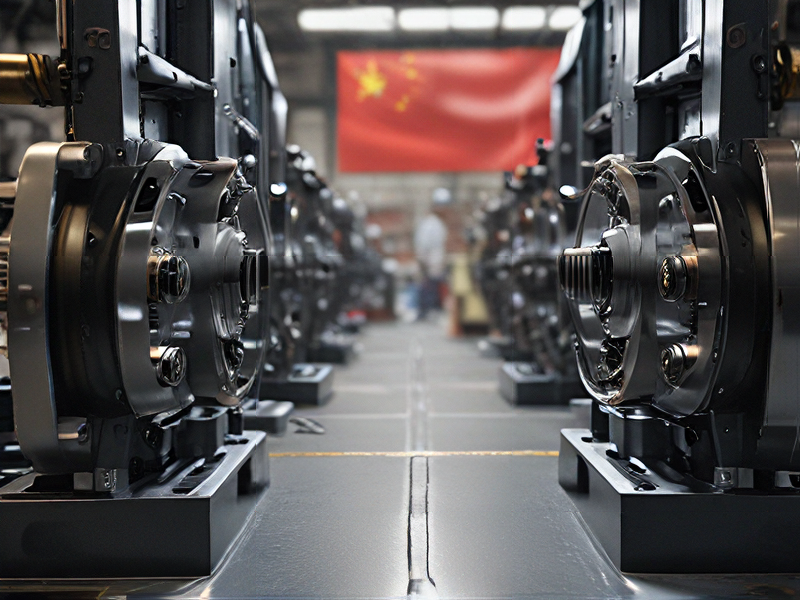
Technology and Applications of cast of the machine
The term “cast of the machine” typically refers to the use of casting technology in manufacturing, which involves creating objects by pouring molten materials into a mold. This process is pivotal in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer products, due to its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision and excellent surface finish.
Technology: The casting process can be executed through various methods, such as sand casting, die casting, investment casting, and lost foam casting. Each method has unique advantages; for instance, die casting is renowned for high-volume production and exceptional dimensional accuracy, while investment casting is favored for intricate designs and fine details.
Applications: The applications of casting are vast. In the automotive industry, it is used to create engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission cases. Aerospace manufacturers rely on precision casting for components like turbine blades, which require high performance under extreme conditions. Additionally, consumer goods such as cookware and decor items benefit from casting techniques, allowing for artistic designs and functional innovations.
Moreover, advancements in casting technology, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D printing of molds, are revolutionizing the field. These technologies enable rapid prototyping, customization, and reduced lead times, making it easier for manufacturers to respond to market demands.
In conclusion, the technology and applications of casting are integral to modern manufacturing, providing flexibility, efficiency, and creativity across a multitude of sectors. As the industry evolves, embracing innovative casting techniques will be vital for sustained growth and competitiveness.
Quality Testing Methods for cast of the machine and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for machine castings are essential to ensure that the cast components meet design specifications and performance requirements. Here are several effective methods and quality control measures:
1. Visual Inspection: The first step in quality control involves visual inspection to identify surface defects such as cracks, voids, or inclusions. This can be done without special equipment.
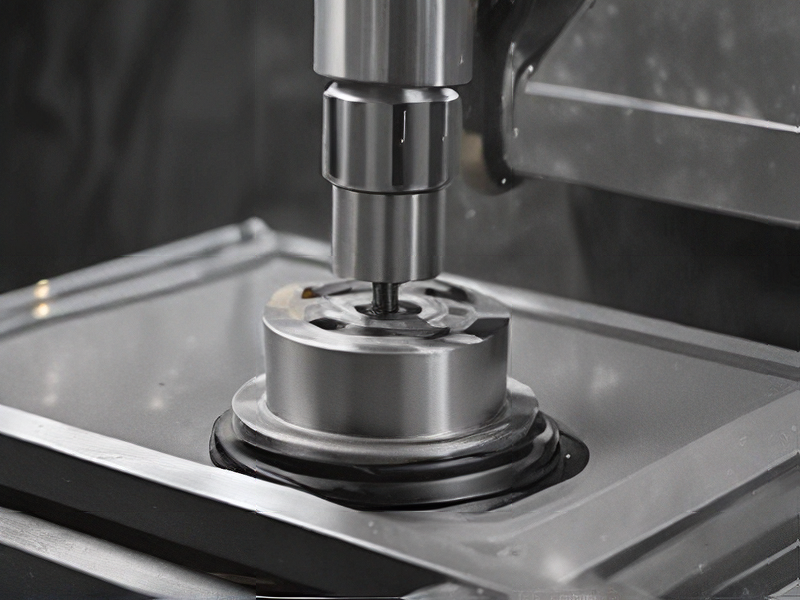
2. Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM), dimensional checks ensure that the casting meets the specified tolerances. This is critical for parts that fit together with other components.
3. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and dye penetrant testing help identify internal flaws without damaging the casting. These methods are important for ensuring structural integrity.
4. Mechanical Testing: Conducting tensile strength, hardness, and impact tests provides data on the mechanical properties of the cast material. Standards like ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) provide guidelines for these tests.
5. Chemical Analysis: Performing spectrometric analysis ensures the chemical composition of the alloy meets specified requirements. This is crucial for ensuring that the material properties, like strength and corrosion resistance, are adequate.
6. Process Control: Implementing process controls such as monitoring temperature during melting and pouring, maintaining mold integrity, and managing cooling rates can significantly enhance quality. Statistical process control (SPC) tools can also be employed to track quality metrics over time.
7. Documentation and Traceability: Keeping accurate records of inspections, test results, and process parameters facilitates quality tracking and provides accountability within the production process.
By combining these methods and maintaining a robust quality management system, manufacturers can effectively control the quality of machine castings, ensuring reliable performance in their applications.

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from cast of the machine
When considering procurement for a machine, there are several essential tips and considerations to ensure a successful purchase.
1. Identify Requirements:
Clearly define your operational needs, including specifications, capacity, and features that the machine must fulfill.
2. Research Suppliers:
Investigate multiple suppliers. Examine their reputation, customer reviews, and history of after-sales support. Build a list of potential manufacturers.
3. Cost Analysis:
Look beyond the initial purchase price. Factor in installation, training, maintenance, and operational costs over the machine’s lifespan.
4. Performance and Quality:
Evaluate the machine’s performance metrics. Request demonstrations or case studies to ensure it meets your productivity expectations and quality standards.
5. Warranty and Support:
Ensure a robust warranty and reliable technical support. Understanding the terms of service agreements is crucial for long-term operation.
6. Compliance and Standards:
Verify that the machine adheres to local regulations and industry standards. This reduces the risk of legal complications and safety issues.
7. Future Scalability:
Consider whether the machine can adapt to future growth or evolving technology needs. This foresight can save costs and disruptions later.
8. Supplier Communication:
Maintain open communication with the supplier. Clarify any doubts and ensure they understand your operational goals.
9. Site Preparation:
Before delivery, ensure your facility is ready for the new machine, including space, utilities, and necessary personnel training.
10. Post-Purchase Review:
After implementation, assess the performance of the machine relative to your expectations. This can inform future procurement decisions and drive continuous improvement.
By adhering to these tips, procurement professionals can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and contribute to overall business success.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from cast of the machine in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing in China
1. What are the benefits of sourcing from China?
Sourcing from China offers advantages such as cost-effectiveness, a vast range of suppliers and manufacturers, and the ability to scale production quickly. Additionally, China has advanced manufacturing technology and expertise in various industries.
2. How do I find reliable suppliers?
To find reliable suppliers, use platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, or Made-in-China. Attend trade fairs, check online directories, and request referrals. Always verify suppliers through background checks and reviews.
3. What should I consider when negotiating prices?
Consider factors like order quantity, payment terms, shipping costs, and lead times. Having a clear comparison with other quotes can help in negotiations. Building a long-term relationship with suppliers can also lead to better deals.
4. How do I ensure quality control?
Establish quality standards before production, and consider hiring a third-party quality control service. Regular inspections during production and final product inspections can help ensure compliance with your standards.
5. What are the common payment terms?
Common payment terms include a 30% deposit upfront and the remainder upon completion or prior to shipping. Discuss payment options with your supplier, including letters of credit or PayPal for safer transactions.
6. What is the typical lead time for manufacturing?
Lead times can vary based on the product complexity and order size. Generally, expect 4-12 weeks. Always confirm timelines with your supplier and factor in additional time for shipping.
7. Are there any legal considerations?
Ensure that you comply with international trade laws, and protect your intellectual property. Consider having contracts in place, specifying terms, obligations, and dispute resolution methods.
8. How to handle shipping logistics?
Work with freight forwarders experienced in shipping from China. They can help navigate customs, tariffs, and the best shipping methods for your needs.

