Description
laser cutting machines metal Safety Certifications
When selecting laser cutting machines for metal, ensuring they meet stringent safety certifications is paramount. Here are the key safety certifications to consider:
1. CE Marking (Conformité Européenne): This certification indicates that the machine complies with the essential health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area. It covers electrical safety, mechanical safety, and electromagnetic compatibility.
2. ISO 11553-1 and ISO 11553-2: These standards focus specifically on the safety of laser processing machines. ISO 11553-1 addresses general safety requirements, while ISO 11553-2 covers machines with enclosed and non-enclosed laser radiation.
3. FDA Compliance (21 CFR 1040): For machines used in the United States, compliance with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s regulations for laser products is crucial. This ensures the machine meets strict guidelines on laser radiation safety.
4. EN 60825-1: This European standard specifies the safety requirements for laser products, ensuring they are classified correctly and provide the necessary safety measures, including appropriate labeling and user instructions.
5. UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification verifies that the laser cutting machine has been tested for safety standards in the U.S. and Canada. This certification covers electrical safety, fire hazards, and risk of personal injury.
6. Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC: This directive applies to machines used within the European Union, ensuring they meet the essential health and safety requirements for mechanical equipment, including risk assessment and compliance documentation.
7. ANSI Z136.1: The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard for the safe use of lasers provides guidelines for controlling laser hazards and outlines protective measures, including engineering controls and safety procedures.
Ensuring a laser cutting machine for metal meets these certifications guarantees it adheres to high safety standards, protecting operators and ensuring compliance with regional regulations.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “laser cutting machines metal”
When evaluating laser cutting machines for metal, several technical parameters are crucial for determining their suitability and performance:
1. Laser Power: Measured in watts (W), higher power (ranging from 500W to over 10kW) enables cutting thicker materials and improves cutting speed.
2. Cutting Speed: Dependent on the material type and thickness. High-powered lasers offer faster cutting speeds.
3. Beam Quality: Described by the beam parameter product (BPP), better beam quality (lower BPP) results in finer, more precise cuts.
4. Wavelength: Commonly 10.6 µm for CO2 lasers, 1.06 µm for fiber lasers. Fiber lasers, with their shorter wavelength, are more efficient for cutting metals.
5. Work Area: Defines the maximum size of the sheet metal that can be cut, typically ranging from small benchtop models to large industrial machines with work areas over 4 meters.
6. Cutting Thickness: Varies with power and type of metal; for example, a 1kW fiber laser can cut up to 10mm of steel, while higher-powered lasers can cut thicker materials.
7. Positioning Accuracy: Indicates the precision of the laser head movement, crucial for intricate designs, typically within ±0.03 mm.
8. Repeatability: The ability to replicate cuts consistently, often within ±0.02 mm, ensuring uniform production quality.
9. Assist Gas: Uses gases like nitrogen, oxygen, or air to blow away molten material, influencing the cut quality and speed.
10. Cooling System: Required to maintain optimal operating temperatures, with water or air cooling being common.
11. Control System: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems provide automated, precise control of the cutting process, often with user-friendly interfaces.
12. Software Compatibility: Supports various design file formats (DXF, DWG) and integrates with CAD/CAM software for streamlined workflows.
13. Maintenance Requirements: Regular upkeep such as lens cleaning, gas refills, and system checks ensures optimal performance.
