Description
fiberglass sheet Safety Certifications
Fiberglass sheets, used widely in construction, automotive, and industrial applications, require various safety certifications to ensure they meet health, safety, and environmental standards. Key certifications include:
1. ISO 9001: This quality management certification ensures that fiberglass sheets are manufactured consistently, meeting customer and regulatory requirements. It focuses on process efficiency and product quality.
2. UL 94: This flammability standard, issued by Underwriters Laboratories, evaluates the material’s ability to extinguish or resist ignition. Fiberglass sheets with UL 94 ratings, such as V-0, V-1, or V-2, indicate varying levels of flame retardancy.
3. ASTM Standards: The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides numerous standards for fiberglass products, such as ASTM D635 for flammability, ASTM D638 for tensile properties, and ASTM E84 for surface burning characteristics. Compliance ensures the material’s physical properties are well-documented and reliable.
4. REACH Compliance: This European Union regulation addresses the production and use of chemical substances and their potential impacts on human health and the environment. REACH-compliant fiberglass sheets meet strict guidelines regarding the presence of hazardous substances.
5. RoHS Compliance: The Restriction of Hazardous Substances directive restricts the use of specific hazardous materials found in electrical and electronic products. Fiberglass sheets adhering to RoHS standards are free from harmful levels of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous substances.
6. NFPA Standards: Compliance with National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards, such as NFPA 701, which tests the flammability of materials, is crucial for ensuring fiberglass sheets are safe for use in fire-prone environments.
7. OSHA Compliance: Adherence to Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations ensures that the manufacturing process and handling of fiberglass sheets do not pose health risks to workers, particularly concerning dust and inhalation hazards.
These certifications and standards collectively ensure that fiberglass sheets are safe, reliable, and suitable for various applications, providing necessary assurances to manufacturers, users, and regulatory bodies.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “fiberglass sheet”
Reference Technical Parameters of Fiberglass Sheet
Material Composition
– Fiber Type: E-glass, S-glass
– Resin Type: Polyester, Epoxy, Vinyl ester
Physical Properties
– Thickness: Typically ranges from 0.5 mm to 50 mm
– Density: 1.8 – 2.0 g/cm³
– Surface Finish: Glossy, matte, textured
Mechanical Properties
– Tensile Strength: 350 – 900 MPa
– Compressive Strength: 150 – 350 MPa
– Flexural Strength: 300 – 600 MPa
– Modulus of Elasticity: 15 – 25 GPa
– Shear Strength: 60 – 100 MPa
– Hardness: Barcol hardness 45 – 55
Thermal Properties
– Thermal Conductivity: 0.05 – 0.35 W/m·K
– Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: 5 – 30 x 10⁻⁶/°C
– Heat Deflection Temperature: 150 – 200°C
– Glass Transition Temperature: 80 – 130°C
Electrical Properties
– Dielectric Strength: 10 – 30 kV/mm
– Dielectric Constant: 4.5 – 6.5 at 1 MHz
– Volume Resistivity: 10¹⁴ – 10¹⁶ Ω·cm
Chemical Resistance
– Acids: Good to excellent resistance
– Bases: Moderate to good resistance
– Solvents: Moderate resistance
Environmental Properties
– Water Absorption: 0.1 – 0.5% over 24 hours
– Weather Resistance: Excellent, with UV stabilizers for outdoor use
Processing Techniques
– Forming Methods: Hand lay-up, spray-up, compression molding, resin transfer molding (RTM), vacuum bagging
These parameters provide a comprehensive overview of the essential technical specifications for fiberglass sheets, useful for selecting the right material for specific applications.
List Product features of “fiberglass sheet”
Fiberglass Sheet Product Features
1. Material Composition: Made from a composite of fine glass fibers and resin, providing strength and durability.
2. Lightweight: Despite its robustness, fiberglass sheets are lightweight, making them easy to handle and install.
3. High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Offers exceptional mechanical strength without the heaviness of traditional materials like metal or wood.
4. Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to rust, chemicals, and environmental elements, ensuring longevity even in harsh conditions.
5. Weather Resistance: Can withstand extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and moisture, making it ideal for outdoor applications.
6. Thermal Insulation: Provides excellent insulation properties, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency.
7. Electrical Insulation: Non-conductive nature makes it suitable for electrical applications and environments requiring high insulation standards.
8. Flexibility: Can be easily molded or shaped during manufacturing to meet specific design requirements.
9. Fire Resistance: Certain fiberglass sheets are treated to be fire-resistant, adding an extra layer of safety.
10. Low Maintenance: Requires minimal upkeep compared to traditional materials, reducing long-term maintenance costs.
11. Dimensional Stability: Maintains its shape and size over time, even under varying temperature and humidity conditions.
12. Acoustic Insulation: Provides soundproofing benefits, making it useful in noise-sensitive environments.
13. Aesthetic Versatility: Available in various colors, finishes, and textures to suit different design preferences.
14. Ease of Installation: Can be cut, drilled, and machined using standard tools, simplifying the installation process.
15. Environmental Benefits: Often made from recyclable materials and has a long lifespan, reducing environmental impact.
16. Cost-Effective: Offers a balance of performance and affordability, making it a practical choice for various applications.
Fiberglass sheets are utilized in construction, automotive, marine, and industrial sectors due to their versatile and durable nature.
List Application of “fiberglass sheet”
Fiberglass sheets are versatile materials used across various industries due to their strength, lightweight nature, and resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. Here are some key applications:
1. Construction: Fiberglass sheets are widely used in roofing, wall panels, and insulation materials. They provide thermal and acoustic insulation, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings.
2. Automotive: In the automotive sector, fiberglass sheets are used to manufacture body panels, hoods, and other structural components. Their lightweight nature improves fuel efficiency and performance.
3. Marine: Fiberglass is commonly used in the construction of boats, yachts, and other marine vessels. Its resistance to water and corrosion makes it ideal for hulls, decks, and superstructures.
4. Industrial: Fiberglass sheets are employed in manufacturing equipment, tanks, and pipes that handle corrosive chemicals. They are also used in the construction of cooling towers and other industrial structures.
5. Electrical: Due to their excellent insulating properties, fiberglass sheets are used in electrical applications such as circuit boards, enclosures, and insulators.
6. Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, fiberglass sheets are used for constructing lightweight and strong components for aircraft and spacecraft, contributing to weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency.
7. Recreational: Fiberglass sheets are used to make various recreational products, including surfboards, canoes, and playground equipment. Their durability and resistance to environmental factors make them suitable for outdoor use.
8. Signage: Fiberglass sheets are used in the production of durable and weather-resistant signs and displays, suitable for both indoor and outdoor advertising.
9. Agricultural: In agriculture, fiberglass sheets are used for greenhouses, providing a strong and lightweight material that allows light transmission while protecting plants from harsh weather conditions.
These applications highlight the versatility and effectiveness of fiberglass sheets across diverse industries.
List Various Types of “fiberglass sheet”
Fiberglass sheets come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and environments. Here are the main types:
1. Plain Fiberglass Sheets:
– Standard Glass Fiber Sheets: Used in general construction and automotive applications for their lightweight and strength.
– E-Glass: Commonly used for electrical insulation and in general-purpose applications due to its good electrical properties and resistance to chemicals.
2. Specialty Fiberglass Sheets:
– S-Glass: Offers higher strength and heat resistance, ideal for aerospace and military applications.
– AR Glass: Alkali-resistant fiberglass used in concrete reinforcement to prevent cracking and improve strength.
– C-Glass: Primarily used for its chemical resistance, suitable for corrosive environments.
3. Textured Fiberglass Sheets:
– Woven Roving: Provides added strength and thickness, used in boat building and large structural parts.
– Chopped Strand Mat (CSM): Made of randomly oriented glass fibers held together by a binder, used for creating molds and laminates.
