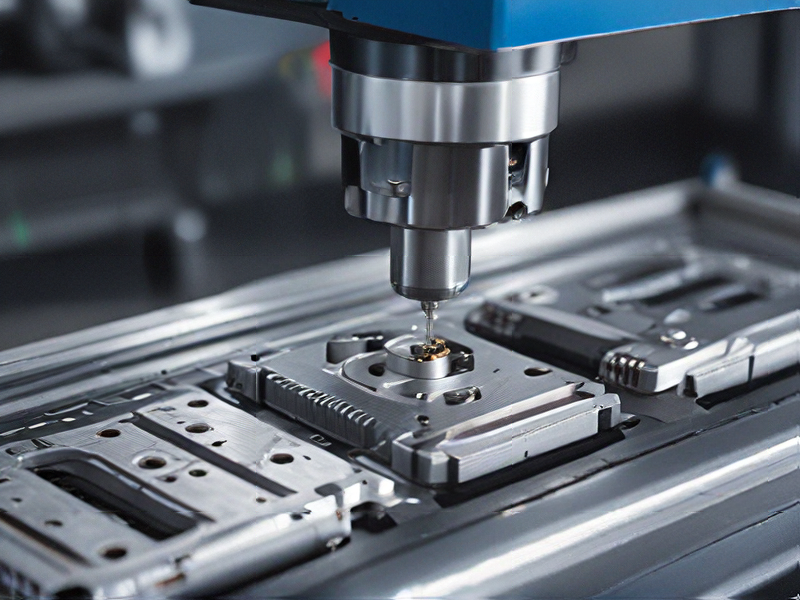
Technology and Applications of cnc programming
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) programming is integral to modern manufacturing, enabling precise control over machining tools through coded instructions. These instructions, typically written in G-code, dictate tool movements, speeds, and other parameters necessary for shaping raw materials into finished components.
The technology behind CNC programming revolves around CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, where engineers design parts digitally before translating these designs into CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. CAM software generates the G-code that CNC machines interpret to execute operations such as milling, drilling, turning, and grinding.
Applications of CNC programming span various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and healthcare. In automotive manufacturing, CNC machines shape engine components with high precision and repeatability, ensuring consistent quality and performance. In aerospace, CNC programming is crucial for producing complex parts like turbine blades that demand exacting specifications for strength and weight.
CNC programming also facilitates rapid prototyping and customization. By quickly reconfiguring G-code, manufacturers can adapt production lines to produce different parts without retooling, reducing downtime and costs associated with changeovers.
Moreover, CNC programming supports automation and integration with other digital technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence). These advancements enhance efficiency, monitor machine performance in real-time, and predict maintenance needs, optimizing overall manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, CNC programming combines precision engineering with digital automation to drive modern manufacturing forward, offering versatility, efficiency, and quality across a wide range of industries.
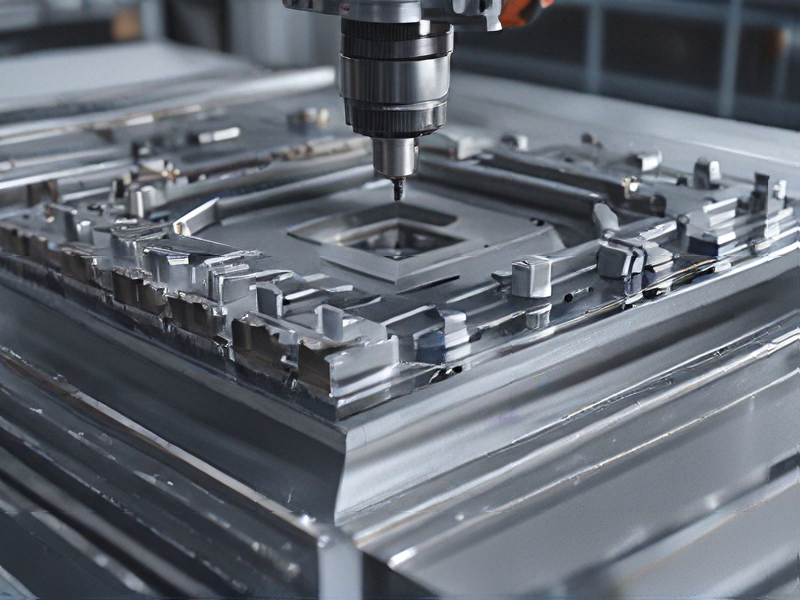

Quality Testing Methods for cnc programming and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for CNC programming primarily involve simulation and verification processes to ensure accuracy and reliability before actual machining begins. Here are key methods and strategies:
1. Simulation Software: Utilize CAD/CAM software to simulate toolpaths and machining operations virtually. This allows detection of potential errors in toolpath movements, collisions, and overall feasibility.
2. Virtual Machining: Implement virtual machining environments where CNC programs are run in a simulated CNC machine environment. This helps identify issues such as tool deflection, excessive vibrations, or inaccurate cutting forces.
3. Toolpath Verification: Conduct thorough verification of toolpaths against CAD models or part drawings to ensure dimensional accuracy and correct machining sequences.
4. Fixture and Tooling Check: Validate fixture designs and tooling setups virtually to ensure they can hold and machine the workpiece correctly without interferences or inaccuracies.
5. Post-Processor Validation: Verify post-processor outputs to ensure correct G-code generation that matches the capabilities and limitations of the CNC machine.