14. Safety Features: Includes enclosures, emergency stops, and protective eyewear to ensure operator safety.
These parameters collectively determine the efficiency, precision, and versatility of laser cutting machines for metalworking applications.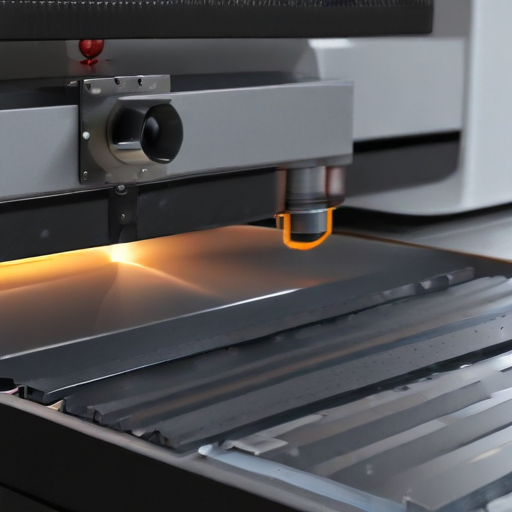
List Product features of “laser cutting machines metal”
Laser cutting machines for metal offer a range of advanced features tailored to precision, efficiency, and versatility. Here are the key product features:
1. High Precision and Accuracy: Laser cutting machines provide exceptional accuracy, often within micrometers, allowing for intricate designs and tight tolerances.
2. Cutting Speed: These machines can cut metals rapidly, significantly reducing production time compared to traditional methods.
3. Versatile Material Compatibility: They can cut various metals, including steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and titanium, accommodating different industry needs.
4. Thickness Range: Capable of cutting metals of varying thicknesses, from thin sheets to thicker plates, depending on the laser power.
5. Automation: Many machines come with automated features such as auto-loading and unloading, and advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems for precise control and repeatability.
6. Energy Efficiency: Modern laser cutters are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
7. Clean Cuts: Produces smooth edges and clean cuts, minimizing the need for additional finishing processes.
8. Reduced Material Waste: The precision of laser cutting reduces waste by optimizing material usage, which is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
9. Safety Features: Equipped with safety enclosures, sensors, and interlocks to protect operators from laser exposure and machine hazards.
10. User-friendly Interfaces: Advanced software and touch-screen interfaces make it easier for operators to design and execute complex cutting tasks.
11. Cooling Systems: Integrated cooling systems prevent overheating, ensuring consistent performance and longevity of the machine.
12. Flexibility in Design: Allows for the cutting of complex geometries and custom designs, enhancing creativity and customization options.
13. Low Maintenance: Modern laser cutting machines require minimal maintenance due to robust construction and reliable components.
14. Integration Capabilities: Can be integrated with other manufacturing systems for seamless workflow in a production line.
15. Cutting Modes: Multiple cutting modes (e.g., pulsed and continuous wave) provide versatility for different cutting requirements.
These features collectively make laser cutting machines an essential tool in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and metal fabrication.
List Application of “laser cutting machines metal”
Laser cutting machines for metal have a wide range of applications across various industries due to their precision, efficiency, and versatility. Here are some key applications:
1. Manufacturing and Fabrication: Laser cutting machines are widely used in the manufacturing of metal parts and components. They allow for the precise cutting of intricate shapes and designs, which is crucial for producing high-quality products in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and machinery.
2. Automotive Industry: In the automotive sector, laser cutting machines are employed to cut complex parts, such as car frames, body panels, and components for engines and transmissions. The high precision of laser cutting ensures that parts fit perfectly, improving the overall quality of the vehicles.
3. Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry requires extremely high precision and quality for its components. Laser cutting is used to manufacture parts like turbine blades, structural components, and intricate assemblies, ensuring reliability and performance in critical applications.
4. Construction: In construction, laser cutting machines are used to cut metal beams, columns, and other structural components. This technology helps in creating custom shapes and sizes for various architectural designs and structural requirements.
5. Medical Devices: Laser cutting is crucial in the medical industry for manufacturing surgical instruments, implants, and other medical devices. The precision of laser cutting allows for the creation of intricate and small components that meet the strict standards of the medical field.
6. Jewelry and Decorative Arts: Laser cutting is also used in creating intricate designs in jewelry and decorative metal art pieces. The ability to cut fine details with high precision makes it ideal for producing unique and complex designs.
7. Electronics: In electronics, laser cutting is used to create precise enclosures, heat sinks, and other components. The accuracy of laser cutting ensures that electronic parts fit perfectly and function correctly.
