies with part size and cooling method; typically minutes to hours.
8. Casting Tolerances:
– Dimensional tolerances: ±0.1-0.5 mm.
– Surface finish: 125-500 microinches RMS.
9. Mechanical Properties:
– Tensile strength: 150-450 MPa.
– Yield strength: 75-400 MPa.
– Elongation: 1-15% depending on the alloy and heat treatment.
10. Heat Treatment:
– Solution heat treatment, quenching, and aging to achieve desired mechanical properties.
11. Density:
– 2.6-2.8 g/cm³ depending on the alloy.
12. Casting Yield:
– Typically 50-75%, influenced by gating design and riser placement.
13. Casting Defects:
– Common defects: Porosity, inclusions, shrinkage, and cold shuts.
– Inspection techniques: X-ray, ultrasonic, dye penetrant, and visual inspection.
14. Gating System:
– Proper design to ensure smooth flow and minimal turbulence.
15. Ventilation:
– Adequate venting to avoid gas entrapment.
These parameters ensure optimal aluminum casting performance, influencing quality, efficiency, and mechanical properties of the final product.
List Product features of “aluminum metal casting”
Aluminum Metal Casting: Product Features
1. Lightweight: Aluminum metal castings are significantly lighter than those made from other metals, which reduces the overall weight of products without compromising strength.
2. High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum castings maintain excellent mechanical strength while being lightweight, making them ideal for applications where reducing weight is crucial.
3. Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, which enhances its resistance to corrosion and makes it suitable for use in harsh environments.
4. Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has high thermal conductivity, which makes it suitable for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation, such as in automotive and electronic components.
5. Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum’s good electrical conductivity makes it an excellent choice for electrical and electronic applications.
6. Machinability: Aluminum castings are easy to machine, allowing for precise and complex geometries to be achieved with minimal tool wear.
7. Versatility in Design: Aluminum can be cast into a wide variety of shapes and sizes, offering flexibility in design and engineering.
8. Recyclability: Aluminum is 100% recyclable without losing its properties, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
9. Surface Finish: Aluminum castings typically have smooth surface finishes, which can be further enhanced through polishing or coating processes.
10. High Dimensional Stability: Aluminum maintains its shape and dimensions well under a wide range of temperatures and mechanical stresses.
11. Cost-Effective: Due to its abundance and the efficiency of the casting process, aluminum castings are often more cost-effective compared to other metal castings.
12. Durability: Aluminum castings offer good wear resistance and longevity, making them suitable for demanding applications.
13. Customization: The aluminum casting process allows for the inclusion of complex features, thin walls, and varying thicknesses, which can be customized to meet specific application requirements.
14. Compatibility with Coatings and Treatments: Aluminum castings can be easily anodized, painted, or treated to enhance their properties and appearance further.
15. Non-Magnetic: Aluminum is non-magnetic, making it suitable for applications where magnetic interference is a concern.
These features make aluminum metal casting a preferred choice in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics.
List Application of “aluminum metal casting”
Aluminum metal casting is a versatile manufacturing process with applications across numerous industries due to aluminum’s lightweight, strength, and resistance to corrosion. Here are some key applications:
1. Automotive Industry: Aluminum casting is extensively used to produce engine blocks, cylinder heads, transmission housings, and wheels. These components benefit from aluminum’s high strength-to-weight ratio, improving fuel efficiency and vehicle performance.
2. Aerospace Industry: Aluminum castings are vital in aerospace for parts like fuselage components, landing gear, and engine parts. Its light weight and high strength make it ideal for reducing aircraft weight and increasing payload capacity.
3. Construction: In construction, aluminum castings are used for structural components, window frames, and decorative elements. Its resistance to corrosion and durability make it suitable for building materials exposed to the elements.
4. Electronics: Aluminum is used in the electronics industry for manufacturing heat sinks, housings, and chassis for various electronic devices. Its excellent thermal conductivity helps in efficient heat dissipation, protecting sensitive components.
5. Marine Industry: The marine industry utilizes aluminum castings for boat hulls, propellers, and various fittings due to their corrosion resistance in saltwater environments and reduced weight for better buoyancy.
