Technology and Applications of metal printer 3d
Metal 3D printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing (AM) for metals, is an innovative technology that allows the creation of complex metal parts directly from digital files. This process typically utilizes methods such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), and Binder Jetting.
One significant advantage of metal 3D printing is design freedom, enabling intricate geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing techniques. This capability reduces material waste since parts are built layer by layer, minimizing off-cuts associated with subtractive methods.
Applications of metal 3D printing span various industries. In aerospace, it is used to create lightweight components, such as turbine blades, that enhance fuel efficiency. The medical field leverages this technology for custom prosthetics and dental implants tailored to individual patient anatomies. In automotive manufacturing, metal 3D printing facilitates rapid prototyping and the creation of specialized tooling and parts, speeding up development cycles.
Moreover, metal 3D printing supports low-volume production, which is ideal for customized or small-batch items without the need for expensive molds. As the technology matures, it aims to improve material properties and increase the variety of metals that can be printed, including high-strength alloys and titanium.
Recent advancements focus on automation and process optimization, making metal 3D printing more cost-effective and accessible. This evolution signifies a transformative shift in manufacturing, paving the way for more sustainable, efficient, and innovative production methods.
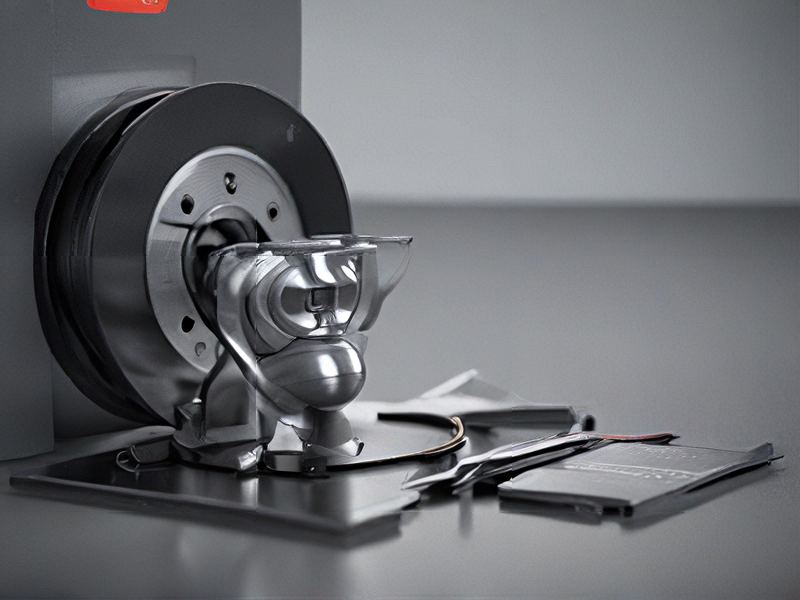

Quality Testing Methods for metal printer 3d and how to control quality
Quality testing of metal 3D printed parts is crucial to ensure the integrity and functionality of the components. Here are some effective methods for quality assurance:
1. Dimensional Inspection: Utilize precision measurement tools like calipers and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify the dimensions and tolerances of printed parts against CAD specifications.
2. Visual Inspection: Conduct thorough visual assessments to identify surface defects such as cracks, porosity, or layer misalignments. This can be done under controlled lighting conditions or using magnification.
3. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods like ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing (X-ray), and magnetic particle inspection can detect internal flaws without damaging the parts.
4. Microstructure Analysis: Use microscopy to analyze the grain structure of the metal. A well-structured grain can indicate good mechanical properties, while irregularities may suggest issues in the printing process.
5. Mechanical Testing: Conduct tensile, fatigue, and hardness tests to evaluate the material properties. These tests provide quantitative data on the strength and durability of the printed components.
6. Post-Processing Evaluation: Assess the effects of post-processing techniques (e.g., heat treatment, surface finishing) on the part’s properties and dimensional accuracy.
Quality Control Measures:
– Process Monitoring: Implement in-situ monitoring during the printing process to detect anomalies in real time, using sensors for temperature, pressure, and laser performance.
– Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and enforce SOPs for machine operation, maintenance, and quality inspections to ensure consistent outcomes.
– Material Control: Ensure the quality of raw materials by conducting verification tests like chemical composition analysis.
– Training and Certification: Provide comprehensive training for operators on best practices in metal 3D printing to minimize human error and enhance quality assurance.
These methods collectively enhance the reliability and performance of metal 3D printed components.
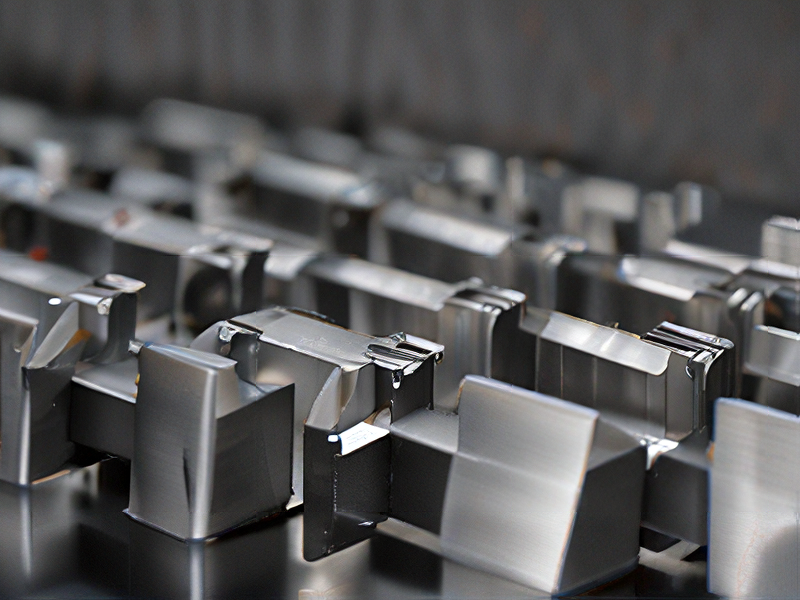