8. Signage and Advertising: Laser cutting machines are used to produce custom metal signs, logos, and other advertising materials. The precision and ability to cut various shapes and sizes make it ideal for creating eye-catching displays.
Overall, laser cutting machines for metal are essential tools in modern manufacturing, offering unmatched precision and versatility for a wide range of applications.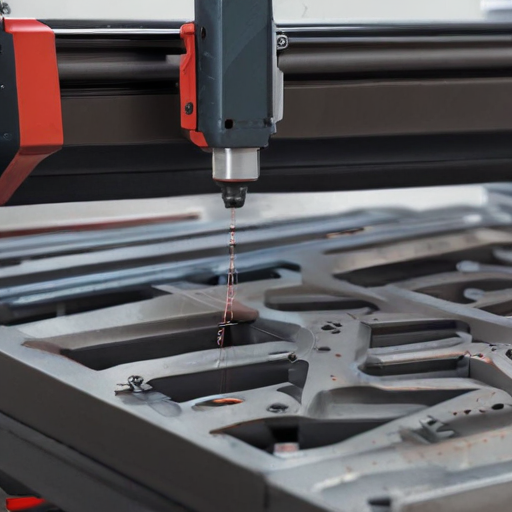
List Various Types of “laser cutting machines metal”
Various types of laser cutting machines for metal are designed to cater to different needs based on the material type, thickness, and precision required. Here are the primary types:
1. CO2 Laser Cutting Machines:
– Uses a gas mixture primarily composed of carbon dioxide.
– Ideal for cutting, engraving, and marking non-metal materials but can also cut metals like stainless steel and aluminum with proper adjustments.
– Known for smooth finishes on cut edges.
2. Fiber Laser Cutting Machines:
– Utilizes a fiber laser source, often providing higher energy efficiency.
– Particularly effective for cutting metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
– Known for high-speed processing and lower maintenance costs.
3. Nd:YAG (Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) Laser Cutting Machines:
– Solid-state laser that can be used for both metals and non-metals.
– Suitable for tasks requiring high peak energy, like deep engraving or cutting thicker metals.
4. Fiber Laser Tube Cutting Machines:
– Specialized for cutting metal tubes and pipes.
– Offers precision cutting for round, square, and rectangular tubes.
5. Disk Laser Cutting Machines:
– A subtype of fiber laser, using a disk-shaped gain medium.
– Provides high precision and efficiency, particularly suited for cutting thin metal sheets.
6. Plasma Laser Cutting Machines:
– Uses an accelerated jet of hot plasma to cut through electrically conductive metals.
– Suitable for cutting thick materials but generally less precise than fiber or CO2 lasers.
7. Hybrid Laser Cutting Machines:
– Combines laser cutting with other technologies like punching.
– Provides versatility in cutting and shaping metals with complex geometries.
Each type of laser cutting machine offers distinct advantages, making them suitable for various industrial applications depending on the specific requirements of metal cutting tasks.
laser cutting machines metal Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Laser cutting machines for metal come with various accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options to enhance their performance and versatility. These enhancements can significantly improve productivity, precision, and the range of materials that can be processed. Below are some key options:
Accessories
1. Nozzles and Lenses: Specialized nozzles and lenses can optimize the cutting process for different metals and thicknesses, enhancing cut quality and speed.
2. Assist Gas Systems: Using gases like oxygen, nitrogen, or air can influence the cutting speed and edge quality. Automated gas control systems allow for quick changes based on material requirements.
3. Chillers: Proper cooling is crucial for maintaining the laser’s performance and longevity. Chillers ensure the laser operates within optimal temperature ranges.
4. Dust and Fume Extractors: Effective extraction systems improve air quality and safety by removing metal dust and fumes generated during cutting.
