Description
laser metal cutting machine Safety Certifications
Safety certifications for laser metal cutting machines are crucial to ensure they operate safely and meet regulatory standards. These certifications typically include:
1. CE Marking (Conformité Européenne):
– Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
– Ensures the machine meets the essential requirements of relevant European directives, such as the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU), and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (2014/30/EU).
2. UL Certification (Underwriters Laboratories):
– Common in the United States and Canada.
– Ensures the machine adheres to UL’s standards for safety and performance, often covering electrical safety and fire hazards.
3. ISO 11553:
– Provides safety requirements for the design and construction of laser processing machines.
– Focuses on controlling laser radiation hazards and ensuring proper safety features are in place, such as protective housings and interlocks.
4. ANSI Z136.1:
– The American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers.
– Provides guidelines for the safe use of lasers, detailing controls and protective measures to minimize laser radiation hazards.
5. IEC 60825:
– International standard for laser safety.
– Specifies requirements for labeling, safety controls, and user information to mitigate risks associated with laser use.
6. OSHA Compliance (Occupational Safety and Health Administration):
– Relevant in the United States.
– Ensures the machine and its operation meet workplace safety standards to protect operators and other personnel.
7. RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive):
– Ensures that the machine does not contain hazardous materials above specified levels.
– Important for environmental and health safety.
These certifications collectively ensure that laser metal cutting machines are designed and operated within stringent safety guidelines, protecting users from potential hazards such as laser radiation, electrical shocks, and mechanical risks. Adhering to these certifications helps manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to safety and regulatory compliance.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “laser metal cutting machine”
Laser metal cutting machines are highly precise and efficient tools used in various industries for cutting and shaping metal components. Here are some key technical parameters to consider:
1. Laser Power: Measured in watts (W), common ranges are 500W to 10kW. Higher power allows cutting thicker materials and increases cutting speed.
2. Laser Type: Includes CO2, fiber, and Nd:YAG lasers. Fiber lasers are popular due to their efficiency, lower maintenance, and ability to cut reflective metals.
3. Wavelength: Fiber lasers typically operate at around 1.06 micrometers, whereas CO2 lasers operate at 10.6 micrometers. The wavelength affects the absorption of the laser by different materials.
4. Cutting Speed: Depends on the laser power, material type, and thickness. Higher power lasers generally provide higher cutting speeds.
5. Material Thickness: Fiber lasers can cut up to 25mm of carbon steel, 20mm of stainless steel, and 12mm of aluminum, depending on the laser power.
6. Beam Quality: Often measured by the beam parameter product (BPP), which affects the precision and quality of the cut. Lower BPP values indicate better beam quality.
7. Focus Spot Size: The diameter of the laser beam at the focal point, influencing the cutting width and precision. Smaller spot sizes yield finer cuts.
8. Cooling System: Essential for maintaining the laser’s performance and longevity. Water-cooled systems are common for high-power lasers.
9. Cutting Area: The maximum size of the material that can be processed, typically described in terms of width and length (e.g., 3000mm x 1500mm).
10. Assist Gas: Gases like oxygen, nitrogen, or air are used to assist in cutting, affecting the cutting speed, quality, and type of metal that can be cut.
11. Control System: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems are standard, allowing precise control over the cutting process and integration with CAD/CAM software.
12. Accuracy and Repeatability: Critical for precision manufacturing, usually within ±0.1mm for high-quality machines.
These parameters determine the suitability of a laser metal cutting machine for specific applications and are crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency.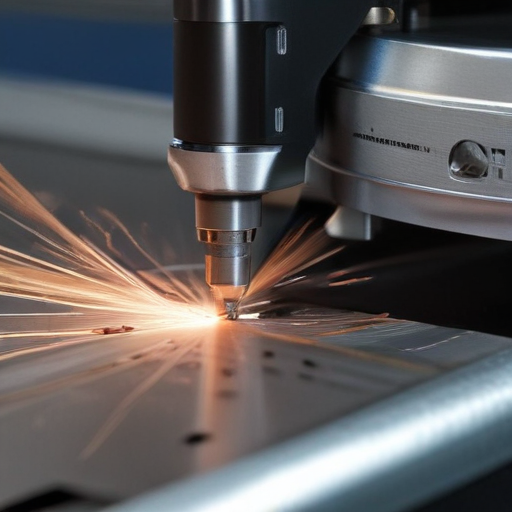
List Product features of “laser metal cutting machine”
Product Features of a Laser Metal Cutting Machine
1. High Precision and Accuracy: Capable of cutting intricate designs and complex shapes with minimal tolerances, ensuring high-quality and consistent results.
