Technology and Applications of cnc machine
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are automated tools that utilize computer-generated commands to control their movement and operations, enhancing precision and efficiency in manufacturing. The fundamental technology behind CNC machines involves converting design files (often created in CAD software) into a language (G-code) that the machine can interpret, allowing it to execute complex tasks with repeatable accuracy.
CNC machines come in various forms, including CNC mills, lathes, routers, and plasma cutters, each tailored for specific applications. They are widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and woodworking, significantly improving productivity and reducing human error. For example, in the aerospace sector, CNC machining produces intricate components with tight tolerances, essential for safety and performance.
Applications of CNC technology extend beyond traditional manufacturing; it has also revolutionized prototyping, enabling rapid design iterations. Additionally, CNC machines facilitate personalized production, allowing small batches of customized products, which is increasingly demanded in today’s market.
Moreover, advancements in CNC technology, such as integrated IoT for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhance operational efficiency and lifespan of machines. The rise of 5-axis CNC milling has further expanded capabilities, allowing for complex geometries that were once difficult to achieve.
In summary, CNC machines are pivotal in modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled accuracy and flexibility, while their diverse applications contribute to innovative solutions across multiple industries. As technology continues to evolve, CNC machining will remain at the forefront of efficient and customizable production processes.
Quality Testing Methods for cnc machine and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for CNC machines are essential to ensure precision, accuracy, and reliability in the manufacturing process. Here are key methods and controls for quality assurance:
1. Calibration: Regularly calibrate CNC machines to ensure they produce the correct dimensions. Use precision measuring tools like calibration blocks and gage pins.
2. First Article Inspection (FAI): Conduct an FAI for the initial run of a new part. Measure critical dimensions, surface finishes, and features to verify compliance with design specifications.
3. In-Process Inspection: Implement real-time monitoring using sensors and inspection tools during machining. Techniques such as laser measurement and probe systems can provide immediate feedback on part dimensions.
4. Statistical Process Control (SPC): Use SPC techniques to analyze process data and maintain consistent quality. Control charts can help identify variations and trigger corrective actions before defects occur.
5. Destructive and Non-Destructive Testing: Utilize methods like X-ray, ultrasound, or magnetic particle inspection to detect internal defects without damaging the part.
6. Final Inspection: After machining, perform a comprehensive inspection of the finished product. Use tools like micrometers, calipers, and surface roughness testers to assess final dimensions and surface quality.
7. Documentation and Feedback: Maintain comprehensive records of inspections, calibrations, and deviations. Implement a feedback loop for continual improvement, addressing any discrepancies or trends in quality issues.
Controlling quality in CNC machining combines systematic measurement, real-time data analysis, and rigorous testing protocols. By integrating these quality testing methods, manufacturers can ensure high standards and reduce waste, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from cnc machine
When procuring a CNC machine, careful consideration is essential to ensure a wise investment that meets your operational needs. Here are key tips and considerations:
1. Define Your Requirements: Assess the specific tasks the CNC machine will perform, such as the types of materials and the complexity of parts. Determine the size and capabilities based on your production volume and accuracy requirements.
2. Evaluate Machine Types: Familiarize yourself with different CNC machine types (e.g., mills, lathes, routers) and their technology (e.g., 3-axis vs. 5-axis). Select one that aligns with your needs.
3. Consider Brand Reputation: Research manufacturers for reliability and support. Established brands often offer better warranties and customer service.
4. Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, consider maintenance, tooling, training, and operational costs. A cheaper machine may incur higher long-term expenses.
5. Review Specifications: Examine spindle speed, feed rates, work envelope, and precision specifications. Ensure compatibility with your current tools and workflow.
6. Visit Showrooms or Expos: If possible, see the machines in action. This firsthand experience can help you assess their performance and ease of use.
7. Assess Software Compatibility: Check whether the machine comes with or is compatible with the required CAM software for your applications.
8. Inspect Training and Support: Inquire about training programs for your staff and the availability of technical support post-purchase.
9. Check Delivery and Installation Services: Understand the timeline and conditions for delivery and installation, as these can impact your production schedule.
10. Negotiate: Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms, as manufacturers may be open to discussing pricing, warranties, or added services.
By following these guidelines, you can make an informed decision that enhances productivity and supports your business goals.
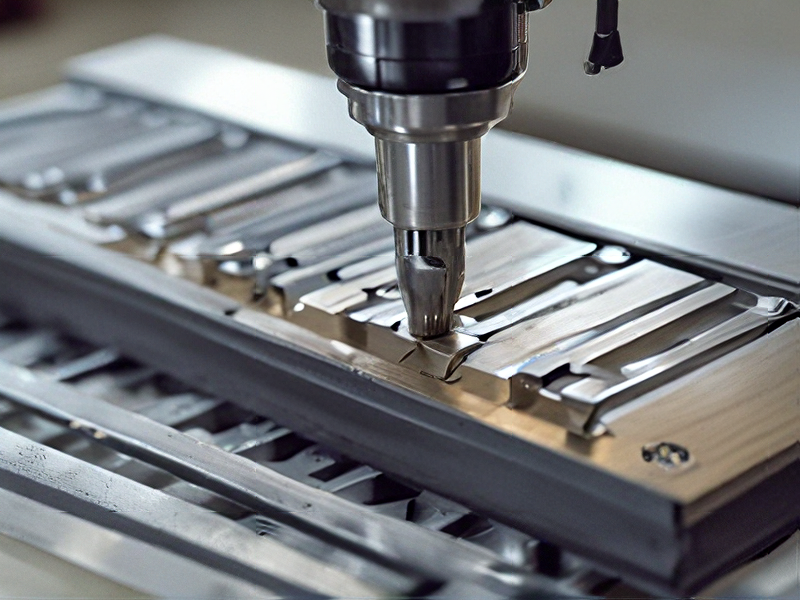

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from cnc machine in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing CNC Machines in China
1. Why source CNC machines from China?
China offers competitive pricing, a wide range of manufacturers, and advanced technology. Many Chinese companies have adopted ISO standards, ensuring quality products.
2. How do I find a reliable manufacturer?
Utilize platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, or attend trade shows such as the China International Machine Tool Show. Check customer reviews, request referrals, and seek third-party verification.
3. What should I look for in a manufacturer?
Evaluate their production capacity, quality control processes, experience in CNC manufacturing, certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and their willingness to communicate clearly.
4. How can I ensure quality control?
Conduct factory audits, require samples, and establish quality assurance processes. You can hire third-party inspection services to monitor production quality during different phases.
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ)?
MOQs vary by manufacturer. Some may produce single units, while others require larger orders. Clarify this upfront to align on your budget and needs.
6. What about shipping and logistics?
Consider shipping options (air vs. sea), costs, and customs duties. Collaborate with a freight forwarder familiar with importing CNC machinery to navigate logistics effectively.
7. Are warranties and support offered?
Most manufacturers provide warranties on machines. Ensure you understand the terms and ask about after-sales support and spare parts availability.
8. What is the lead time for production?
Lead times can vary based on demand, complexity, and order size, typically ranging from a few weeks to several months. Communicate your timeline needs early on.
For a successful partnership, establish clear communication and agreements upfront.