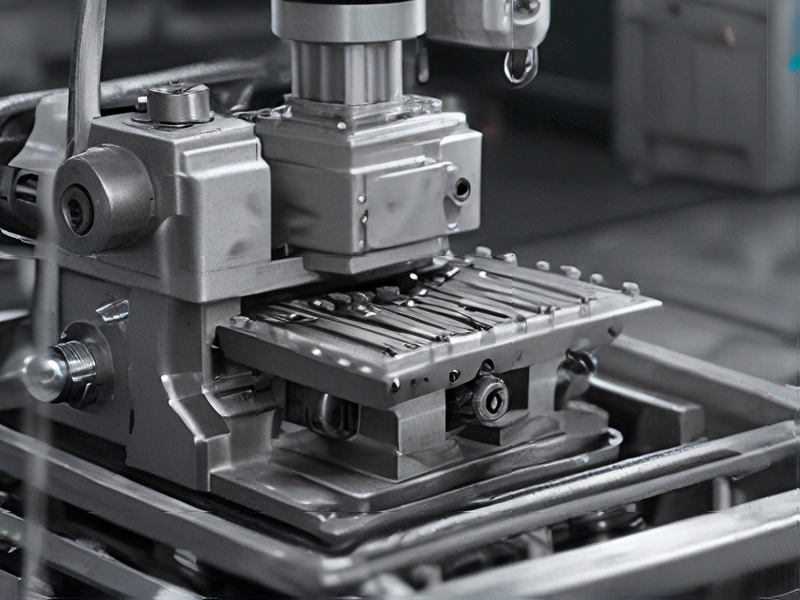
Technology and Applications of mill milling machine
A milling machine is a versatile tool typically used in manufacturing and machining for shaping materials such as metal, wood, and plastic. It operates by removing material from a workpiece using rotary cutters, allowing for precise cuts and intricate designs.
Technology:
Modern milling machines incorporate advanced technologies such as Computer Numerical Control (CNC), which enables automated, programmable control of the milling process. CNC milling machines significantly improve accuracy and efficiency, allowing for the production of complex parts with minimal human intervention. Additionally, some machines feature multi-axis capabilities, providing enhanced maneuverability and the ability to create more intricate geometries. Features like high-speed spindles, live tooling, and automatic tool changers further increase productivity and precision.
Applications:
Milling machines are widely used across various industries. In aerospace and automotive manufacturing, they produce critical components like engine parts and structural elements, where dimensional accuracy is paramount. The medical industry utilizes milling for creating custom prosthetics and orthopedic implants. In the realm of electronics, milling helps in fabricating circuit boards and enclosures. Furthermore, milling finds applications in woodworking for creating furniture, cabinetry, and intricate designs.
Overall, the technology advancements in milling machines have made them indispensable in modern manufacturing, enabling companies to meet high standards of quality and efficiency across diverse applications. Their ability to handle small-scale prototypes to large production runs makes them a cornerstone of the machining process.
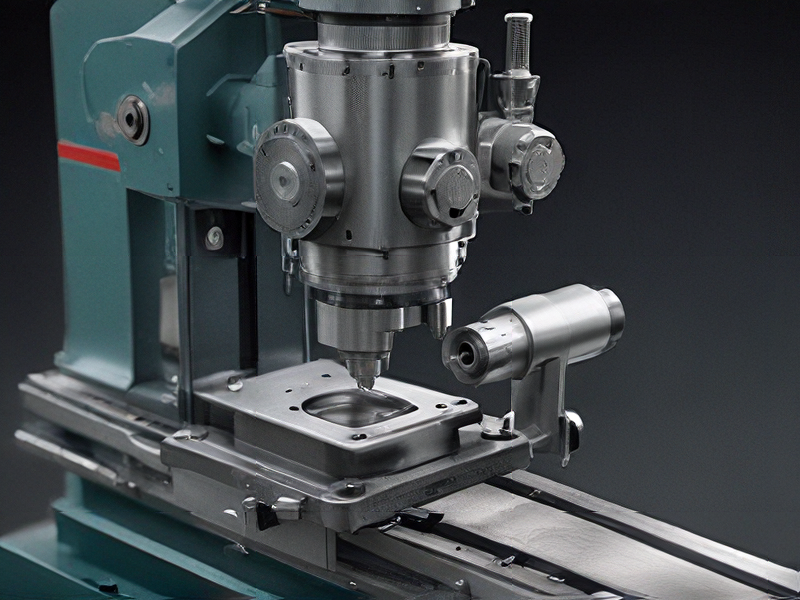
Quality Testing Methods for mill milling machine and how to control quality
Quality testing for milling machines is crucial to ensure optimal performance, precision, and safety. Here are some effective methods to test and control quality:
1. Dimensional Inspection: Use calibrated gauges, micrometers, and calipers to measure critical dimensions of the machined parts. This ensures adherence to specifications and tolerances.
