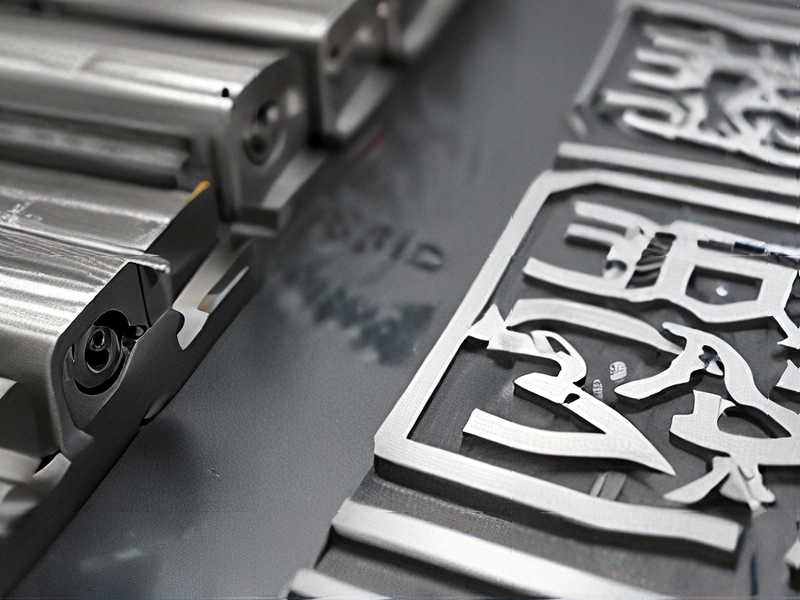
Technology and Applications of laser for metal engraving
Laser technology has revolutionized metal engraving, offering precision, speed, and versatility. The primary technology used for metal engraving includes fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) lasers.
1. Fiber Lasers:
– Technology: Fiber lasers use optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements like ytterbium. The fiber amplifies the laser beam, making it highly efficient and capable of delivering high power.
– Applications: Ideal for marking and engraving metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. They are used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics for serial numbers, barcodes, and intricate designs.
2. CO2 Lasers:
– Technology: CO2 lasers employ a gas mixture, primarily carbon dioxide, excited by electricity to produce a laser beam. They are less efficient on metals without an applied coating.
– Applications: While more commonly used for non-metals, they can engrave metals with the help of marking solutions or coatings. They are used for applications requiring large workspaces, such as signage and architectural components.
3. DPSS Lasers:
– Technology: DPSS lasers use a laser diode to pump a solid gain medium, often a crystal. This method produces high beam quality and stability.
– Applications: Suitable for precision engraving and micro-machining of metals, these lasers are used in the production of microelectronics, medical devices, and fine jewelry.
Advantages:
– Precision: Laser engravers provide fine detail and consistent quality, essential for intricate designs and high-resolution images.
– Speed: High engraving speeds increase productivity, making them suitable for mass production.
– Versatility: Capable of engraving various metals and other materials, enhancing their applicability across multiple industries.
Considerations:
– Initial Cost: High upfront investment in laser engraving equipment.
– Material Compatibility: Different lasers work better with specific materials; choosing the right laser is crucial for optimal results.
Overall, laser engraving technology is integral to modern manufacturing and craftsmanship, offering unmatched precision and efficiency.