2. Speed and Efficiency: Rapid cutting speeds allow for high production rates, reducing downtime and increasing throughput.
3. Versatility in Materials: Effective on a wide range of metals including steel, aluminum, copper, and brass, making it suitable for various industries.
4. Cutting Thickness Range: Ability to cut through different material thicknesses, from thin sheets to thicker plates, depending on the machine’s power.
5. Non-contact Cutting: Laser cutting is a non-contact process, which means there is no wear and tear on cutting tools, leading to longer machine life and lower maintenance costs.
6. Automation Capabilities: Integration with CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems for automated operation, allowing for precise control and repeatability.
7. Minimal Heat Affected Zone: The concentrated laser beam minimizes the heat affected zone, reducing the risk of material warping or distortion.
8. Clean and Smooth Edges: Produces clean and burr-free edges, often eliminating the need for secondary finishing processes.
9. Energy Efficiency: Modern laser cutters are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
10. Safety Features: Equipped with safety enclosures, emergency stop buttons, and fume extraction systems to ensure operator safety and maintain a clean working environment.
11. Software Integration: Compatible with various design software for easy importing of cutting designs and optimization of cutting paths.
12. Customizable Settings: Adjustable power and speed settings to tailor the cutting process to specific material properties and desired outcomes.
13. Maintenance and Support: Designed for easy maintenance with readily available support and service options to minimize downtime.
14. Compact and Ergonomic Design: Many models offer a compact footprint and user-friendly interfaces, making them suitable for various workshop sizes and environments.
These features collectively enhance the functionality, efficiency, and versatility of laser metal cutting machines, making them a valuable asset in manufacturing and fabrication industries.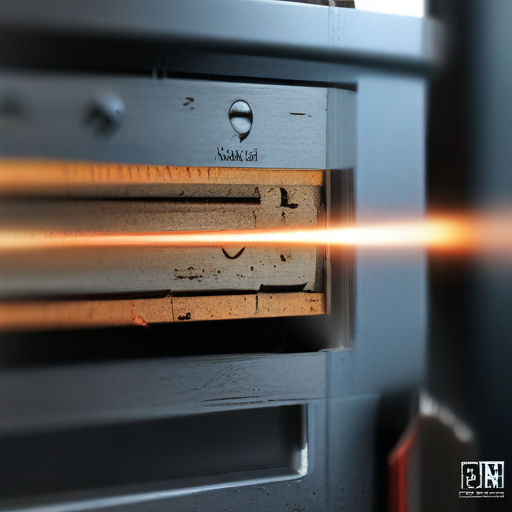
List Application of “laser metal cutting machine”
Laser metal cutting machines are versatile tools with a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some key applications:
1. Automotive Industry: Laser cutting is used to manufacture precise automotive parts, such as body panels, exhaust systems, and intricate components. It ensures high accuracy and smooth edges, which are crucial for the performance and safety of vehicles.
2. Aerospace Industry: The aerospace sector relies on laser cutting for producing lightweight and high-strength components. It is used to cut complex shapes from materials like titanium and aluminum, essential for aircraft and spacecraft manufacturing.
3. Metal Fabrication: Metal fabrication shops use laser cutting machines to create custom metal parts for various projects. This includes cutting, shaping, and engraving metals for construction, machinery, and artistic purposes.
4. Medical Device Manufacturing: Precision is critical in the medical field. Laser cutting machines are used to produce intricate parts for medical devices, surgical instruments, and implants, ensuring high precision and minimal thermal damage to materials.
5. Electronics Industry: In electronics, laser cutting is used to create precise metal enclosures, connectors, and other small components. The technology allows for high repeatability and fine detail required for electronic devices.
6. Jewelry Making: Laser cutting machines enable jewelers to craft intricate designs in metals like gold, silver, and platinum. This allows for customization and precision in creating detailed and delicate jewelry pieces.
7. Signage and Advertising: Laser cutting is used to produce high-quality metal signs, letters, and decorative elements. It allows for the creation of intricate designs and smooth edges, enhancing the visual appeal of advertising materials.
