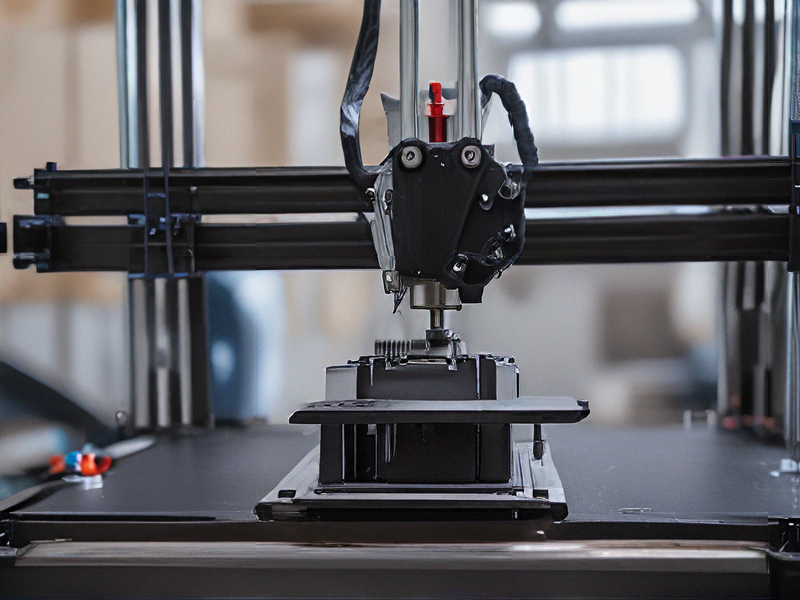
Technology and Applications of customize 3d printing
Customized 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, revolutionizes various industries by enabling personalized production at scale. This technology utilizes CAD software to design objects, which are then printed layer by layer using materials like plastics, metals, and ceramics.
In healthcare, customized 3D printing creates patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and surgical models tailored to individual anatomy. This enhances treatment outcomes and reduces surgery time. Similarly, in aerospace and automotive sectors, 3D printing allows for lightweight parts with complex geometries, improving fuel efficiency and performance.
Education benefits from 3D printing by visualizing complex concepts through tangible models, enhancing learning and innovation. In architecture and construction, firms use this technology to prototype structures and create intricate designs quickly.
Consumer goods industries utilize 3D printing for personalized products like jewelry, fashion accessories, and home décor. This customization meets consumer demands for unique items while reducing waste from mass production.
Moreover, 3D printing supports sustainable practices by minimizing material waste and energy consumption compared to traditional manufacturing methods. This technology continues to evolve with advancements in materials, printing speed, and precision, expanding its applications across diverse sectors.
In conclusion, customized 3D printing offers versatile solutions across healthcare, education, manufacturing, and consumer markets, driving innovation and efficiency in product development and customization.
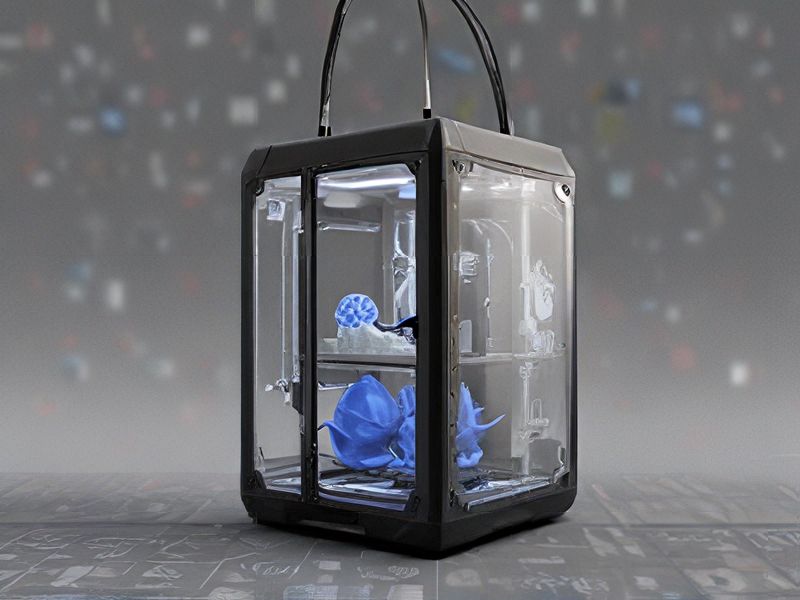

Quality Testing Methods for customize 3d printing and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for customized 3D printing involve several key approaches to ensure the final product meets specified standards. First, dimensional accuracy is crucial, often verified using calipers or coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to compare dimensions against CAD models. Surface finish is assessed visually and sometimes with surface roughness testers.