4. Composite Fiberglass Sheets:
– FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic): Combines fiberglass with a plastic matrix, offering excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight properties, used in automotive and industrial applications.
– GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic): Similar to FRP but with enhanced strength, used in roofing, cladding, and piping.
5. Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Fiberglass Sheets:
– Foam Core Fiberglass Sheets: Provides thermal insulation, often used in building insulation and HVAC systems.
– Acoustic Fiberglass Panels: Designed to absorb sound, used in studios, theaters, and office spaces.
6. UV Resistant Fiberglass Sheets:
– Gel-Coated Fiberglass: Has a protective coating to resist UV radiation, used in outdoor applications like roofing and cladding.
– UV Stabilized Fiberglass: Enhanced with UV inhibitors, suitable for prolonged outdoor exposure.
7. Fire-Retardant Fiberglass Sheets:
– Class A Fire Retardant Sheets: Meets stringent fire safety standards, used in public buildings and transportation sectors.
Each type of fiberglass sheet offers unique properties making them suitable for a wide range of applications from construction and automotive to aerospace and marine industries.
fiberglass sheet Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Fiberglass sheets are versatile materials used in various industries, including construction, automotive, and marine. To enhance their functionality, several accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options are available.
Accessories
1. Fasteners and Mounting Systems: Specialized screws, bolts, and brackets designed to secure fiberglass sheets without causing damage or compromising their integrity.
2. Edge Trims and Seals: Protect edges from wear and tear while providing a clean, finished look. These accessories also help in sealing joints to prevent water ingress.
3. Reinforcement Strips: Added to increase the structural strength of fiberglass sheets, making them more durable under heavy loads.
Upgrades
1. UV Protection Coatings: Applied to prevent degradation from prolonged exposure to sunlight, extending the lifespan of fiberglass sheets used outdoors.
2. Fire Retardant Additives: Enhance the fire resistance of fiberglass sheets, making them safer for use in high-risk environments.
3. Antimicrobial Treatments: Prevent the growth of mold, mildew, and bacteria, ideal for applications in humid or medical settings.
Custom Manufacturing Options
1. Custom Sizes and Shapes: Fiberglass sheets can be manufactured in specific dimensions and shapes to meet unique project requirements, reducing waste and installation time.
2. Color Customization: Available in various colors and finishes, including translucent options, to match aesthetic needs or functional requirements such as light diffusion.
3. Texture Variations: Different surface textures, such as smooth, matte, or embossed, provide various aesthetic and functional properties, like slip resistance or reduced glare.
4. Composite Layers: Incorporating additional materials like carbon fiber or Kevlar to enhance specific properties such as strength, stiffness, or impact resistance.
By leveraging these accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options, fiberglass sheets can be tailored to meet the specific demands of any project, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “fiberglass sheet”
Quality Control in Fiberglass Sheet Manufacturing
Quality control (QC) in fiberglass sheet manufacturing ensures product consistency, durability, and safety. The QC process involves several steps:
1. Raw Material Inspection: Verify the quality of glass fibers and resin. Glass fibers must meet specific diameter and strength criteria, while resins must have precise chemical properties.
2. Process Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of temperature, pressure, and speed during the production ensures consistency. Deviations can affect the final product’s properties.
3. In-Process Testing: Conducting tests such as tensile strength, thickness, and resin-to-glass ratio during the manufacturing process helps identify and rectify issues early.
4. Final Product Testing: Finished sheets undergo rigorous testing, including impact resistance, flexural strength, and thermal stability. Non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic testing can detect internal flaws.
5. Visual Inspection: Inspect for surface defects like cracks, bubbles, and uniformity. High-definition cameras and trained inspectors often perform this task.
6. Compliance and Certification: Ensuring products meet industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) and acquiring necessary certifications validates the quality.
Manufacturing Process of Fiberglass Sheet
1. Raw Material Preparation: Fiberglass sheets start with glass fibers, which are produced by melting raw materials and extruding them into thin filaments. Resins, often polyester or epoxy, are prepared with additives for enhanced properties.