8. Architecture and Interior Design: Architects and designers use laser cutting to create custom metal elements for buildings and interiors. This includes decorative panels, railings, and fixtures that add unique aesthetic value to structures.
9. Shipbuilding: In shipbuilding, laser cutting is used to cut large metal sheets and plates with high precision, ensuring proper fitting and reducing waste. This is crucial for the construction and repair of ships and submarines.
10. Tool and Die Making: Laser cutting is essential for creating precise molds, dies, and tools used in various manufacturing processes. It ensures high accuracy and durability of the tools produced.
These applications highlight the versatility and precision of laser metal cutting machines in modern manufacturing and design.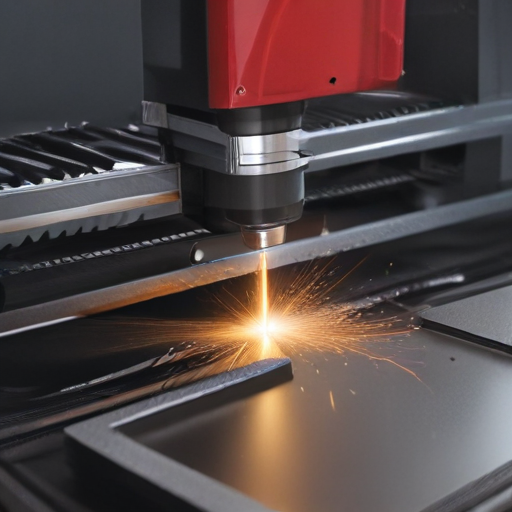
List Various Types of “laser metal cutting machine”
Laser metal cutting machines come in several types, each suited to different applications based on the technology used and the metal cutting requirements. Here are the main types:
1. Fiber Laser Cutting Machines: These use optical fibers as the laser source. Known for their high efficiency and cutting speed, they are ideal for cutting thin to medium-thick sheets of metal, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
2. CO2 Laser Cutting Machines: Utilizing a carbon dioxide laser, these machines are effective for cutting thicker metals. They provide high precision and smooth cuts, suitable for materials like mild steel and stainless steel, as well as non-metallic materials.
3. Crystal Laser Cutting Machines: These use crystal mediums like Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) and Nd:YVO4 (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Orthovanadate). They are effective for both metal and non-metal materials, offering high precision but are less common due to higher costs and maintenance needs.
4. MOPA Fiber Laser Cutting Machines: A variation of the standard fiber laser, MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) lasers offer adjustable pulse durations, making them suitable for a variety of metals and thicknesses. They provide greater control over the cutting process and are excellent for marking and engraving as well.
5. Plasma Laser Cutting Machines: While technically not a laser, plasma cutters are often categorized similarly due to their metal cutting capabilities. They use electrically conductive gas to cut through thick metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper alloys.
6. Hybrid Laser Cutting Machines: These combine the benefits of fiber and CO2 lasers, allowing for versatile cutting capabilities. They are designed to handle a wide range of materials and thicknesses, providing flexibility for diverse industrial applications.
Each type of laser cutting machine offers unique advantages, making them suitable for specific applications depending on the material type, thickness, and desired precision.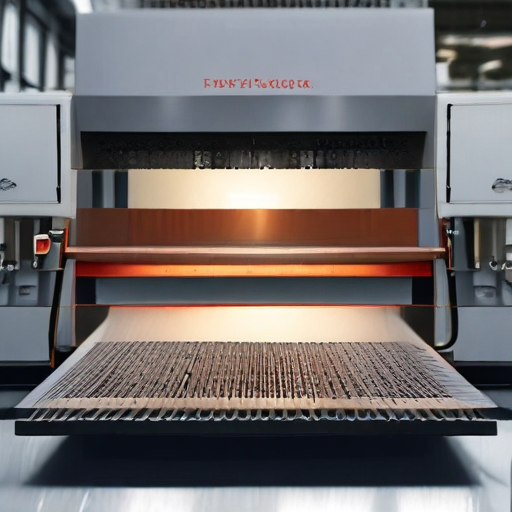
laser metal cutting machine Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Laser metal cutting machines are essential tools in modern manufacturing, offering precision and efficiency. Upgrading accessories and customizing manufacturing options can significantly enhance their performance and versatility. Here are some key upgrades and options:
1. Nozzle and Lens Upgrades: High-quality nozzles and lenses improve cutting accuracy and consistency. Options like anti-reflective lenses and high-performance nozzles reduce maintenance and enhance beam focus.
