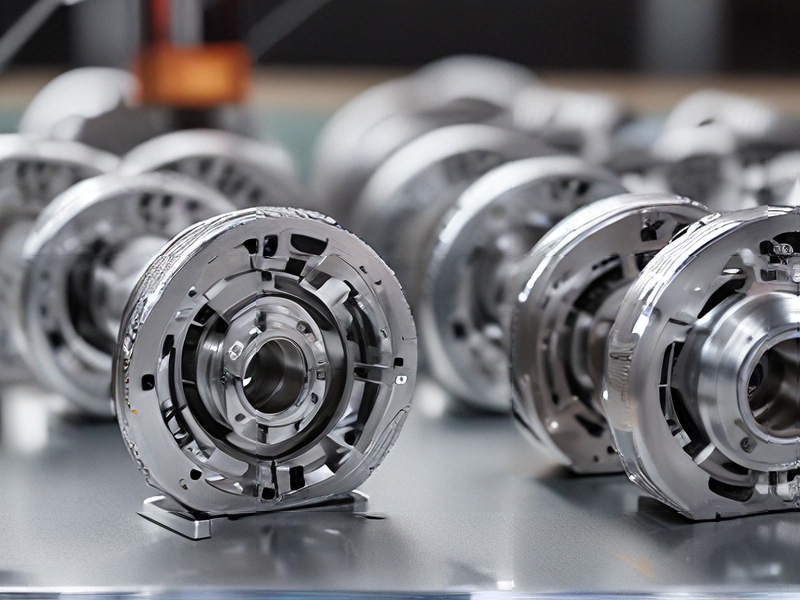
Technology and Applications of metallic 3d printer
Metallic 3D printing, also known as metal additive manufacturing, has revolutionized various industries by enabling complex designs and high-performance applications. The primary technologies used in metallic 3D printing include Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and Binder Jetting.
Key Technologies:
1. Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): Both technologies utilize high-powered lasers to melt and fuse metal powders layer by layer. They are ideal for producing components with intricate geometries, high strength-to-weight ratios, and tailored material properties.
2. Electron Beam Melting (EBM): EBM uses an electron beam in a vacuum to melt metal powder. This technique is particularly effective for high-temperature alloys and is commonly used in aerospace and medical applications.
3. Binder Jetting: This method involves depositing a binder onto metal powders, which are subsequently sintered in a furnace. It allows for faster production of complex parts and is cost-effective for large series.
Applications:
Metallic 3D printing is gaining traction in various sectors:
– Aerospace: Production of lightweight, complex components such as turbine blades and engine parts.
– Automotive: Custom parts for high-performance vehicles, prototyping, and tooling.
– Medical: Creation of patient-specific implants and prosthetics, enhancing personalization and fit.
– Tooling: Manufacturing of molds and fixtures that require intricate designs for efficiency.
In summary, metallic 3D printing is a transformative technology that streamlines production processes, minimizes waste, and allows for innovative designs across multiple industries, driving advancements in performance and functionality.
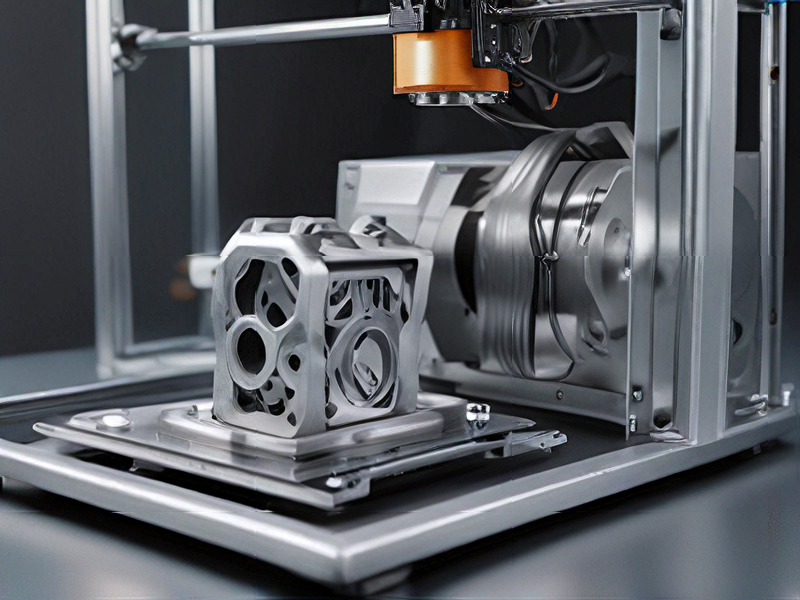
Quality Testing Methods for metallic 3d printer and how to control quality
Quality testing for metallic 3D printing involves several methods to ensure the integrity and reliability of the printed components. Here are key testing techniques and quality control practices:
1. Visual Inspection: Examine printed parts for surface defects, layer misalignment, or irregularities. This initial check can help identify obvious flaws.