2. Sheet Formation:
– Layup Process: Continuous glass fibers are laid out in layers. The number of layers depends on the desired thickness and strength.
– Resin Application: Resin is applied to the glass fiber layers. This can be done manually (hand lay-up) or using automated spray or injection systems (resin transfer molding).
3. Curing: The resin-saturated fiberglass layers are placed in a mold and subjected to heat and pressure. This process, known as curing, solidifies the resin, binding the fibers into a rigid sheet.
4. Cooling and Demolding: The cured fiberglass sheet is allowed to cool before being removed from the mold.
5. Trimming and Finishing: Edges are trimmed, and surfaces are finished to meet precise specifications. This may involve sanding, cutting, or additional surface treatments.
6. Quality Assurance: The final sheets undergo a series of quality control tests to ensure they meet all specified criteria before being shipped to customers.
Materials of “fiberglass sheet”
Materials of Fiberglass Sheet
Fiberglass sheets are composite materials made primarily of glass fibers and a polymer resin matrix. Here are the key components:
1. Glass Fibers:
– E-glass: The most common type, known for its good electrical insulation properties and moderate strength. It is composed mainly of silica (SiO₂), alumina (Al₂O₃), calcium oxide (CaO), and other minor oxides.
– S-glass: Offers higher tensile strength and modulus, used in applications requiring higher mechanical performance. It is made from silica (SiO₂), alumina (Al₂O₃), and magnesium oxide (MgO).
– C-glass: Known for its chemical resistance, commonly used in corrosive environments. It consists of silica (SiO₂), alumina (Al₂O₃), calcium oxide (CaO), and boron oxide (B₂O₃).
2. Polymer Resin Matrix:
– Polyester Resin: The most widely used resin in fiberglass production due to its cost-effectiveness and good mechanical properties. It is made from polyester and is cured using a catalyst, typically methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP).
– Epoxy Resin: Known for superior mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and better adhesion to fibers. It is often used in high-performance applications. Epoxy resins are cured using various hardeners, such as amines.
– Vinyl Ester Resin: Offers better corrosion resistance and mechanical properties than polyester, used in more demanding environments. It is a hybrid of polyester and epoxy resins.
3. Additives and Fillers:
– Curing Agents: Chemicals like MEKP (for polyester) or amines (for epoxy) initiate the curing process.
– Fillers: Materials such as calcium carbonate, talc, or silica may be added to enhance properties or reduce cost.
– Pigments: Added to impart color to the fiberglass sheets.
These components combine to produce fiberglass sheets that are lightweight, strong, corrosion-resistant, and versatile for various industrial, marine, automotive, and construction applications.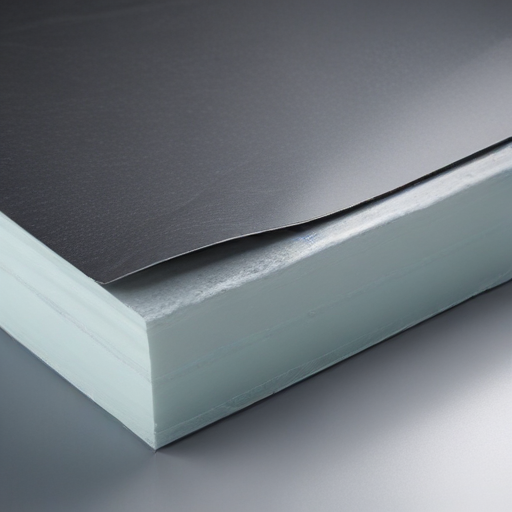
“fiberglass sheet” Comparative Analysis
Fiberglass sheets are versatile materials widely used in various industries due to their unique properties. Here is a comparative analysis highlighting the key aspects:
Properties and Composition
Fiberglass sheets are made from fine fibers of glass woven into a mat and bonded with resin. They offer high strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for applications requiring durable yet lightweight materials. These sheets also provide excellent thermal insulation, corrosion resistance, and electrical non-conductivity, making them suitable for both industrial and consumer applications.