2. Surface Finish Testing: Utilize surface roughness testers (profilometers) to evaluate the surface quality of machined components. A consistent finish contributes to improved functionality and aesthetics.
3. Tool Wear Analysis: Monitor cutting tools for wear and damage. Regularly inspect them under a microscope to assess edge conditions, ensuring they are replaced before they compromise quality.
4. Vibration Analysis: Implement vibration monitoring tools to assess machine stability. Excessive vibrations can indicate misalignment or wear, affecting precision.
5. Process Capability Studies: Conduct Cp and Cpk analyses to evaluate the capability of the milling process. This helps identify variations and assures that the process meets quality standards.
6. Statistical Process Control (SPC): Utilize control charts to monitor production processes in real-time. This allows for the early detection of anomalies and helps maintain consistent quality.
7. Calibration and Maintenance: Regularly calibrate all measuring instruments and maintain the milling machine to prevent any drift in performance that could impact quality.
8. Training and Documentation: Provide training for operators on best practices and ensure thorough documentation of processes and quality checks to maintain consistency.
By incorporating these methods, manufacturers can effectively control and enhance the quality of products produced by milling machines. Quality assurance not only improves product reliability but also boosts customer satisfaction.
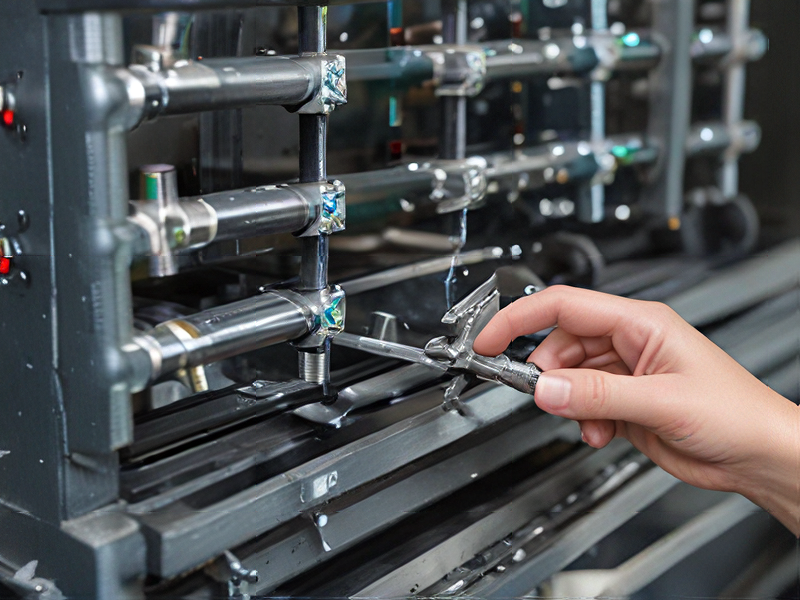

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from mill milling machine
When procuring a milling machine, consider the following key tips and factors to ensure you make an informed decision:
1. Define Requirements: Determine the specific applications, materials, and production volume you need the milling machine for. Consider features like size, speed, and precision.
2. Budget: Establish a budget that encompasses not just the purchase price but also maintenance, training, and operational costs.
3. Manufacturer Reputation: Research manufacturers for reliability and service support. Read reviews and case studies to assess performance and customer satisfaction.