2. Automatic Height Adjusters: These devices maintain the optimal distance between the laser head and the metal surface, ensuring consistent cutting quality even on uneven materials.
3. Cooling Systems: Advanced cooling systems prevent overheating and extend the machine’s lifespan. Water chillers and air cooling units are common upgrades that enhance performance during prolonged operation.
4. Dust and Fume Extractors: Effective extraction systems remove dust and fumes generated during cutting, improving workplace safety and cutting quality by keeping the laser optics clean.
5. Software Upgrades: Up-to-date software enhances machine capabilities with features like real-time monitoring, improved user interfaces, and advanced cutting algorithms. Some software solutions offer remote operation and diagnostics.
6. Rotary Attachments: Adding a rotary axis allows for the cutting of cylindrical and tubular materials, expanding the machine’s versatility to create complex shapes and structures.
7. Material Handling Systems: Automated loading and unloading systems, including conveyors and robotic arms, increase productivity and reduce manual handling, leading to faster and more efficient operations.
8. Custom Jigs and Fixtures: Custom-made jigs and fixtures hold materials securely in place during cutting, ensuring precision and reducing waste.
9. Advanced Laser Sources: Upgrading to fiber lasers or CO2 lasers with higher power outputs can cut thicker materials faster and more accurately, broadening the range of applications.
10. Protective Enclosures: Enclosures enhance safety by containing the laser beam and reducing exposure to harmful emissions, essential for compliance with safety regulations.
Investing in these upgrades and custom options can maximize the efficiency, precision, and safety of laser metal cutting machines, providing a significant return on investment through improved operational capabilities.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “laser metal cutting machine”
Quality Control in Laser Metal Cutting Machine Manufacturing
Quality control for laser metal cutting machines involves a series of rigorous checks and measures to ensure high precision, safety, and reliability. Key elements include:
1. Material Inspection: Verify the quality of raw materials, including laser sources, machine frames, and electronic components.
2. Precision Testing: Utilize advanced measuring tools to ensure cutting accuracy and repeatability.
3. Calibration: Regularly calibrate lasers and sensors to maintain consistent performance.
4. Software Validation: Test control software for bugs and ensure it integrates seamlessly with the hardware.
5. Safety Checks: Ensure all safety features, such as emergency stops and protective housings, meet regulatory standards.
6. Performance Testing: Run the machine under various conditions to test its performance, speed, and efficiency.
7. Final Inspection: Conduct a thorough final inspection, including aesthetic checks and functional tests, before packaging and shipment.
Manufacturing Process of Laser Metal Cutting Machines
1. Design and Engineering: Develop detailed designs and technical specifications using CAD software. Engineers simulate performance and troubleshoot potential issues.
2. Material Sourcing: Source high-quality materials and components, including lasers, electronics, and mechanical parts.
3. Frame Construction: Fabricate the machine frame using robust materials. Ensure structural integrity and alignment through precision machining.
4. Component Assembly: Assemble the laser source, cutting head, motion systems, and electronic controls. Components are installed according to the design specifications.
5. Wiring and Integration: Wire all electrical components, ensuring proper connections and integration with control systems.
6. Software Installation: Load and configure the machine’s operating software, integrating it with the hardware for optimal performance.
7. Calibration and Testing: Calibrate the laser and motion systems. Perform initial testing to fine-tune accuracy and efficiency.
8. Quality Control: Conduct extensive quality checks, including precision testing, safety inspections, and performance evaluations.
9. Packaging and Shipping: Securely package the machine to prevent damage during transit. Prepare documentation, including user manuals and compliance certificates, for shipment.
This process ensures that each laser metal cutting machine meets high standards of quality, reliability, and performance.
Materials of “laser metal cutting machine”
A laser metal cutting machine consists of several key components, each made from specific materials to ensure precision, durability, and performance. Here’s a breakdown of the primary materials used:
1. Laser Source: The core of the machine is the laser source, often a CO2 laser, fiber laser, or Nd:YAG laser. Fiber lasers use a doped glass fiber as the medium, while CO2 lasers use a mixture of gases including carbon dioxide. The laser housing is typically made from high-strength, heat-resistant metals or alloys, such as stainless steel or aluminum, to withstand high temperatures and protect internal components.
