Technology and Applications of laser engraver metal
Laser engraver technology for metal involves using concentrated laser beams to engrave designs, text, or patterns onto metal surfaces. This technology leverages the precision and power of laser beams to create detailed and permanent marks on various metals, including steel, aluminum, brass, and titanium.
Technology:
Laser engravers use a high-powered laser source, often CO2 or fiber lasers, which emit a focused beam of light. The laser beam is directed onto the metal surface through a series of mirrors and lenses, which focus the light to a fine point. The energy from the laser heats the metal to the point of vaporization or melting, allowing it to engrave or cut into the material. The process can be controlled with high precision, often managed by computer numerical control (CNC) systems, enabling complex and intricate designs.
Applications:
1. Industrial Marking: Laser engravers are widely used in manufacturing for marking parts and products with serial numbers, barcodes, logos, and other identification marks. This ensures traceability and compliance with industry standards.
2. Jewelry and Crafting: In the jewelry industry, laser engravers are used to create intricate designs, personalize items, and add fine details that would be difficult to achieve with traditional methods.
3. Automotive and Aerospace: These industries use laser engraving for part identification, adding serial numbers, and applying precise, durable markings that can withstand harsh conditions.
4. Medical Devices: Laser engraving ensures that medical instruments and implants are permanently marked with important information without compromising the integrity of the material.
5. Customization and Personalization: From custom gifts to promotional items, laser engravers allow for high-quality personalization on metal objects, making them popular for unique and customized products.
The precision, speed, and versatility of laser engravers make them indispensable in various industries, providing a reliable method for marking and decorating metal surfaces with high accuracy and durability.

Quality Testing Methods for laser engraver metal and how to control quality
Quality testing for laser engraved metal involves several key methods to ensure precise, durable, and aesthetically pleasing results.
Visual Inspection: This is the first and most basic method. Examine the engraved surface for imperfections like uneven lines, overburning, undercutting, or missing areas. Use a magnifying glass for detailed scrutiny.
Dimensional Measurement: Use calipers or micrometers to check the depth, width, and spacing of engraved features against the design specifications.
Surface Roughness: Measure the surface roughness using a profilometer to ensure the engraving meets the desired smoothness and texture.
Material Analysis: Techniques like X-ray fluorescence (XRF) can be used to analyze the surface composition after engraving, verifying material changes or potential contamination.
Durability Testing: Assess the engraving’s resistance to wear and tear through abrasion, scratch, or corrosion tests.
Quality Control:
* Establish clear specifications: Define acceptable tolerances for each quality parameter.
* Regular calibration: Calibrate equipment to ensure accurate measurements.
* Process monitoring: Continuously monitor laser parameters like power, speed, and focus to maintain consistency.
* Material optimization: Select the right metal type and surface treatment for the desired engraving quality.
By implementing these testing methods and quality control measures, you can ensure consistent and high-quality laser engraving on metal.

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from laser engraver metal
When procuring a laser engraver for metal, consider these tips:
1. Define Your Needs:
Determine the materials you’ll engrave (stainless steel, aluminum, etc.), the desired engraving depth and quality, and the project volume.
2. Laser Type:
* CO2 lasers: Best for lighter metals and wood.
* Fiber lasers: Offer higher precision and work on a wider range of metals, including stainless steel and titanium.
3. Power and Speed:
Higher power lasers engrave deeper and faster but are more expensive. Match the power to your material and desired outcome.
4. Software and Ease of Use:
Look for intuitive software with design capabilities and compatibility with your computer.
5. Safety Features:
Ensure the engraver has adequate safety features like emergency stop buttons, interlocks, and ventilation.
6. Maintenance and Support:
Consider the cost of consumables (lasers, lenses) and the availability of technical support.
7. Budget:
Laser engravers range widely in price. Set a realistic budget and prioritize features that matter most.
Remember to research reputable manufacturers and compare specifications before making a purchase.
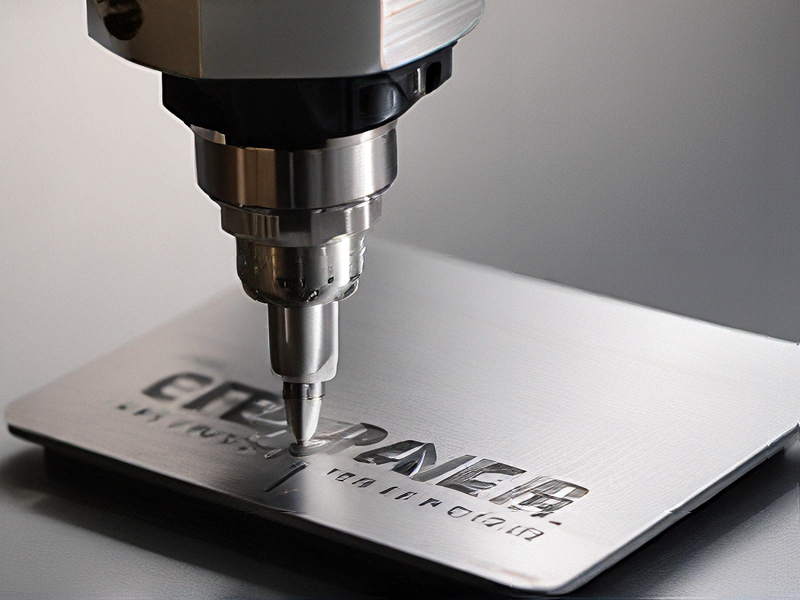
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from laser engraver metal in China
## FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from Laser Engraver Metal in China
Where can I find reliable laser engraver metal manufacturers in China?
Several online platforms connect you with manufacturers, including Alibaba, Global Sources, and Made-in-China.com. Research companies thoroughly, check reviews, and request samples before committing.
What are the typical lead times for laser engraving metal projects in China?
Lead times vary depending on order size, complexity, and manufacturer capacity. Generally, expect 2-4 weeks for prototyping and 4-8 weeks for bulk production.
How do I ensure quality control for my laser engraved metal products?
Request detailed product specifications, including material types, engraving techniques, and quality standards. Conduct on-site inspections if possible, or utilize third-party quality control services.
What are the common payment methods for sourcing from China?
Secure payment methods like Letter of Credit (LC) or escrow services are recommended for large orders. Smaller orders may utilize PayPal or bank transfers.
What are the shipping options for laser engraved metal products?
Sea freight is cost-effective for large shipments, while air freight is faster for smaller, urgent orders. Consider insurance and customs regulations for international shipping.
Remember:
* Communicate clearly with manufacturers about your requirements.
* Negotiate prices and payment terms upfront.
* Protect your intellectual property rights.
* Factor in potential language barriers and cultural differences.