Mechanical properties such as tensile strength and flexibility are evaluated through standardized tests like ASTM standards for specific materials. Layer adhesion and bonding strength are tested through peel or shear tests. Additionally, assessing geometric tolerances ensures parts fit as intended.
To control quality, implementing process parameters like temperature, speed, and layer thickness is essential. Regular calibration of 3D printers and inspection equipment maintains accuracy. Employing quality management systems like ISO 9001 helps establish protocols for monitoring and improving processes.
Furthermore, conducting in-process inspections minimizes errors early. Utilizing software for simulation and analysis aids in predicting part behavior before printing, enhancing design feasibility and print success.
By combining these methods and controls, manufacturers can consistently achieve high-quality customized 3D printed products, meeting client expectations and industry standards.
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from customize 3d printing
When procuring customized 3D printing services, consider the following tips and key considerations:
1. Define Your Requirements Clearly: Clearly outline what you need in terms of size, material, complexity, and quantity of the 3D printed items. This helps in selecting the right service provider.
2. Quality Standards: Ensure the supplier has a track record of delivering high-quality prints. Request samples or references to assess their workmanship.
3. Technology and Capabilities: Verify that the 3D printing technology they use aligns with your project needs. Different technologies offer varying resolutions, materials, and build sizes.
4. Experience and Expertise: Choose a supplier with relevant experience in your industry or with similar projects. Experienced providers can offer insights and optimize designs for better results.
5. Cost and Value: Compare quotes from different suppliers, but prioritize value over cost alone. Consider factors like post-processing, support, and reliability in addition to initial price.
6. Communication and Support: Effective communication is crucial. Ensure the supplier is responsive and provides clear timelines and updates throughout the project.
7. Material Selection: Understand the materials offered by the supplier and their suitability for your application in terms of strength, flexibility, durability, and aesthetic qualities.
8. Post-Processing and Finishing: Evaluate the supplier’s capabilities for post-processing and finishing services such as painting, polishing, or assembly if required.
9. Intellectual Property and Confidentiality: Discuss ownership of designs, confidentiality agreements, and data security protocols to protect your intellectual property.
10. Scalability and Flexibility: Consider the supplier’s ability to scale production as needed and their flexibility to accommodate changes or revisions during the project.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a 3D printing service provider that meets your specific requirements, ensuring quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in your procurement process.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from customize 3d printing in China
Certainly! Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about sourcing and manufacturing custom 3D printing in China:
1. What are the advantages of sourcing 3D printing from China?
– China offers competitive pricing due to lower labor and manufacturing costs.
– Access to a wide range of manufacturing capabilities and materials.
– Ability to scale production quickly to meet demand.
2. How do I find a reliable 3D printing manufacturer in China?
– Research and verify manufacturers through online platforms, trade shows, and referrals.
– Request samples and conduct quality checks.
– Look for certifications and assess their experience with similar projects.
3. What types of 3D printing technologies are available in China?
– Common technologies include FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), SLA (Stereolithography), SLS (Selective Laser Sintering), and MJF (Multi Jet Fusion).
– Each technology offers different material options, resolutions, and production speeds.
4. What are the typical lead times for custom 3D printing orders from China?
– Lead times can vary based on complexity, quantity, and chosen technology.
– Generally, they range from a few days to several weeks, including shipping.
5. How can I ensure quality control when manufacturing in China?
– Establish clear quality standards and specifications.
– Conduct regular inspections during production and before shipment.
– Maintain open communication with the manufacturer to address any issues promptly.
6. What are the potential challenges of sourcing 3D printing from China?
– Language barriers and cultural differences may affect communication.
– Intellectual property protection and confidentiality concerns.
– Logistics and shipping complexities, especially for large or fragile items.
Navigating these considerations can help ensure a successful partnership with a Chinese manufacturer for your custom 3D printing needs.