Types
1. E-glass: The most common type, offering a balance of strength, durability, and affordability. It is used in general-purpose applications such as automotive parts, marine structures, and sporting goods.
2. S-glass: Offers higher tensile strength and is used in applications demanding superior mechanical properties, like aerospace and military industries.
3. C-glass: Known for its chemical resistance, it is used in applications exposed to harsh chemical environments.
Applications
– Construction: Used in panels, roofing, and reinforcement materials.
– Automotive and Transportation: Utilized in body panels, bumpers, and interior components due to their lightweight and strength.
– Electrical: Employed in circuit boards and electrical insulation due to their non-conductive properties.
– Marine: Favored for boat hulls and other marine structures due to their corrosion resistance.
Advantages
– Durability: High resistance to wear, impact, and environmental factors.
– Lightweight: Easier handling and lower transportation costs.
– Cost-Effective: Provides long-term savings due to reduced maintenance and repair needs.
Disadvantages
– Brittleness: Can be prone to cracking under high impact or stress.
– Health Risks: Fine fibers can pose health risks during manufacturing or if inhaled during handling.
Alternatives
– Carbon Fiber: Offers higher strength and stiffness but at a significantly higher cost.
– Kevlar: Provides exceptional impact resistance but is also more expensive.
In conclusion, fiberglass sheets are an excellent choice for a wide range of applications due to their balanced properties, affordability, and versatility. However, their selection should consider specific needs, potential health risks, and alternative materials for optimal results.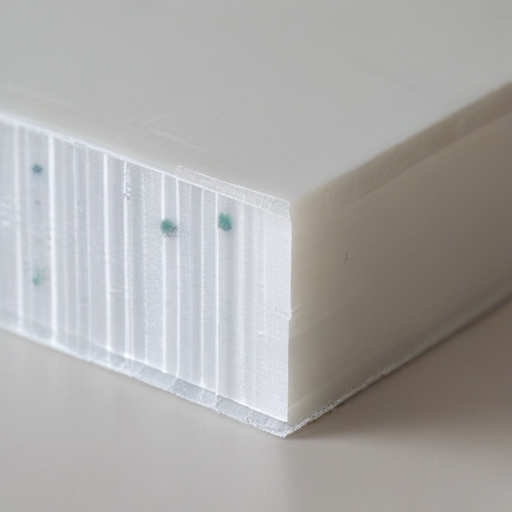
“fiberglass sheet” Warranty and Support
Fiberglass Sheet Warranty and Support
#### Warranty
Our fiberglass sheets come with a comprehensive warranty to ensure customer satisfaction and product reliability. The standard warranty period is five years from the date of purchase. This warranty covers manufacturing defects, including delamination, structural integrity, and material flaws under normal use and conditions. Should any defects arise within the warranty period, the product will be repaired or replaced at no additional cost to the customer.
Exclusions: The warranty does not cover damages caused by:
– Improper installation or handling
– Exposure to chemicals not recommended for fiberglass
– Accidents, misuse, or natural disasters
– Unauthorized modifications or repairs
#### Claim Process
To file a warranty claim, customers should contact our customer service department with proof of purchase and a detailed description of the issue. We may require photographs or an inspection to validate the claim. Approved claims will be processed promptly to minimize disruption.
#### Support
We are committed to providing exceptional support to our customers. Our knowledgeable support team is available to assist with:
– Product selection and specifications
– Installation guidelines and best practices
– Troubleshooting and maintenance tips
Contact Us:
– Phone: 1-800-555-1234
– Email: [email protected]
– Live Chat: Available on our website from 9 AM to 5 PM (EST), Monday to Friday
For detailed technical documentation, installation guides, and FAQs, please visit our website’s support section. We also offer instructional videos and webinars to ensure you get the most out of your fiberglass sheets.
Your satisfaction is our priority. Trust in our products and support services to meet your fiberglass needs efficiently and effectively.