6. Consumer Goods: Aluminum casting is used to manufacture a wide range of consumer goods, including cookware, sports equipment, and furniture. Its lightweight and aesthetic appeal make it ideal for products requiring both form and function.
7. Industrial Equipment: In industrial applications, aluminum castings are used for pumps, valves, and various machinery parts. The material’s durability and ability to withstand harsh operating conditions are crucial for these applications.
8. Energy Sector: Aluminum castings are employed in the energy sector for components in wind turbines, solar panels, and electrical transformers. Its conductivity and lightweight properties are advantageous for efficient energy transfer and structural support.
Aluminum metal casting thus plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance, efficiency, and longevity of products across diverse sectors.
List Various Types of “aluminum metal casting”
Aluminum metal casting is a process where aluminum is melted and poured into molds to create desired shapes. There are several methods, each suited to specific applications and characteristics. Here are the main types:
1. Sand Casting: This is the most common method where a sand mold is used to shape the aluminum. It’s versatile and economical, suitable for producing large components like engine blocks and industrial parts.
2. Die Casting: In this high-pressure technique, molten aluminum is injected into a steel mold. It’s ideal for mass production of small to medium-sized parts with intricate designs, such as automotive components and consumer electronics housings.
3. Permanent Mold Casting: Also known as gravity die casting, this process uses reusable metal molds. It’s good for high-volume production of parts with better mechanical properties and surface finish compared to sand casting.
4. Investment Casting (Lost Wax Casting): This precision casting technique involves creating a wax model, coating it with ceramic, and melting the wax away. It produces complex shapes with excellent surface finish and accuracy, often used for aerospace and medical components.
5. Centrifugal Casting: This method involves pouring molten aluminum into a rotating mold, which forces the metal against the mold walls. It’s used to create cylindrical parts like pipes and bushings with high integrity and strength.
6. Continuous Casting: In this process, molten aluminum is continuously poured into a mold and solidified, then pulled out in a continuous length. It’s primarily used for producing aluminum billets, rods, and sheets.
7. Shell Mold Casting: Similar to sand casting, but uses a resin-covered sand to create a mold. It offers a better surface finish and is used for producing small to medium-sized parts with more precise dimensions.
8. Vacuum Die Casting: This is a variant of die casting where a vacuum is applied to remove air and gases from the mold cavity before injecting the molten metal. It enhances the mechanical properties and surface finish, suitable for high-performance parts.
Each method offers unique benefits and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the component being produced, including size, complexity, and production volume.
aluminum metal casting Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Aluminum metal casting is a versatile manufacturing process widely used for producing intricate and durable components. Accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options enhance the efficiency, quality, and functionality of this process.
Accessories:
1. Molds and Dies: High-quality molds and dies are crucial for precise casting. Options include permanent molds for high-volume production and sand molds for custom, complex shapes.
2. Furnaces: Efficient melting furnaces, such as electric resistance or induction furnaces, ensure uniform temperature and quality.
3. Pouring Systems: Automated pouring systems improve accuracy and reduce waste.
4. Cooling Systems: Controlled cooling systems, including water-cooled and air-cooled options, enhance the casting quality by minimizing defects.
Upgrades:
1. Automation: Upgrading to automated systems for mold handling, metal pouring, and cooling can significantly increase production speed and consistency.
2. Quality Control: Implementing advanced quality control technologies like X-ray inspection and ultrasonic testing ensures defect-free castings.
3. Material Handling: Upgrades in material handling systems, including automated conveyor belts and robotic arms, streamline the manufacturing process.
4. Energy Efficiency: Upgrading to energy-efficient furnaces and equipment reduces operational costs and environmental impact.
Custom Manufacturing Options:
1. Prototyping: Custom prototyping services, including 3D printing for mold making, allow for rapid iteration and testing of new designs.
2. Alloy Variations: Customizing aluminum alloys to meet specific mechanical properties or corrosion resistance requirements.
3. Surface Treatments: Offering custom surface treatments like anodizing, powder coating, or plating to enhance durability and aesthetics.
4. Complex Geometries: Utilizing advanced casting techniques such as lost-wax or investment casting to create intricate and complex components.