4. Specifications and Features: Compare technical specifications, such as spindle speed, power consumption, and tooling options. Ensure the machine has modern features like CNC capabilities if automation is needed.
5. Quality and Durability: Assess the materials and construction. A durable machine will have a longer lifespan and require fewer repairs.
6. Support and Service: Check the availability of warranties, technical support, and spare parts. A robust service network can minimize downtime.
7. Training and Integration: Evaluate the training provided for operators and how well the machine integrates into your existing setup. This can significantly affect productivity.
8. Consider Future Needs: Think about scalability and whether the machine can accommodate increased production or new technology in the future.
9. Consult Experts: If uncertain, consult industry experts or suppliers for recommendations tailored to your specific requirements.
10. Visit Facilities: If possible, visit manufacturing facilities that use the milling machines you are considering to see performance in real-world scenarios.
By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that your milling machine purchase aligns with your operational goals and delivers value over time.
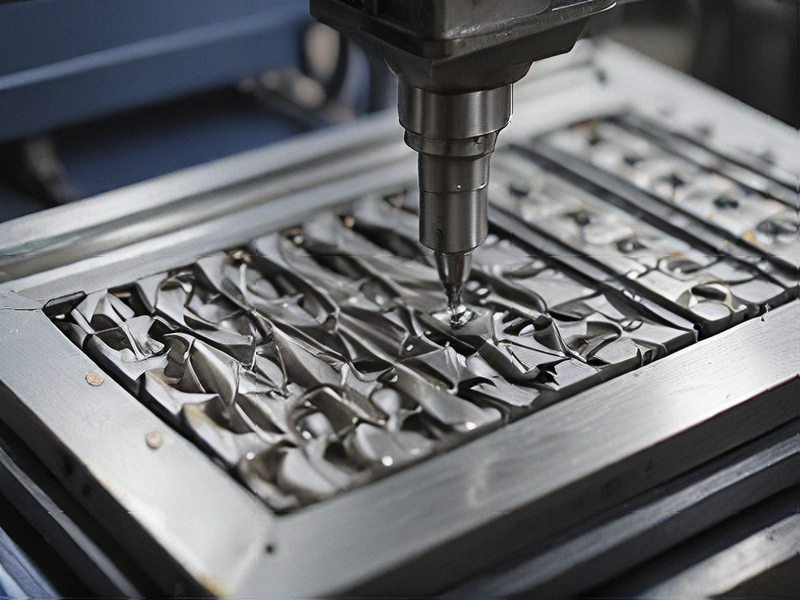

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from mill milling machine in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing Mill Milling Machines in China
1. What is the process of sourcing milling machines in China?
– Start by researching reputable manufacturers through online platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, and Global Sources. Verify their credentials, read reviews, and request certifications. Once you identify potential suppliers, reach out for quotes and technical specifications.
2. What are the common types of milling machines?
– Common types include vertical and horizontal milling machines, CNC milling machines, and universal milling machines. Your choice depends on the material and complexity of the workpieces you intend to process.
3. How can I ensure quality control?
– Request samples before finalizing orders. It’s advisable to conduct inspections during various production stages and before shipment. You can hire third-party inspection services to assess quality.
4. What should I consider regarding costs?
– Factor in costs like machine price, shipping, customs duties, and potential import taxes. Compare quotes from multiple suppliers and assess the total landed cost.
5. What are the payment terms?
– Payment terms vary by supplier, but common methods include T/T (telegraphic transfer), PayPal, and L/C (letter of credit). Be cautious of suppliers demanding full payment upfront.
6. How long does the manufacturing process take?
– Manufacturing timelines can vary. Standard lead times are typically 4-12 weeks depending on machine complexity. It’s crucial to discuss timelines upfront.
7. What after-sales support should I expect?
– Inquire about warranty, technical support, and spare parts availability. A reliable supplier will offer training and assistance for machine operation and maintenance.
8. Are there language barriers?
– While many suppliers speak English, some may not. Using clear, written communication and a translator can help mitigate misunderstandings.
Ensure thorough research and communication for successful sourcing from China.