List “fiberglass sheet” FAQ
Fiberglass Sheet FAQ
What is a fiberglass sheet?
A fiberglass sheet is a flat panel made from fiberglass-reinforced plastic, offering high strength and durability while being lightweight. It’s commonly used in various industries, including construction, automotive, and marine.
What are the benefits of using fiberglass sheets?
Fiberglass sheets are known for their strength, lightweight, corrosion resistance, non-conductivity, and flexibility. They also resist weathering, chemicals, and impact, making them suitable for many applications.
How thick are fiberglass sheets?
Fiberglass sheets come in various thicknesses, typically ranging from 0.5 mm to over 25 mm. The appropriate thickness depends on the specific application and required strength.
Can fiberglass sheets be cut or shaped?
Yes, fiberglass sheets can be easily cut, drilled, and shaped using standard tools like saws, drills, and routers. However, proper safety gear, such as masks and goggles, should be used to avoid inhaling fiberglass dust.
Are fiberglass sheets heat resistant?
Fiberglass sheets have good thermal resistance and can typically withstand temperatures up to 150°C (302°F). Special formulations can handle even higher temperatures for specific applications.
How do you clean fiberglass sheets?
Cleaning fiberglass sheets is straightforward. Use a mild detergent and water for regular cleaning. Avoid abrasive cleaners and harsh chemicals that can damage the surface.
Can fiberglass sheets be painted?
Yes, fiberglass sheets can be painted. For best results, use paints and primers designed specifically for fiberglass surfaces. Proper surface preparation, including sanding and cleaning, is essential for good adhesion.
Are fiberglass sheets UV resistant?
Standard fiberglass sheets may degrade under prolonged UV exposure. UV-resistant formulations or protective coatings can be applied to enhance durability in outdoor applications.
What are common applications of fiberglass sheets?
Common applications include roofing, cladding, insulation panels, automotive parts, marine components, and industrial flooring. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of uses.
Is fiberglass sheet environmentally friendly?
Fiberglass sheets are durable and have a long lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements. However, they are not biodegradable and require proper disposal or recycling at the end of their life cycle.
This concise FAQ covers the essential aspects of fiberglass sheets, providing a quick reference for users.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about fiberglass sheet for Buyer Sourcing from China
Top 10 FAQ about Fiberglass Sheets for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What are the main types of fiberglass sheets available?
– The main types include standard fiberglass, woven roving, chopped strand mat, and surface mat. They vary in strength, thickness, and finish.
2. What is the typical application of fiberglass sheets?
– They are used in construction, automotive, marine, and aerospace industries for parts like panels, roofs, and reinforcements due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
3. What are the key properties of fiberglass sheets?
– Fiberglass sheets are known for their high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and lightweight characteristics.
4. How do I ensure the quality of fiberglass sheets from China?
– Look for suppliers with ISO certifications, request material test reports, and consider third-party inspections. Visiting factories can also be beneficial.
5. What is the standard size and thickness of fiberglass sheets?
– Common sizes are 4’ x 8’ with thicknesses ranging from 0.5mm to 50mm, but custom sizes and thicknesses can be ordered.
6. What is the typical lead time for orders?
– Standard lead times range from 15 to 30 days, depending on order size and customization requirements.
7. Can fiberglass sheets be customized?
– Yes, most suppliers offer customization in terms of size, thickness, color, and specific property enhancements.
8. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for fiberglass sheets?
– The MOQ varies by supplier, typically starting from 100 to 500 sheets. Smaller quantities may be available at a higher price per unit.
9. What are the payment terms for sourcing from China?
– Common terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and sometimes PayPal for smaller orders. Negotiating favorable terms is advisable.
10. How is shipping handled and what are the costs?
– Shipping is usually by sea or air, depending on urgency. Costs vary based on volume, weight, and destination. It’s crucial to factor in customs duties and taxes.
By understanding these key aspects, buyers can effectively source high-quality fiberglass sheets from China, ensuring they meet their specific needs and standards.