5. Rotary Attachments: These enable cutting and engraving on cylindrical objects, expanding the machine’s capabilities.
Upgrades
1. Higher Wattage Lasers: Upgrading to higher wattage lasers can increase cutting speed and the ability to cut through thicker materials.
2. Advanced Control Software: Upgrading the software can provide better control over cutting parameters, nesting capabilities, and integration with CAD/CAM systems.
3. Automatic Focus Adjust: This feature adjusts the focus based on material thickness, improving cutting accuracy and efficiency.
4. High-Performance Motion Systems: Enhanced motion systems can increase the machine’s precision and speed, reducing cycle times.
Custom Manufacturing Options
1. Tailored Bed Sizes: Custom bed sizes can accommodate larger or uniquely shaped materials, providing flexibility for specific applications.
2. Specialized Cutting Heads: Custom cutting heads can be designed for specific applications, such as bevel cutting or piercing thick materials.
3. Automated Loading and Unloading Systems: Custom automation solutions can streamline material handling, increasing productivity and reducing manual labor.
4. Multi-Laser Configurations: For high-volume production, machines can be configured with multiple laser sources to operate simultaneously.
These accessories, upgrades, and custom options allow manufacturers to optimize their laser cutting machines for specific needs, improving efficiency and expanding their capabilities.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “laser cutting machines metal”
Quality Control and Manufacturing Process of Laser Cutting Machines for Metal
Manufacturing Process:
1. Design and Planning: The process begins with designing the laser cutting machine using CAD software to create precise blueprints. This includes specifications for cutting metal efficiently.
2. Component Fabrication: Key components like laser resonators, optics, and motion control systems are manufactured. High-precision methods, such as CNC machining, are used to ensure accuracy.
3. Assembly: Components are assembled in a controlled environment. The laser source, cooling systems, cutting head, and motion systems are integrated into the machine’s framework.
4. Software Integration: Advanced control software is integrated to manage laser parameters and motion controls, allowing for precise cutting patterns and adjustments.
5. Testing: The assembled machine undergoes rigorous testing, including laser alignment, power output, and motion accuracy, to ensure all components function correctly together.
6. Calibration: Fine-tuning is performed to achieve optimal cutting performance. This includes adjusting the laser’s focal point, power settings, and motion controls for different metal types and thicknesses.
7. Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to verify that the machine meets all design specifications and performance criteria before it is shipped to customers.
Quality Control:
1. Material Inspection: Incoming materials are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications to ensure reliability and performance.
2. Component Testing: Each component undergoes detailed testing, including stress tests and durability assessments, to ensure they meet high standards.
3. Assembly Verification: The assembly process is closely monitored, with each step checked for accuracy and quality adherence.
4. Functional Testing: The machine’s performance is tested under various conditions to ensure it cuts metals precisely and reliably. This includes cutting speed, accuracy, and edge quality assessments.
5. Certification: Machines are certified to meet international safety and quality standards, such as ISO and CE, to ensure they are safe and effective for industrial use.
6. Continuous Improvement: Feedback from users is collected for continuous improvement, ensuring that any issues are addressed, and future models meet evolving needs.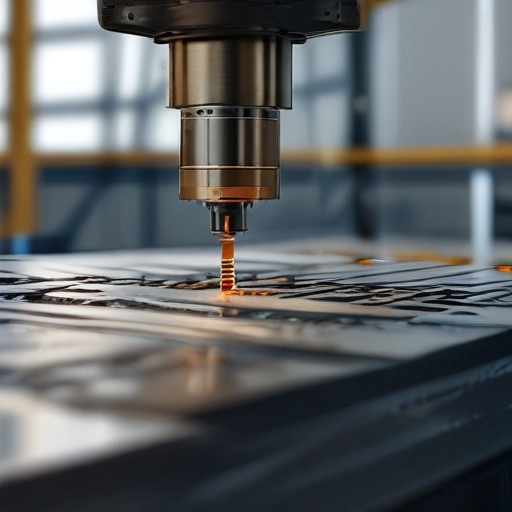
Materials of “laser cutting machines metal”
Laser cutting machines for metal utilize different materials in their construction to ensure precision, durability, and efficiency. Key materials involved include:
1. Laser Source: The core component, typically made from materials such as carbon dioxide (CO2), neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG), and fiber. Fiber lasers use rare-earth elements like ytterbium for high power and efficiency.