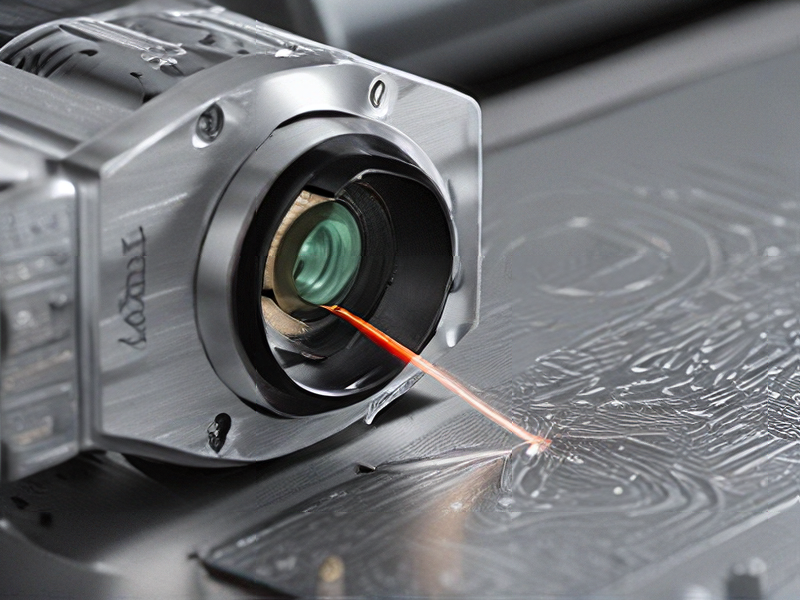

Quality Testing Methods for laser for metal engraving and how to control quality
Quality testing for laser metal engraving involves several methods to ensure precision, durability, and consistency. Here are some key methods and controls:
Quality Testing Methods
1. Visual Inspection:
– Microscopy: Using microscopes to check for fine details, ensuring no imperfections.
– Surface Finish: Inspecting the smoothness and consistency of the engraved area.
2. Dimensional Accuracy:
– Calipers and Micrometers: Measuring engraved features to ensure they meet specified dimensions.
– Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM): High-precision equipment for measuring complex geometries.
3. Surface Roughness:
– Profilometers: Measuring the roughness of the engraved surface to ensure it meets required specifications.
4. Material Integrity:
– Microhardness Testing: Assessing if the engraving process affected the hardness of the material.
– Microstructure Analysis: Checking for changes in the metal’s microstructure using techniques like metallography.
5. Consistency Testing:
– Repeatability Tests: Engraving multiple samples and comparing them for consistency in quality.
– Batch Testing: Testing samples from different batches to ensure uniform quality.
Quality Control Measures
1. Calibration:
– Regular Calibration of Equipment: Ensuring laser engravers and measuring tools are regularly calibrated to maintain accuracy.
2. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
– Documented Procedures: Establishing and following SOPs for the engraving process to maintain consistency.
3. Operator Training:
– Skilled Technicians: Ensuring operators are well-trained and understand the impact of different parameters on engraving quality.
4. Environmental Controls:
– Controlled Environment: Maintaining a stable environment (temperature, humidity) to prevent variations in engraving quality.
5. Process Parameters:
– Monitoring Laser Parameters: Regularly checking and adjusting laser power, speed, and focus to maintain optimal engraving conditions.
– Material Selection: Using metals with consistent properties and verifying them before engraving.
6. Inspection and Testing Protocols:
– In-Process Inspections: Conducting inspections during the engraving process to catch defects early.
– Final Quality Checks: Performing thorough final inspections before delivery.
By integrating these testing methods and quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure high-quality, reliable laser engravings on metal.
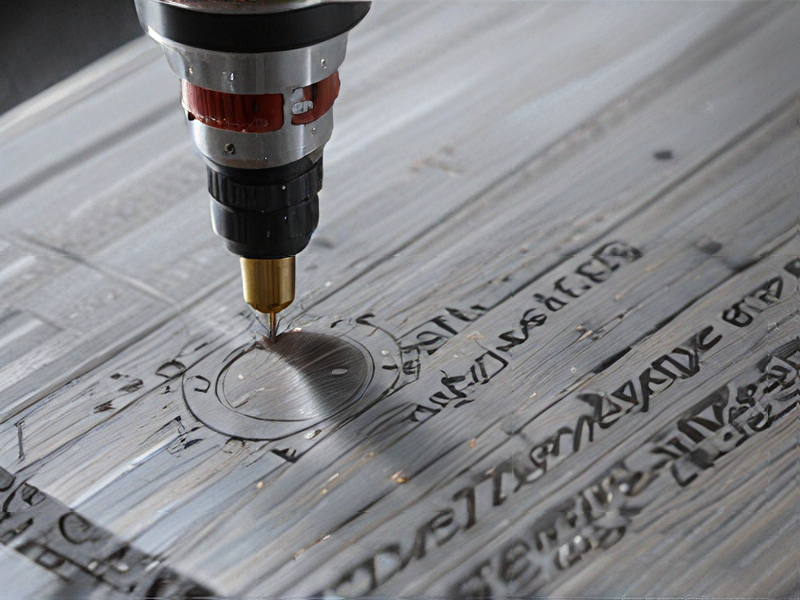

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from laser for metal engraving
When procuring a laser for metal engraving, it’s essential to consider several factors to ensure you choose the right equipment for your needs. Here are some tips and considerations:
1. Power and Wattage: The power of the laser affects its ability to engrave different types of metal. Higher wattage lasers can engrave thicker and harder metals more efficiently. Common wattages for metal engraving range from 20W to 100W.