To control quality effectively:
– Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and follow detailed SOPs for CNC programming, simulation, and verification processes.
– Training and Skill Development: Provide training to programmers and operators on effective use of CAD/CAM software and simulation tools.
– Documentation and Version Control: Maintain comprehensive documentation of CNC programs, simulations, and verification results. Use version control to track changes and revisions.
– Continuous Improvement: Implement feedback loops from machining operations to programming to continuously refine and improve CNC programs and processes.
By integrating these methods and strategies into CNC programming workflows, manufacturers can significantly enhance quality control and ensure precise and efficient machining operations.
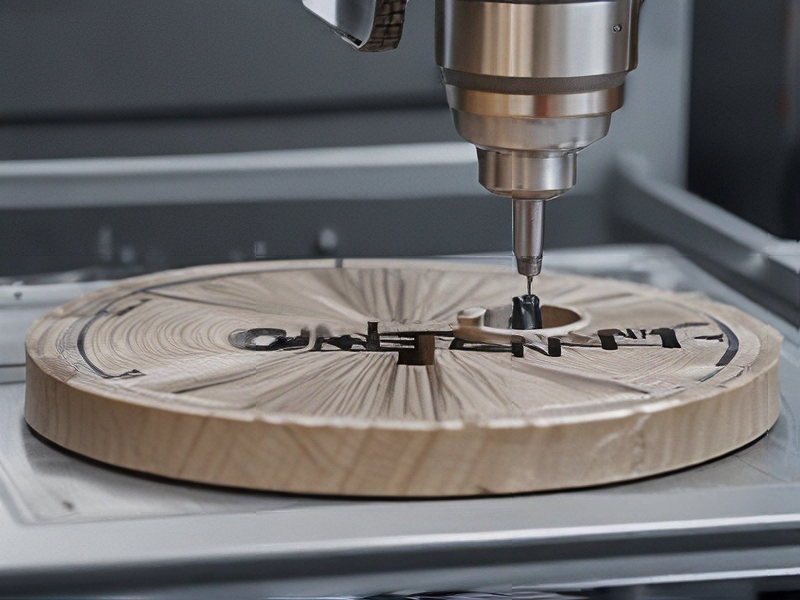

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from cnc programming
When considering procurement from CNC programming services, several key tips and considerations can streamline the process and ensure optimal outcomes:
1. Supplier Selection: Choose CNC programming providers with proven expertise in your specific industry and type of machining. Look for certifications, client testimonials, and case studies to assess their capabilities.
2. Technical Competence: Evaluate the CNC programmers’ proficiency in using advanced software like CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) systems relevant to your machining needs. Ensure they can handle complex geometries and materials required for your projects.
3. Quality Assurance: Prioritize suppliers with robust quality control processes. Request information on their inspection methods, adherence to industry standards (e.g., ISO 9001), and track record in delivering defect-free parts.
4. Cost-effectiveness: Compare quotes from different CNC programming services while considering not just the initial price but also factors like lead times, shipping costs, and potential for rework or rejects.
5. Communication and Collaboration: Opt for suppliers who communicate effectively and are responsive to your inquiries. Establish clear channels for feedback and updates throughout the procurement process.
6. Flexibility and Scalability: Choose CNC programming services that can accommodate changes in project scope or volume requirements. Scalability ensures they can handle both small prototype runs and large production orders.
7. Intellectual Property Protection: Discuss confidentiality agreements and intellectual property rights to safeguard your designs and proprietary information.
8. Sustainability Practices: Inquire about the supplier’s environmental policies, such as waste management and energy efficiency, to align with your organization’s sustainability goals.
9. Long-term Relationship: Consider the potential for a long-term partnership with the CNC programming service provider. A reliable partner can offer continuity, consistency, and potentially better pricing over time.
By focusing on these considerations, you can effectively navigate the procurement process for CNC programming services, ensuring quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness aligned with your project requirements.
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from cnc programming in China
Certainly! Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) regarding sourcing and manufacturing through CNC programming in China:
1. What are the advantages of sourcing CNC programming services from China?
China offers competitive pricing due to lower labor costs and a well-established manufacturing infrastructure. Additionally, Chinese firms often have extensive experience in CNC programming and can handle large volumes efficiently.
2. How can I ensure quality when sourcing CNC programming from China?
Quality assurance can be ensured through thorough supplier vetting, including certifications (ISO, CE), client references, and possibly visiting the facilities. Implementing clear specifications and regular quality checks during production are also crucial.
3. What are common challenges when manufacturing through CNC programming in China?
Challenges may include language barriers, cultural differences, longer lead times due to shipping, and intellectual property concerns. It’s essential to address these by clear communication, legal agreements, and choosing reputable partners.
4. What types of CNC programming services are available in China?
Chinese manufacturers offer a wide range of CNC programming services, including milling, turning, drilling, and custom machining for various materials such as metals, plastics, and composites.
5. How can I manage logistics and shipping when sourcing from China?
Partnering with logistics companies experienced in international shipping and choosing suppliers with efficient shipping capabilities (like proximity to ports) can streamline the process. Clear agreements on incoterms and delivery schedules are crucial.
6. What are the typical lead times for CNC programming projects in China?
Lead times can vary based on project complexity, materials, and current production schedules. Generally, they range from a few weeks to several months, so planning ahead and regular communication with suppliers are advisable.
These FAQs provide a foundational understanding for sourcing and manufacturing through CNC programming in China, helping businesses navigate the complexities and maximize their operational efficiencies.