2. Optics: Mirrors and lenses in the laser cutting path are crucial for directing and focusing the laser beam. These optical components are usually made from specialized materials like zinc selenide, fused silica, or gallium arsenide, which have excellent thermal and optical properties.
3. Cutting Head: The cutting head, which houses the focusing optics, is typically made from high-quality aluminum or other lightweight, durable metals to ensure precise movement and reduce wear. It includes a nozzle, often made from copper or brass, which directs assist gases like oxygen or nitrogen to the cutting area.
4. Frame and Gantry: The structural frame and gantry are typically constructed from welded steel or aluminum. Steel offers superior rigidity and stability, reducing vibrations and ensuring high cutting accuracy. Aluminum may be used in parts requiring lower weight for faster movement.
5. Motion System: The motion system, including rails and linear guides, is generally made from hardened steel or stainless steel to ensure longevity and precision. Ball screws or rack and pinion mechanisms, also usually steel, provide the necessary movement precision.
6. Control Electronics: The control system, including the CNC (Computer Numerical Control) unit, uses a variety of materials. The housing is often made from metal or high-grade plastics to protect the sensitive electronic components inside.
These materials are chosen to ensure the machine can handle the high stresses and temperatures involved in laser cutting, maintaining precision and durability over prolonged use.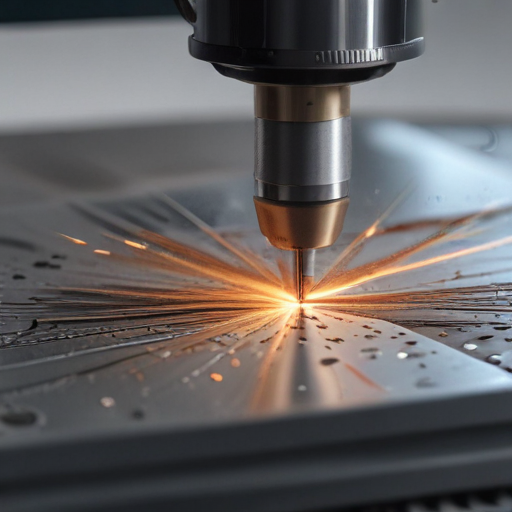
“laser metal cutting machine” Comparative Analysis
When comparing laser metal cutting machines, several factors are crucial: cutting speed, precision, power, cost, and versatility. Here’s a comparative analysis of key aspects:
1. Cutting Speed:
– Fiber Laser: Known for high-speed cutting, especially on thin metals. It is efficient and faster than CO2 lasers on materials like stainless steel and aluminum.
– CO2 Laser: Slower compared to fiber lasers, particularly on thicker metals. It excels in cutting non-metal materials as well.
2. Precision:
– Fiber Laser: Offers high precision due to a smaller focal diameter, which results in a narrow kerf width and cleaner cuts. Ideal for intricate designs and fine details.
– CO2 Laser: Generally less precise than fiber lasers, but still capable of delivering good quality cuts on thicker metals.
3. Power:
– Fiber Laser: Typically available in higher power outputs (up to 12 kW and more), making it suitable for cutting thicker metals and increasing productivity.
– CO2 Laser: Available in lower power ranges compared to fiber lasers, which can limit its efficiency on very thick materials.
4. Cost:
– Fiber Laser: Higher initial investment but lower operating costs due to greater energy efficiency and less maintenance. Its longevity also justifies the higher upfront cost.
– CO2 Laser: Lower initial cost but higher operating expenses due to more frequent maintenance and higher energy consumption.
5. Versatility:
– Fiber Laser: Best for cutting metals and excels in industrial applications. Limited in cutting non-metal materials.
– CO2 Laser: More versatile in cutting a variety of materials, including wood, acrylic, glass, and certain plastics, in addition to metals.
Conclusion:
Fiber lasers are superior for high-speed, precision metal cutting, particularly in industrial settings requiring high productivity and efficiency. CO2 lasers, while slower and less precise for metals, offer versatility across different materials and are suitable for businesses with diverse cutting needs. The choice between the two depends on specific requirements such as the type of materials being cut, desired precision, and budget considerations.
“laser metal cutting machine” Warranty and Support
When purchasing a laser metal cutting machine, warranty and support are critical considerations to ensure long-term operational efficiency and reliability. Most manufacturers offer a standard warranty period ranging from one to three years, covering defects in materials and workmanship. Some companies may extend this period or offer additional coverage for an extra fee. It is essential to check if the warranty includes parts and labor, as well as the availability of on-site repairs.
