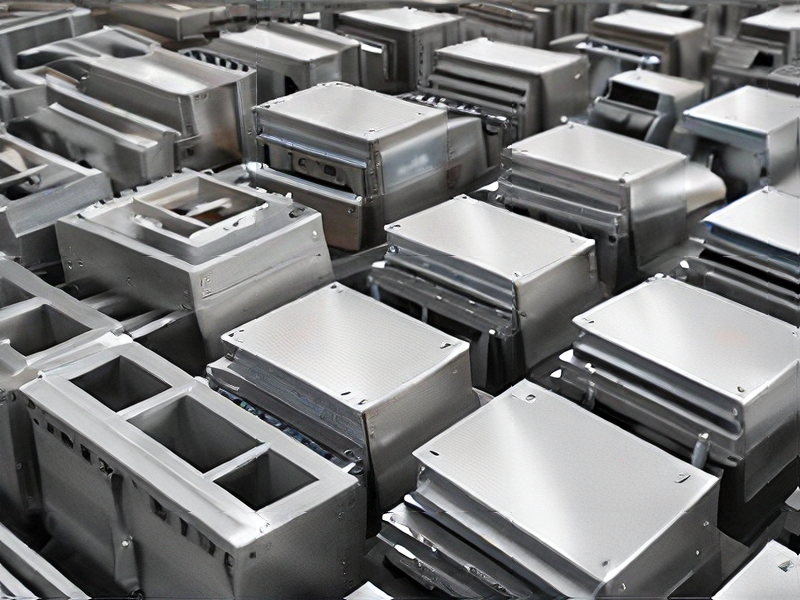
Technology and Applications of sheetmetal fabrications
Sheet metal fabrication involves cutting, bending, and assembling thin metal sheets into various shapes and structures. This process utilizes materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper, depending on the required properties like strength, malleability, and resistance to corrosion.
Technology in Sheet Metal Fabrication:
1. Cutting: Laser cutting, waterjet cutting, and plasma cutting are popular methods. Laser cutting offers high precision and speed, making it ideal for intricate designs.
2. Bending: Press brakes are used to bend the metal sheets. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) press brakes provide precise control over the bending process, ensuring consistency in production.
3. Punching: CNC punching machines create holes and cutouts by exerting high pressure on the metal sheet.
4. Assembling: Techniques include welding, riveting, and adhesive bonding. Modern fabrication often uses robotic welding for improved accuracy and efficiency.
5. Finishing: Processes like painting, powder coating, and anodizing enhance the appearance and durability of the final product.
Applications of Sheet Metal Fabrication:
1. Automotive Industry: Manufacturing car bodies, chassis, and other components.
2. Aerospace: Creating aircraft parts, including fuselage panels and wing structures.
3. Construction: Producing metal roofing, HVAC systems, and structural components.
4. Electronics: Fabricating enclosures for computers, appliances, and other electronic devices.
5. Furniture: Designing metal furniture, including office desks, chairs, and cabinets.
6. Medical Devices: Producing equipment like surgical tools, hospital beds, and casings for medical devices.
Advancements in technology have significantly improved the precision, efficiency, and capabilities of sheet metal fabrication, making it a vital process in modern manufacturing and construction industries.
Quality Testing Methods for sheetmetal fabrications and how to control quality
Quality testing for sheet metal fabrications ensures products meet specifications and standards. Key methods include:
1. Visual Inspection: Checking for obvious defects such as cracks, scratches, and corrosion. This is a quick and cost-effective method.
2. Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify dimensions and tolerances.
3. Thickness Testing: Employing ultrasonic or micrometer measurements to ensure uniform thickness.
4. Surface Finish Inspection: Assessing surface roughness with profilometers to meet aesthetic and functional requirements.
5. Hardness Testing: Using Rockwell or Vickers hardness testers to confirm material hardness.
6. Tensile Testing: Conducting tensile tests to measure strength and ductility.
7. Weld Inspection: Applying non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like X-ray, ultrasonic, and dye penetrant tests to check weld quality.
8. Flatness and Straightness Tests: Using straight edges, feeler gauges, and surface plates to ensure components are flat and straight.
9. Coating Thickness Measurement: Using magnetic or eddy current devices to measure paint or coating thickness.
10. Environmental Testing: Exposing samples to conditions such as humidity, salt spray, or temperature variations to test durability.