By leveraging these accessories, upgrades, and custom options, manufacturers can achieve higher efficiency, superior quality, and tailored solutions to meet diverse industry needs.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “aluminum metal casting”
Quality Control in Aluminum Metal Casting
Quality control in aluminum metal casting ensures that the final product meets the required standards and specifications. Key aspects include:
1. Raw Material Inspection: Ensuring the quality of aluminum alloys used, often by analyzing chemical composition.
2. Mold and Die Inspection: Checking molds and dies for wear and tear to maintain dimensional accuracy.
3. Process Monitoring: Monitoring temperature, pressure, and other parameters during casting to ensure consistency.
4. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like X-ray, ultrasonic testing, and dye penetrant inspection to detect internal and surface defects.
5. Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers, micrometers, and CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines) to ensure dimensional accuracy.
6. Mechanical Property Testing: Testing for tensile strength, hardness, and other mechanical properties to ensure they meet specifications.
7. Surface Finish Inspection: Ensuring the surface finish meets aesthetic and functional requirements.
8. Final Inspection and Testing: Comprehensive testing of the final product, including fit and function tests.
Manufacturing Process of Aluminum Metal Casting
The manufacturing process of aluminum metal casting involves several steps:
1. Pattern Making: Creating a pattern, often from wood, plastic, or metal, which forms the mold cavity.
2. Mold Making: Producing molds from materials like sand, plaster, or metal. In sand casting, the pattern is packed in sand, which is then removed to leave a cavity.
3. Melting: Melting aluminum in a furnace to reach the required temperature for pouring.
4. Pouring: Pouring the molten aluminum into the mold cavity. This can be done manually or using automated pouring systems.
5. Cooling and Solidification: Allowing the molten aluminum to cool and solidify within the mold. Cooling rates can be controlled to affect the grain structure.
6. Mold Removal: Breaking or separating the mold to retrieve the solidified aluminum casting.
7. Cleaning and Finishing: Removing any residual mold material, flash, or sprues, and performing any necessary surface finishing.
8. Heat Treatment: Optional heat treatment to enhance mechanical properties like strength and ductility.
9. Inspection and Testing: Performing quality control inspections and tests to ensure the casting meets specifications.
This process ensures the production of high-quality aluminum castings for various industrial applications.
Materials of “aluminum metal casting”
Aluminum metal casting involves several materials, each serving a unique purpose in the casting process. Here are the primary materials:
1. Aluminum Alloys: The core material for casting, aluminum alloys are chosen for their properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight. Common alloys include:
– Al-Si Alloys: Known for good casting properties and strength.
– Al-Cu Alloys: Offer high strength and are used in aerospace applications.
– Al-Mg Alloys: Provide excellent corrosion resistance and are often used in marine environments.
2. Mold Materials: These are used to shape the molten aluminum. Types include:
– Sand: Commonly used for larger castings, sand molds are inexpensive and versatile.
– Permanent Molds: Made of metal (usually steel), these molds are reusable and provide better surface finishes.
– Die Casting Molds: Also metal molds, but designed for high-pressure die casting, offering high production rates and precision.
3. Core Materials: Used to form internal cavities within the casting. Materials include:
– Sand Cores: Bonded with resins to provide the necessary strength and stability.
– Ceramic Cores: Used for high-temperature applications, providing excellent dimensional accuracy.
4. Binders: Essential for creating sand molds and cores, binders include:
– Clay: Traditional binder for green sand molds.
– Resins: Used in resin-bonded sand systems to enhance strength and mold integrity.
5. Coatings: Applied to molds and cores to improve surface finish and prevent defects. Common coatings are:
– Zircon-based Coatings: Provide a smooth surface finish and protect against thermal shock.
– Graphite Coatings: Reduce friction and improve metal flow.
6. Fluxes and Degassing Agents: Used to purify the molten aluminum by removing oxides and gases, ensuring high-quality castings. Examples include:
– Chlorine or Nitrogen Gas: For degassing.
– Salt-based Fluxes: For removing impurities and oxides.
These materials collectively ensure the efficiency and quality of aluminum casting processes, enabling the production of a wide range of components for various industries.
