Technology and Applications of laser etching machines
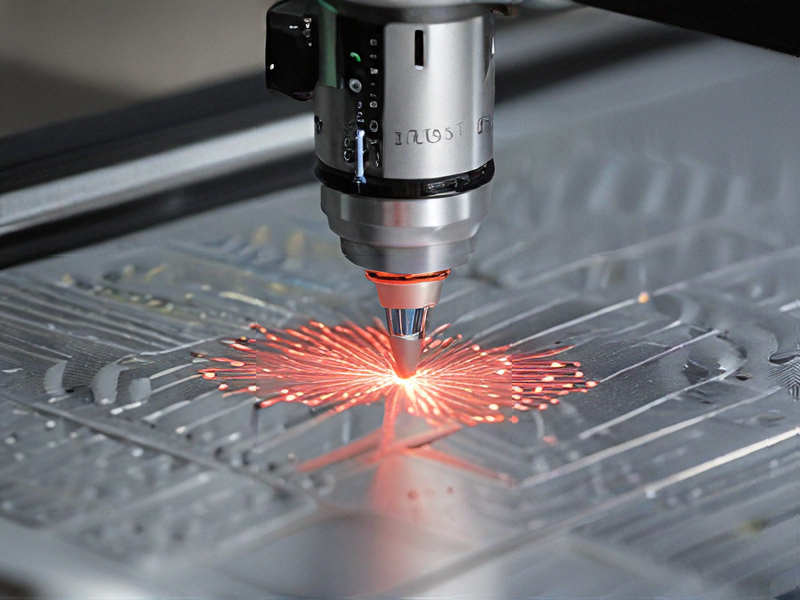
Laser etching machines utilize focused laser beams to engrave designs or text onto a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, glass, and ceramics. This technology provides precise and intricate markings, making it popular across multiple industries, ranging from manufacturing to art.
Applications of Laser Etching Machines:
1. Manufacturing and Production: In industrial settings, laser etching is used for marking products with serial numbers, barcodes, and batch numbers. This enhances traceability and helps with quality control processes.
2. Personalization: Many businesses use laser etching to create personalized items, such as custom gifts, trophies, and awards. Users can add names, dates, or unique designs, enhancing the emotional value of products.
3. Jewelry Making: Laser etching is commonly employed in the jewelry industry to engrave intricate patterns or inscriptions on rings, pendants, and bracelets, enabling high levels of detail and customization.
4. Signage: Laser etching is also utilized in creating durable and aesthetically pleasing signage. From office plaques to outdoor signs, the finish is often more resilient to weather and wear than traditional methods.
5. Art and Decoration: Artists leverage laser etching for creating artworks or decorative pieces on various materials, allowing for precision and repeatability.
The technology behind laser etching, including CO2 and fiber lasers, enables high-speed operations with minimal material waste. Additionally, advancements in software have simplified design processes, making it increasingly accessible to both professionals and hobbyists. Overall, laser etching machines represent an innovative solution that combines precision and versatility, catering to a wide range of applications.

Quality Testing Methods for laser etching machines and how to control quality
Quality testing for laser etching machines involves several key methods to ensure precision and consistency in etching processes. Here are some effective methods and quality control measures:
1. Visual Inspection: Regularly conduct visual checks on etched samples to assess clarity, depth, and uniformity. Any irregularities like charring or incomplete etching should be noted.
2. Dimensional Measurement: Utilize calipers and micrometers to measure the dimensions of etched patterns against design specifications. This helps verify that the scale and proportions are accurate.
3. Power and Speed Calibration: Test different power settings and speeds to determine optimal parameters for various materials. Use a test material to establish guidelines for future etching.
4. Repeatability Testing: Execute a series of identical etching jobs using the same parameters to ensure consistency over multiple runs. Document results to identify any variations.
5. Material Compatibility Tests: Assess how different materials respond to laser etching by conducting sample runs. This helps in understanding the limits and optimal conditions for various substrates.
6. Post-Etching Cleanliness Tests: After etching, check for residue or debris that could affect the quality. Implement cleaning protocols to ensure the machine remains in peak condition.
7. Software and Firmware Updates: Regularly update machine software to ensure optimal performance and address any issues that arise.
8. Training and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Train operators thoroughly and have clear SOPs to maintain quality during operation, ensuring all settings are correct before initiating an etching job.
By integrating these methods and practices, laser etching operations can systematically control quality, reduce errors, and enhance overall output consistency.

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from laser etching machines
When procuring a laser etching machine, consider the following tips and factors to ensure a successful purchase:
1. Define Your Needs: Determine the type of materials you plan to engrave or etch (e.g., wood, metal, glass) and the desired precision and speed. Define your project sizes and production volume to guide your choice.
2. Machine Specifications: Look at the machine’s wattage, speed, and engraving area. Higher wattage often means faster cutting and engraving, while a larger engraving area allows for bigger projects.
3. Technology Type: Understand the differences between CO2 and fiber laser machines. CO2 lasers are typically suited for non-metal materials, while fiber lasers excel in engraving metals.
4. Software Compatibility: Ensure the machine is compatible with the design software you intend to use. Some machines come with proprietary software, while others may support more versatile programs.
5. Budget Considerations: Factor in not only the initial cost of the machine but also ongoing expenses such as maintenance, replacement parts, and consumables (e.g., lenses).
6. Warranty and Support: Choose a supplier that offers a solid warranty and reliable technical support. This can be invaluable for troubleshooting and repairs.
7. Supplier Reputation: Research suppliers’ reviews and ratings to gauge their reliability. A reputable supplier will provide good after-sales service and technical assistance.
8. Training and Resources: Consider if the manufacturer offers training resources or manuals that can help you efficiently operate the machine.
9. Future-Proofing: Think about scalability and whether the machine can accommodate future projects or expansions in your business.
By carefully evaluating these points, you can make an informed decision when purchasing a laser etching machine.
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from laser etching machines in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing Laser Etching Machines from China
1. Why source laser etching machines from China?
China is a leading manufacturer of laser etching machines, offering competitive pricing, a wide range of technology options, and advanced production capabilities, making it an attractive choice for many businesses.
2. What should I consider when choosing a supplier?
Key factors include the supplier’s reputation, production capacity, certifications (e.g., ISO), product quality, after-sales support, and ability to customize machines to your specific requirements.
3. How can I verify the quality of the machines?
Request samples, check for relevant certifications, and conduct factory audits or third-party inspections. Reading reviews and testimonials from previous customers is also helpful.
4. What are the typical lead times for manufacturing?
Lead times can vary based on complexity and order size, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. Always confirm timelines with the supplier.
5. What customization options are available?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including size, laser power, software compatibility, and additional features tailored to specific applications, such as engraving or cutting.
6. How do I handle shipping and logistics?
Discuss shipping options with your supplier. Depending on your location, you can choose air freight for quicker delivery or sea freight for cost-effective solutions. Ensure proper shipping documentation is in place.
7. What about after-sales support and warranty?
Confirm the warranty terms and after-sales support options, including technical assistance, spare parts availability, and maintenance services. A reliable supplier should provide clear terms.
8. Are there any hidden costs?
Always clarify pricing details upfront, including shipping, customs duties, taxes, and potential tariffs, to avoid unexpected expenses.