2. Dimensional Analysis: Use calipers or coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify that the final dimensions match the design specifications, ensuring tolerances are met.
3. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Employ methods such as ultrasonic testing, X-ray, or magnetic particle inspection to detect internal defects or inconsistencies without damaging the part.
4. Mechanical Testing: Conduct tensile, compression, and fatigue tests to evaluate the mechanical properties of the printed material. This assesses strength, ductility, and overall performance.
5. Microstructure Examination: Utilize optical or electron microscopy to analyze the microstructure of the material, which can reveal issues such as porosity, grain size, and phase distribution.
6. Chemical Analysis: Apply techniques like X-ray fluorescence (XRF) or energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) to ensure material composition meets specifications and to detect contaminants.
To control quality, establish a robust quality management system (QMS) that includes:
– Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and follow SOPs for the entire printing process, from design to post-processing.
– Regular Calibration: Ensure that all testing equipment is regularly calibrated to maintain accuracy.
– Employee Training: Invest in training staff on quality assessment techniques and the importance of quality assurance.
– Feedback Loops: Implement continuous improvement practices based on feedback from testing results to refine processes and prevent future errors.
By systematically applying these methods, manufacturers can ensure high-quality output in metallic 3D printing.
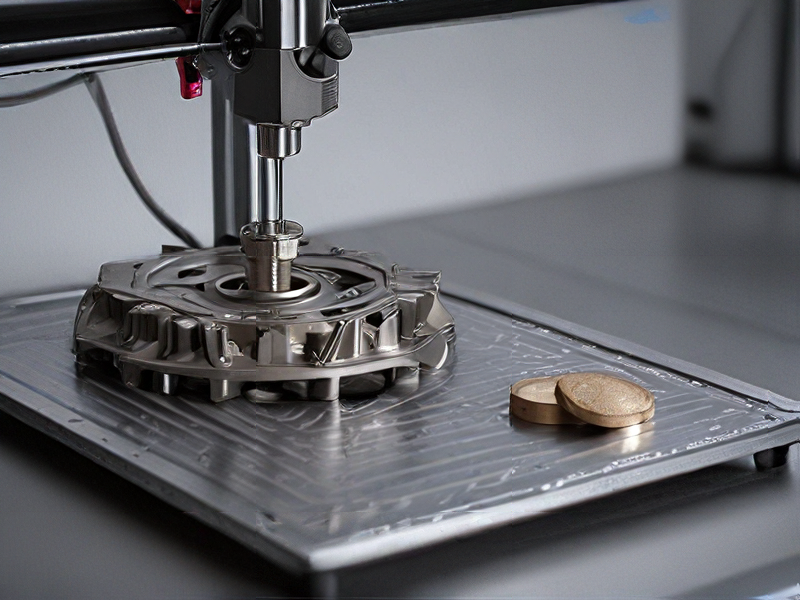

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from metallic 3d printer
When considering the procurement of a metallic 3D printer, several key factors and tips should guide your decision-making process:
1. Assess Your Needs: Define the specific applications for the printer, such as prototyping, tooling, or production. Determine the types of metals you’ll work with (e.g., titanium, stainless steel) and the desired part characteristics (e.g., strength, precision).