2. Optical Components: Mirrors and lenses are made from materials like fused silica or zinc selenide to handle high-intensity laser beams without degrading.
3. Cutting Head: Typically made from durable metals such as stainless steel or aluminum alloys, providing rigidity and precision in the laser beam delivery.
4. Frame and Housing: The machine’s structure is usually constructed from high-strength steel or cast iron to provide stability and minimize vibrations during operation.
5. Cooling System: Components such as heat exchangers and radiators often use copper or aluminum for efficient thermal management.
6. Guide Rails and Bearings: Made from hardened steel to ensure smooth and precise movement of the cutting head.
7. Control Systems: Consist of electronic materials, including silicon-based semiconductors, for processing and controlling the laser’s operations.
These materials are selected for their specific properties such as strength, thermal conductivity, and resistance to wear and tear, ensuring the laser cutting machine performs effectively and has a long operational life.
“laser cutting machines metal” Comparative Analysis
Comparative Analysis of Metal Laser Cutting Machines
#### Types and Technologies
Metal laser cutting machines primarily use three types of laser sources: CO2, Fiber, and Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet).
1. CO2 Lasers:
– Pros: Versatile for cutting, engraving, and boring metals. Effective for a variety of materials beyond metals, like wood and plastics.
– Cons: Larger footprint and higher operational costs due to gas consumption and maintenance requirements.
2. Fiber Lasers:
– Pros: High efficiency and lower operational costs. Ideal for cutting reflective metals like aluminum, copper, and brass. They have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance.
– Cons: Higher initial investment compared to CO2 lasers. Limited flexibility for non-metal materials.
3. Nd:YAG Lasers:
– Pros: Suitable for high-precision tasks and materials requiring deep penetration. Effective for a wide range of materials.
– Cons: Higher operational costs and complex maintenance. Less efficient compared to fiber lasers.
#### Performance Metrics
1. Cutting Speed and Precision: Fiber lasers offer superior cutting speeds and precision, especially for thin metals. CO2 lasers provide good quality cuts but are slower. Nd:YAG lasers excel in precision but are slower than fiber lasers.
2. Material Compatibility:
– Fiber Lasers: Best for reflective and non-ferrous metals.
– CO2 Lasers: Versatile across various materials but less efficient with reflective metals.
– Nd:YAG Lasers: Broad material compatibility with excellent penetration for thicker metals.
3. Operational Costs:
– Fiber Lasers: Low operational costs, high energy efficiency, and minimal maintenance.
– CO2 Lasers: Higher operational costs due to gas usage and frequent maintenance.
– Nd:YAG Lasers: High operational costs and complex maintenance.
#### Applications and Industries
– CO2 Lasers: Used in signage, automotive, and aerospace industries due to versatility.
– Fiber Lasers: Preferred in electronics, precision engineering, and metal fabrication industries.
– Nd:YAG Lasers: Utilized in medical device manufacturing, aerospace, and other high-precision applications.