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from metal printer 3d
When considering procurement from a metal 3D printer, several key factors should guide your decision-making process:
1. Material Compatibility: Ensure the printer supports the specific metals you intend to use, such as titanium, aluminum, or stainless steel. Different 3D printers have varying capabilities with material compositions.
2. Technology Type: Familiarize yourself with the printing technologies available—Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and Binder Jetting are common options. Each has its advantages and limitations regarding build quality, speed, and cost.
3. Build Volume: Assess the build size of the printer. Ensure it meets your project specifications and can accommodate the size of the components you need to produce.
4. Print Resolution and Accuracy: Investigate the layer height and precision of the printer. High resolution and accuracy are essential for functional parts and detailed designs.
5. Post-Processing Needs: Consider any necessary post-processing requirements, including heat treatment or surface finishing. Understanding these needs upfront can impact overall costs and turnaround time.
6. Supplier Reputation: Research the supplier’s track record, customer reviews, and case studies to gauge their reliability and support services.
7. Cost of Ownership: Factor in not just the purchase price, but also operating costs, maintenance, and material expenses. Total cost of ownership should align with your budget and long-term objectives.
8. Technical Support and Training: Ensure that the supplier offers sufficient technical support and training for your team to operate the printer efficiently.
9. Scalability: Consider whether the printer can scale with your production needs and future applications.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your operational goals and enhances your manufacturing capabilities.
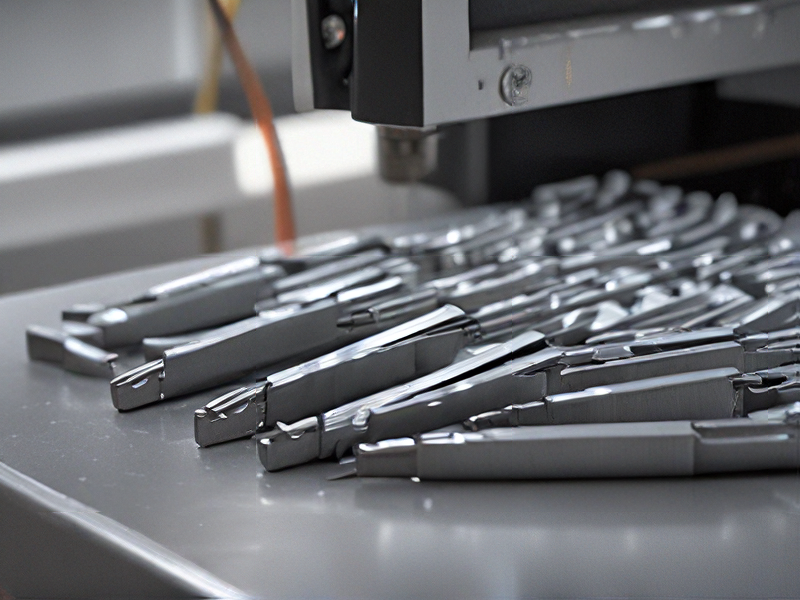

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from metal printer 3d in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from Metal 3D Printers in China
1. What are the benefits of sourcing metal 3D printing from China?
China offers competitive pricing, vast manufacturing capabilities, and advanced technology in metal 3D printing. The extensive supply chain and skilled workforce make it a preferred choice for many businesses.
2. What types of metal can be used in 3D printing?
Common materials for metal 3D printing include stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and copper. Each material has unique properties suited for specific applications.
3. How do I find a reliable manufacturer?
Research potential manufacturers using platforms like Alibaba or Made-in-China. Look for reviews, certifications, and request sample work to evaluate quality.
4. What is the typical lead time for production?
Lead times vary based on order size and complexity but generally range from a few weeks to several months. Always confirm timelines with the manufacturer before placing an order.
5. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
MOQs can vary significantly between manufacturers. Some may accept small batch orders, while others may require larger quantities. Always clarify this upfront.
6. Are there quality control measures in place?
Reputable manufacturers will have quality assurance processes, including material inspections, dimensional checks, and post-processing quality tests. Request documentation of these processes.
7. How do I handle shipping and customs?
Good manufacturers often assist with logistics. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with importing metal parts into your country to handle customs clearance.
8. What are the payment terms?
Payment terms vary, but many manufacturers require upfront deposits. It’s crucial to discuss and agree on payment conditions before finalizing orders.
These FAQs should help you navigate the complexities of sourcing and manufacturing in China’s metal 3D printing sector.