2. Laser Type: There are different types of lasers, such as fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and diode lasers. Fiber lasers are typically preferred for metal engraving due to their high precision and efficiency.
3. Engraving Speed: Consider the speed of the laser, as it affects productivity. Faster engraving speeds are beneficial for high-volume production environments.
4. Precision and Resolution: The precision and resolution of the laser determine the quality of the engraving. Look for lasers that offer high DPI (dots per inch) for finer details.
5. Software Compatibility: Ensure the laser system is compatible with your design software. Some lasers come with proprietary software, while others can integrate with popular design programs like AutoCAD or Adobe Illustrator.
6. Cooling System: Laser engraving generates heat, so a good cooling system is crucial to maintain performance and prolong the life of the laser.
7. Safety Features: Look for lasers with safety features such as protective enclosures, emergency stop buttons, and proper ventilation to ensure safe operation.
8. Maintenance and Support: Consider the availability of technical support and the ease of maintenance. Regular maintenance is necessary to keep the laser in optimal condition.
9. Cost: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including the initial purchase price, operating costs, and maintenance expenses. Balance your budget with the required features and performance.
10. Warranty and Service: A good warranty and reliable after-sales service can save you from costly repairs and downtime.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select a laser engraving machine that meets your specific needs and ensures efficient, high-quality engraving on metal surfaces.
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from laser for metal engraving in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from Laser for Metal Engraving in China
1. Why source laser engraving machines from China?
– China offers competitive pricing, advanced technology, and a wide range of options. Manufacturers often provide customization and support services, making it a cost-effective choice.
2. How to identify reliable suppliers?
– Use platforms like Alibaba and Global Sources. Check supplier ratings, customer reviews, certifications (ISO, CE), and request product samples. Conduct video factory tours if possible.
3. What are the key features to look for in a laser engraving machine?
– Consider power (wattage), engraving speed, precision, compatible materials, software compatibility, and after-sales support. Fiber lasers are preferred for metal engraving due to their efficiency and precision.
4. What is the typical cost of a laser engraving machine from China?
– Prices vary widely based on specifications. Entry-level machines start around $2,000, while high-end models can exceed $10,000. Always compare features and warranty terms.
5. How to ensure quality and compliance?
– Request detailed specifications, quality control reports, and certifications. Engage third-party inspection services to verify machine quality and compliance with international standards.
6. What about shipping and logistics?
– Confirm the supplier’s shipping options and costs. Use reliable freight forwarders. Be aware of import duties and taxes in your country. Consider insurance for high-value shipments.
7. How is after-sales support handled?
– Verify the supplier’s warranty terms, technical support availability, and spare parts supply. Many reputable suppliers offer online support, training videos, and manuals.
8. Are there any common issues with Chinese laser engraving machines?
– Potential issues include software compatibility, spare parts availability, and language barriers. Mitigate these by choosing well-established suppliers with good reputations.
9. How long does the delivery take?
– Delivery times vary based on machine complexity and shipping method, typically ranging from 2 to 8 weeks.
10. Can I get customized laser engraving machines?
– Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization based on specific needs, including power, size, and additional features.
By addressing these FAQs, you can make informed decisions when sourcing laser engraving machines from China.