Conclusion
Fiber lasers generally offer the best performance and efficiency for metal cutting, particularly for reflective metals, despite the higher initial cost. CO2 lasers remain a versatile choice for mixed material cutting, while Nd:YAG lasers are ideal for specialized, high-precision applications.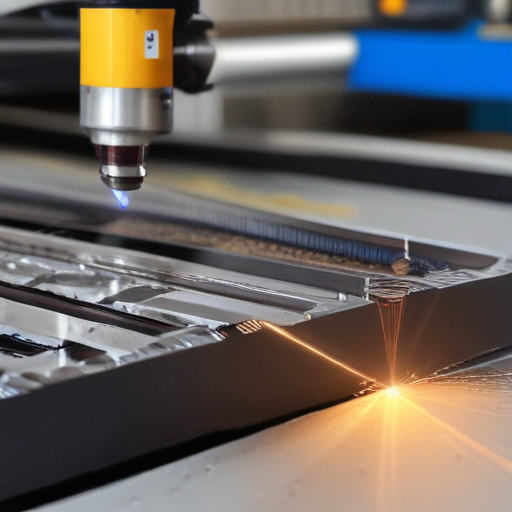
“laser cutting machines metal” Warranty and Support
When purchasing a laser cutting machine for metal, considering the warranty and support options is crucial for ensuring long-term reliability and performance. Here are key points to look for:
Warranty Coverage:
1. Duration: Warranties typically range from 1 to 3 years. Some manufacturers might offer extended warranties for an additional fee.
2. Scope: Ensure the warranty covers critical components like the laser source, control systems, motors, and other major parts.
3. Exclusions: Be aware of what is not covered, such as consumables (lenses, nozzles), normal wear and tear, and damages due to improper use or maintenance.
4. Service and Repairs: Check if the warranty includes on-site repairs, parts replacement, and labor costs.
Support Services:
1. Technical Support: Look for manufacturers that provide 24/7 technical support via phone, email, or online chat. Immediate access to technical assistance can minimize downtime.
2. Training: Comprehensive training programs for machine operation, maintenance, and software use are beneficial. This can include in-person sessions, online tutorials, and user manuals.
3. Maintenance Contracts: Some manufacturers offer optional maintenance contracts that include regular check-ups, software updates, and preventive maintenance services.
4. Spare Parts Availability: Ensure the manufacturer has a reliable supply chain for spare parts, which is critical for quick repairs and reducing machine downtime.
5. Service Centers: Proximity to authorized service centers can significantly impact the turnaround time for repairs and part replacements.
Customer Feedback:
– Research customer reviews and testimonials about the manufacturer’s warranty and support services. This can provide insights into the actual performance and reliability of these services.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure that your investment in a laser cutting machine for metal is protected and that you have the necessary support to maintain optimal performance.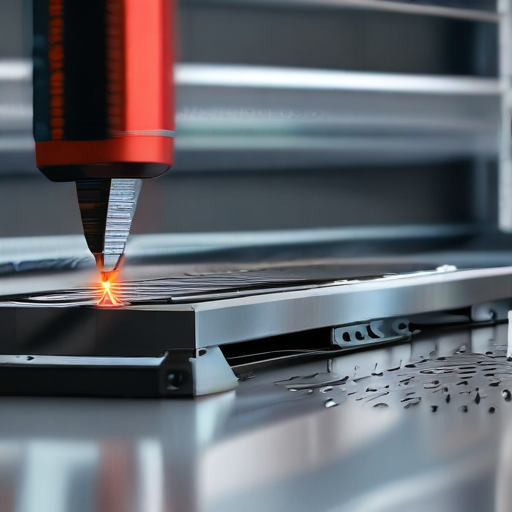
List “laser cutting machines metal” FAQ
FAQ: Laser Cutting Machines for Metal
1. What is a laser cutting machine for metal?
A laser cutting machine for metal uses a high-powered laser beam to cut, engrave, or mark metal materials with precision. These machines are commonly used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
2. How does laser cutting work?
Laser cutting involves directing a laser beam onto the metal surface, which heats the material to its melting or boiling point. A jet of gas, usually nitrogen or oxygen, blows away the molten material, resulting in a clean cut.
3. What types of metals can be cut with a laser?
Laser cutting machines can handle a variety of metals, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and titanium. Each metal may require specific settings and types of lasers (e.g., fiber or CO2).