2. Technology Type: Familiarize yourself with different metallic 3D printing technologies, such as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and Material Extrusion. Each has its advantages and limitations regarding speed, cost, and material compatibility.
3. Budget Considerations: Establish a budget that encompasses not just the printer but also ongoing costs like materials, maintenance, training, and operational expenses. Understand the return on investment (ROI) and potential cost savings from in-house production.
4. Supplier Reputation: Research manufacturers’ reliability, customer service, and support. Look for reviews, case studies, and testimonials from existing users to ensure the vendor offers robust technical support and training.
5. Material Availability: Verify the availability of compatible metal powders and whether the supplier provides them. Evaluate the quality of these materials, as they directly affect the final part properties.
6. Post-Processing Needs: Consider the required post-processing steps, such as heat treatment or surface finishing, and ensure your facility is equipped to handle them.
7. Scalability and Future-Proofing: Ensure the printer can meet future production needs and is compatible with advancements in technology. This foresight can save costs and time in the long run.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision on your metallic 3D printer purchase that aligns with your production goals.
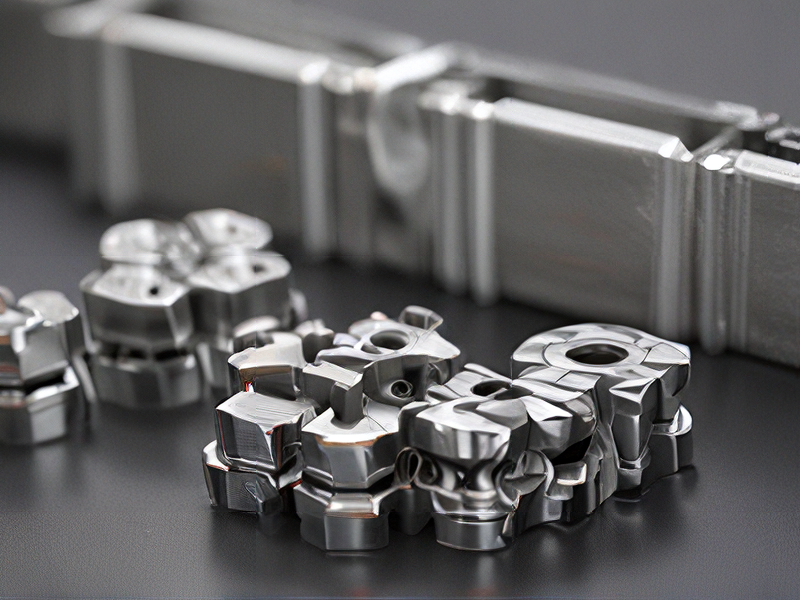

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from metallic 3d printer in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from Metallic 3D Printers in China
1. What advantages does China offer for metallic 3D printing?
China boasts a vast ecosystem of advanced manufacturing technologies, competitive pricing, and a skilled workforce. The country is also home to numerous suppliers and innovative companies specializing in metallic 3D printing, ensuring access to cutting-edge technology and materials.
2. What materials are commonly used in metallic 3D printing?
Common materials include stainless steel, titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, and cobalt-chrome. The choice of material depends on the specific application and desired mechanical properties.
3. What industries benefit from metallic 3D printing?
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and energy are major beneficiaries. Metallic 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, lightweight components, and complex geometries, leading to enhanced performance and reduced lead times.
4. How do I choose the right manufacturer?
Look for manufacturers with a proven track record, certifications (like ISO 9001), and expertise in your specific industry. Request samples and conduct factory audits to assess capabilities and quality control processes.
5. What are the typical lead times for production?
Lead times vary but generally range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the design, material availability, and production capacity.
6. What are the shipping options for products made in China?
Shipping options include air freight for expedited delivery or sea freight for cost-effective bulk shipping. Consider logistics providers that specialize in cross-border shipping to streamline the process.
7. How do I handle quality assurance?
Implement quality checks during production, and consider third-party inspections before shipping. Establish clear communication and quality standards with the manufacturer from the outset.