“aluminum metal casting” Comparative Analysis
Comparative Analysis of Aluminum Metal Casting Methods
Aluminum metal casting is a versatile and widely used manufacturing process, primarily due to aluminum’s favorable properties such as lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. The most prevalent aluminum casting methods include sand casting, die casting, and investment casting, each with distinct advantages and limitations.
#### Sand Casting
Sand casting is the most traditional method, involving the creation of a mold from a sand mixture. It is highly adaptable and cost-effective, especially for large and complex parts. The process is suitable for low to medium volume production. Its primary disadvantage is a rough surface finish, which often requires post-processing. The dimensional accuracy is moderate, and the process is relatively slow.
Advantages:
– Low cost for small to medium batches.
– Flexibility in size and shape of the cast parts.
– Suitable for large and complex parts.
Disadvantages:
– Rough surface finish.
– Moderate dimensional accuracy.
– Longer production time.
#### Die Casting
Die casting involves injecting molten aluminum into a metal mold under high pressure. This method is ideal for high-volume production due to its high efficiency and ability to produce parts with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. However, die casting has high initial tooling costs and is less suitable for large parts due to the size limitations of the molds.
Advantages:
– High production efficiency.
– Excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
– Suitable for high-volume production.
Disadvantages:
– High initial tooling cost.
– Limited to smaller parts.
– Less flexibility in design changes.
#### Investment Casting
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, uses a wax pattern surrounded by a ceramic shell to form the mold. This method produces parts with exceptional detail and accuracy, making it suitable for complex and intricate designs. It is cost-effective for low to medium volumes but is more expensive and time-consuming than sand casting.
Advantages:
– High precision and excellent surface finish.
– Suitable for complex and intricate designs.
– Low to medium volume production.
Disadvantages:
– Higher cost than sand casting.
– Time-consuming process.
– Limited to smaller parts.
Conclusion
Each aluminum casting method has unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different applications. Sand casting is versatile and cost-effective for larger, less precise parts. Die casting is optimal for high-volume, high-precision production, while investment casting is ideal for intricate designs with high detail requirements. The choice of casting method depends on the specific requirements of the part, including volume, complexity, size, and budget constraints.
“aluminum metal casting” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Aluminum Metal Casting
Warranty
Our aluminum metal casting products are backed by a comprehensive warranty to ensure customer satisfaction and product reliability. We offer a one-year warranty from the date of purchase, covering any defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and service. This warranty does not cover damage caused by misuse, neglect, or unauthorized modifications. If a defect is found within the warranty period, we will repair or replace the defective product at no additional cost to the customer.
Support
We are committed to providing exceptional support to our customers. Our dedicated customer service team is available to assist with any inquiries or issues related to our aluminum metal casting products. Support can be reached via phone, email, or our website’s contact form. We strive to respond to all inquiries within 24 hours.
Technical Assistance
Our experienced technical support team is available to provide guidance on the use, maintenance, and troubleshooting of our aluminum metal casting products. We offer detailed technical documentation, including installation guides and maintenance manuals, which can be accessed on our website.
Replacement Parts and Services
In the event that a component of your aluminum metal casting product needs replacement, we stock a comprehensive range of spare parts to ensure minimal downtime. Our service centers are equipped to handle repairs and maintenance, ensuring that your equipment is returned to optimal working condition promptly.
Extended Warranty Options
For additional peace of mind, we offer extended warranty plans that can be purchased at the time of the original sale or before the standard warranty expires. These plans provide extended coverage and additional benefits, such as priority service and discounted parts and labor.
We are dedicated to ensuring the highest level of customer satisfaction and product performance. Please contact us for more information about our warranty and support services.
List “aluminum metal casting” FAQ
Aluminum Metal Casting FAQ
1. What is aluminum metal casting?
Aluminum metal casting is a process where molten aluminum is poured into a mold to create a desired shape. This method is used for producing complex geometries that are difficult to achieve with other manufacturing processes.
2. What are the common methods of aluminum casting?
The most common methods include die casting, sand casting, and permanent mold casting. Die casting involves forcing molten aluminum into a mold under high pressure. Sand casting uses a sand mold, while permanent mold casting uses reusable metal molds.
