Technology and Applications of 3d print with metal
3D printing with metal, also known as metal additive manufacturing, has transformed various industries by enabling the production of complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. This technology primarily uses processes like Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and Binder Jetting, which allow for precise layering of metal powders to create durable parts.
Key applications of 3D metal printing include aerospace, automotive, medical, and tooling sectors. In aerospace, companies utilize it to produce lightweight components, resulting in fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. The automotive industry benefits from custom-made parts, rapid prototyping, and intricate designs that weigh less while maintaining strength.
In the medical field, metal 3D printing is used for creating patient-specific implants, such as prosthetics and dental devices, enhancing comfort and fit. Tooling and manufacturing have also improved with metal additive processes, allowing for the rapid production of molds and dies, which speeds up production cycles.
Moreover, the ability to consolidate multiple components into a single complex part reduces assembly time and material waste, thereby promoting sustainability. The customization potential of metal 3D printing leads to innovations such as low-volume production runs without significant cost increases.
In summary, metal 3D printing not only enhances design freedom and manufacturing efficiency but also fosters innovation across various industries, aligning with modern demands for customization and sustainability in production processes.

Quality Testing Methods for 3d print with metal and how to control quality
Quality testing for 3D-printed metal parts is vital to ensure structural integrity and functional performance. Here are key methods and control strategies:
1. Visual Inspection: Begin with a thorough visual examination to identify surface defects such as cracks, pores, or inconsistencies. This initial step can quickly highlight major issues.
2. Dimensional Analysis: Use precision measurement tools like calipers or coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to ensure that the printed part meets specified tolerances. This is crucial in critical applications where dimensions directly affect performance.
3. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, X-ray computed tomography (CT), and dye penetrant testing assess internal and external flaws without damaging the part. These methods help identify hidden defects that could compromise performance.
4. Mechanical Testing: Conduct tensile, fatigue, and hardness tests to evaluate the mechanical properties of the printed metal. Understanding these factors is essential for ensuring the part can withstand operational stresses.
5. Microstructural Analysis: Use metallography to examine the microstructure of the printed parts. Techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can reveal grain structure and defects that impact performance.
6. Post-Processing Inspection: Assess the effects of post-processing methods like heat treatment or surface finishing to ensure they enhance part quality without introducing new issues.
Quality Control Strategies:
– Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop clear SOPs for each stage of the printing and post-processing workflow.
– Process Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring of printing parameters (temperature, speed, and feed rates) to ensure consistency.
– Regular Calibration: Ensure all measurement and testing equipment is regularly calibrated for accuracy.
By incorporating these methods and strategies, manufacturers can maintain high quality in 3D-printed metal components, ultimately ensuring reliability and customer satisfaction.
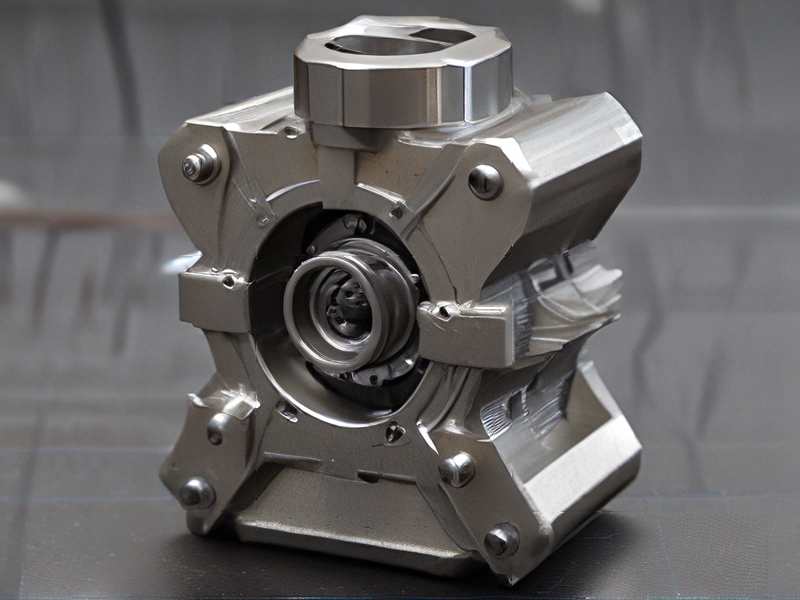
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from 3d print with metal
When considering procurement for metal 3D printing, several key factors should be taken into account to ensure a successful purchase:
1. Material Selection: Understand the specific metal alloys available for 3D printing, such as titanium, aluminum, or stainless steel. Each has different mechanical properties and applications. Choose based on the part’s intended use and performance requirements.
2. Supplier Evaluation: Research prospective suppliers for their capabilities, certifications (like ISO 9001), and experience in metal 3D printing. Request samples of previous work and inquire about their quality control measures.
3. Design Optimization: Before printing, ensure that the design is optimized for the 3D printing process. This might include adjusting geometries for better printability, reducing weight without compromising strength, or integrating features that are unique to additive manufacturing.
4. Cost Analysis: Calculate the total cost, which includes raw material, printing time, post-processing, and shipping. Be cautious of the price for metal powders, as they can be significantly higher than traditional materials.
5. Post-Processing Needs: Determine what post-processing will be required after printing, such as heat treating, machining, or surface finishing, and ensure the supplier has the capability to deliver on these needs.
6. Lead Times: Discuss lead times with suppliers, as metal 3D printing can take longer than traditional manufacturing methods. Ensure that the supplier can meet your delivery schedules.
7. Intellectual Property: Address any concerns related to intellectual property and proprietary designs. Incorporate agreements to protect sensitive information during the procurement process.
By focusing on these considerations, you can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your procurement when purchasing metal 3D printed items.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from 3d print with metal in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing 3D Printed Metal Parts in China
1. What are the benefits of 3D printing metal parts in China?
China offers competitive pricing, access to advanced technology, and a vast network of skilled manufacturers. The country’s growing expertise in additive manufacturing allows for high-quality and innovative designs.
2. What types of metal can be 3D printed?
Common metals used in 3D printing include stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and inconel. The choice depends on the application, properties required, and cost considerations.
3. What are the typical lead times for production?
Lead times can vary based on complexity, volume, and materials. Generally, you might expect a timeframe of 2-8 weeks from design approval to delivery.
4. Is quality control an issue?
Quality control is vital, especially in metal 3D printing. Work with reputable manufacturers that have certifications (such as ISO) and experience in the field to ensure standards are met.
5. How can I ensure my intellectual property is protected?
Always sign a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) before sharing designs or proprietary information. Choose manufacturers with a reputation for respecting IP rights.
6. What software is typically used for design and modeling?
Popular software includes CAD programs like SolidWorks, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360. Ensure your manufacturer can work with files from the design software you use.
7. What are the payment options?
Payment methods may include wire transfers, letters of credit, or escrow services. Discuss and agree upon terms before proceeding.
8. Are there risks involved?
Risks include quality inconsistencies, delays, and potential language barriers. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and establish strong communication with your manufacturer.