Quality Control Methods:
1. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Implementing detailed SOPs for each stage of production.
2. In-process Inspections: Conducting inspections at various stages of the fabrication process to catch defects early.
3. Statistical Process Control (SPC): Using SPC tools to monitor and control the manufacturing process.
4. Training: Ensuring all personnel are properly trained in quality standards and procedures.
5. Documentation and Traceability: Maintaining thorough documentation of all inspections and tests for traceability.
6. Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA): Implementing CAPA procedures to address and prevent recurring issues.
By employing these testing and control methods, manufacturers can ensure high-quality sheet metal fabrications that meet specifications and customer expectations.

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from sheetmetal fabrications
When procuring sheet metal fabrications, it is crucial to consider several key factors to ensure quality, cost-efficiency, and timely delivery. Here are some essential tips and considerations:
1. Material Selection: Choose the appropriate material based on the application. Common options include stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel, each offering different strengths, weights, and corrosion resistance.
2. Vendor Experience and Reputation: Select vendors with proven experience and positive reputations in sheet metal fabrication. Check reviews, ask for references, and review their past projects.
3. Precision and Quality: Ensure the fabricator uses advanced machinery and adheres to strict quality control standards. Precision in cutting, bending, and welding is critical for the integrity and functionality of the final product.
4. Design and Engineering Support: Opt for fabricators that offer design and engineering support. This can help optimize the design for manufacturability, potentially reducing costs and lead times.
5. Lead Times and Capacity: Assess the vendor’s production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your project deadlines without compromising quality.
6. Cost Considerations: While cost is important, it should not be the only deciding factor. Evaluate the overall value, including material quality, fabrication precision, and reliability of the vendor.
7. Compliance and Standards: Ensure the fabricator complies with industry standards and regulations, such as ISO certifications, to guarantee high-quality and safe products.
8. Communication and Collaboration: Maintain clear and open communication with the vendor throughout the procurement process. Collaborative relationships can lead to better outcomes and address any issues promptly.
9. Logistics and Delivery: Consider the logistics of shipping and delivery. Ensure the fabricator has reliable packaging and shipping practices to prevent damage during transit.
10. Sustainability Practices: If important to your organization, consider vendors that implement sustainable practices, such as recycling scrap metal and minimizing waste.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make informed decisions that align with your project requirements and business goals.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from sheetmetal fabrications in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing Sheet Metal Fabrications in China
1. Why source sheet metal fabrications from China?
– China offers competitive pricing, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and a wide range of suppliers. This makes it a cost-effective option for high-quality sheet metal fabrication.
2. What types of sheet metal fabrication services are available in China?
– Services include laser cutting, bending, stamping, welding, CNC machining, and finishing options such as powder coating and plating.
3. How do I find reliable sheet metal fabrication suppliers in China?
– Utilize online platforms like Alibaba, attend trade shows such as the Canton Fair, or hire sourcing agents who specialize in manufacturing.
4. What should I consider when selecting a supplier?
– Consider factors like the supplier’s experience, certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), production capabilities, quality control processes, and customer reviews.
5. How can I ensure the quality of the products?
– Request samples before placing bulk orders, conduct factory audits, and implement a stringent quality control process. Hiring third-party inspection companies can also help ensure product quality.
6. What are the common payment terms?
– Typical terms include a 30% deposit before production and the balance paid before shipment. Payment methods often include wire transfers, PayPal, or letters of credit.
7. How do I manage shipping and logistics?
– Work with freight forwarders experienced in international shipping. They can handle customs clearance, documentation, and transportation logistics to ensure timely delivery.
8. What are the potential challenges?
– Language barriers, cultural differences, and varying quality standards can pose challenges. Mitigate these by clear communication, detailed contracts, and regular updates.
9. Are there any legal considerations?
– Ensure compliance with both Chinese regulations and your home country’s import laws. Protect intellectual property by signing non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and registering patents/trademarks as necessary.
10. How do I handle returns or defects?
– Establish clear terms for returns and refunds in your contract. Promptly address issues with the supplier and negotiate replacements or refunds for defective items.
By addressing these key questions, you can effectively manage the sourcing and manufacturing process for sheet metal fabrications in China.