3. What are the advantages of aluminum casting?
Aluminum casting offers several benefits such as high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, excellent thermal conductivity, and the ability to produce intricate shapes. It is also recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
4. What are the typical applications of aluminum castings?
Aluminum castings are widely used in the automotive industry (engine blocks, wheels), aerospace sector (aircraft components), and consumer electronics (housing for gadgets). They are also used in construction, marine, and industrial machinery.
5. How does the casting process affect the quality of aluminum parts?
The quality of aluminum castings depends on factors such as mold design, casting method, and cooling rate. Proper control of these variables ensures minimal defects like porosity, shrinkage, and surface imperfections.
6. What are the limitations of aluminum casting?
Despite its advantages, aluminum casting has limitations including lower melting point compared to other metals, which can restrict its use in high-temperature applications. Additionally, the initial cost of molds can be high, especially for complex shapes.
7. How can defects in aluminum castings be minimized?
Defects can be minimized by optimizing the mold design, using quality raw materials, and maintaining precise control over the casting process parameters. Techniques like vacuum casting and improved cooling systems also help in reducing defects.
8. What is the environmental impact of aluminum casting?
Aluminum casting has a relatively low environmental impact due to aluminum’s recyclability. However, the process itself requires significant energy and produces emissions. Sustainable practices and energy-efficient technologies are employed to mitigate these effects.
This FAQ provides a brief overview of aluminum metal casting, highlighting its methods, benefits, applications, and considerations.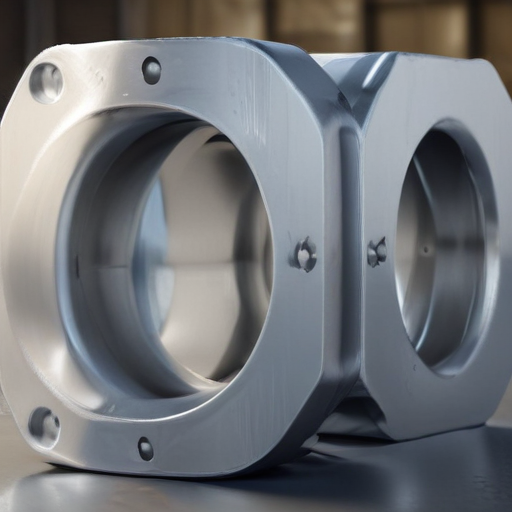
Top 10 FAQ with answer about aluminum metal casting for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 FAQs with answers about aluminum metal casting for buyer sourcing from China:
1. What are the common aluminum alloys used in casting?
– Common alloys include A356, A380, and A319, known for their good casting properties and mechanical strength.
2. What are the typical lead times for aluminum casting orders?
– Lead times vary but typically range from 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the order size and complexity.
3. What quality control measures are in place for aluminum castings?
– Chinese suppliers often use X-ray inspection, dimensional checks, and chemical analysis to ensure quality. ISO 9001 certification is common.
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for aluminum casting?
– MOQs vary by supplier but generally start from 100 to 500 pieces per order.
5. What are the advantages of sourcing aluminum castings from China?
– Competitive pricing, a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, and a large pool of experienced manufacturers.
6. What are the common casting methods used for aluminum?
– Methods include sand casting, die casting, and permanent mold casting, each suitable for different applications and volume requirements.
7. How do I ensure the supplier meets my specific requirements?
– Provide detailed specifications, request samples, and perform factory audits or inspections.
8. What are the common surface finishes available for aluminum castings?
– Options include powder coating, anodizing, painting, and polishing to meet aesthetic and functional needs.
9. Can Chinese manufacturers assist with design and engineering support?
– Yes, many manufacturers offer design and engineering services to optimize casting designs for manufacturability and cost-effectiveness.
10. What are the shipping and logistics considerations?
– Most suppliers handle international shipping. Choose between sea freight for cost efficiency or air freight for faster delivery. Ensure clear communication about Incoterms and customs documentation.
These answers should help buyers navigate the process of sourcing aluminum metal castings from China effectively.