4. What are the advantages of laser cutting metal?
– High precision and accuracy
– Smooth and clean edges
– Minimal material waste
– Ability to cut complex shapes and fine details
– Fast cutting speeds
– Reduced risk of material deformation
5. Are there any limitations to laser cutting metal?
– Thickness limitations: Lasers are less effective on very thick metals.
– Reflective materials: Metals like copper and aluminum can reflect the laser beam, requiring specialized settings.
– Initial setup cost: Laser cutting machines can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
6. What safety precautions should be taken?
– Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety goggles and gloves.
– Ensure proper ventilation to avoid inhaling fumes and gases.
– Follow manufacturer guidelines for machine operation and maintenance.
– Regularly inspect and maintain the machine to prevent accidents.
7. How do I choose the right laser cutting machine?
Consider factors such as the type and thickness of metal you’ll be cutting, the required precision, machine power, and your budget. Consulting with manufacturers and experts can help you make an informed decision.
8. What maintenance is required for laser cutting machines?
Regular cleaning of the laser lens and mirrors, checking the alignment of the laser beam, and routine inspection of the cooling system and exhaust fans are essential for optimal performance and longevity of the machine.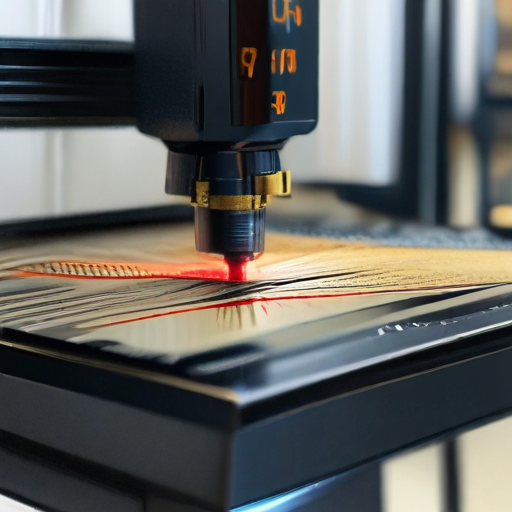
Top 10 FAQ with answer about laser cutting machines metal for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 FAQs with answers about laser cutting machines for metal, focusing on buyer sourcing from China:
1. What types of metal can laser cutting machines handle?
– Laser cutting machines can cut various metals including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and titanium.
2. What is the difference between fiber laser and CO2 laser cutting machines?
– Fiber lasers are more efficient for cutting metals, providing faster speeds and higher precision, while CO2 lasers are versatile for cutting both metals and non-metals but are slower and less energy-efficient for metals.
3. How do I choose the right power level for a laser cutting machine?
– The power level depends on the thickness and type of metal. For example, 1000W is suitable for thin metals, while thicker metals may require 3000W or more.
4. What is the typical lead time for manufacturing and delivering a laser cutting machine from China?
– Lead times can vary but generally range from 30 to 60 days, including manufacturing and shipping.
5. Are Chinese laser cutting machines reliable and of good quality?
– Many Chinese manufacturers offer high-quality machines with competitive prices. It’s crucial to choose reputable suppliers with positive reviews and certifications.
6. What certifications should I look for when sourcing laser cutting machines from China?
– Look for certifications such as CE, ISO, and FDA, which indicate compliance with international safety and quality standards.
7. Can I get custom features or specifications for the laser cutting machine?
– Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific needs, such as different bed sizes, power levels, and additional features.
8. What after-sales support and warranty options are available?
– Reputable manufacturers provide comprehensive after-sales support, including installation, training, and technical assistance. Warranty periods typically range from one to three years.
9. What are the payment terms when buying from China?
– Common payment terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and sometimes Escrow. Initial deposits and milestone payments are often required.
10. How do I ensure the quality of the machine before shipment?
– Request a pre-shipment inspection or third-party inspection services to verify the machine’s quality and functionality before it leaves the factory.
These FAQs should help you navigate the process of sourcing laser cutting machines for metal from China effectively.