Support services typically encompass technical assistance, maintenance, and training. Reputable manufacturers provide comprehensive support, including 24/7 customer service, remote troubleshooting, and regular maintenance visits. Training sessions for operators and maintenance personnel are often part of the support package, ensuring users can maximize the machine’s capabilities and lifespan.
Additionally, manufacturers may offer software updates and upgrades as part of their support services. This ensures that the machine stays current with the latest technological advancements and continues to perform efficiently. It’s also beneficial to inquire about the availability of spare parts and the manufacturer’s response time for service calls.
Choosing a supplier with a robust warranty and support system can significantly reduce downtime and enhance the overall productivity of the laser metal cutting machine. Always read the warranty terms carefully and ask for clarifications if needed, ensuring you fully understand the coverage and support provided.
List “laser metal cutting machine” FAQ
FAQ: Laser Metal Cutting Machine
1. What is a laser metal cutting machine?
A laser metal cutting machine uses a high-powered laser beam to cut, engrave, or etch metal materials with precision.
2. How does it work?
The machine directs a laser beam onto the metal surface, heating it to a point where it melts, burns, or vaporizes, leaving a clean cut edge.
3. What materials can be cut?
Common metals include steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. Each material may require different settings for optimal cutting.
4. What are the advantages of using a laser cutter?
– High precision and accuracy
– Clean and smooth edges
– Minimal waste and reduced need for post-processing
– Fast cutting speeds for increased productivity
– Ability to cut complex shapes and fine details
5. What types of laser cutting machines are available?
There are mainly three types: CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and Nd:YAG lasers. Fiber lasers are most commonly used for cutting metals.
6. Is laser cutting safe?
Yes, with proper safety measures such as protective eyewear, ventilation, and adherence to safety protocols, laser cutting is safe.
7. How thick can the machine cut?
The thickness varies by machine power and material type. Generally, fiber lasers can cut up to 20 mm of stainless steel and 30 mm of mild steel.
8. What is the maintenance required?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning optics, checking and replacing consumables, and ensuring proper cooling system function.
9. What software is needed?
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is commonly used to create designs, which are then translated into machine instructions by CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software.
10. What are the costs involved?
Costs vary based on machine type, power, and features. Initial investment can be high, but the efficiency and precision offer long-term savings.
11. Can it be used for mass production?
Yes, laser cutting machines are ideal for both prototyping and mass production due to their speed and consistency.
12. Are there any limitations?
Limitations include the initial cost, the need for technical expertise, and potential issues with reflective metals like copper and brass.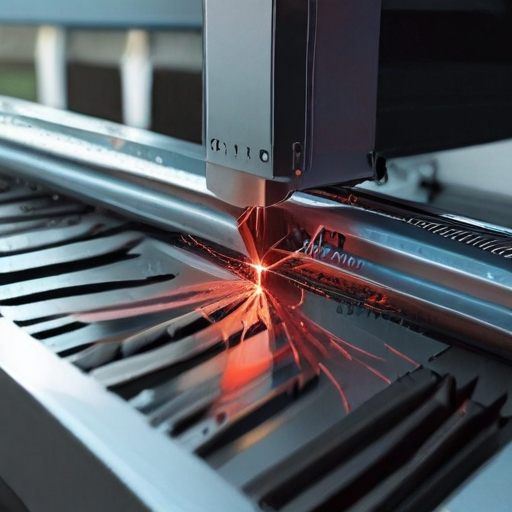
Top 10 FAQ with answer about laser metal cutting machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
Top 10 FAQ about Sourcing Laser Metal Cutting Machines from China
1. What types of laser metal cutting machines are available?
– Common types include fiber laser cutters, CO2 laser cutters, and YAG laser cutters. Fiber lasers are popular for their efficiency and precision in cutting various metals.
2. How do I choose the right laser cutting machine for my needs?
– Consider factors like material type, thickness, cutting speed, precision, and your budget. Fiber lasers are suitable for most metals, while CO2 lasers can handle non-metals as well.
3. What is the typical price range for laser metal cutting machines?
– Prices range from $10,000 to $500,000, depending on power, size, and features. Entry-level machines are cheaper, while high-end models for industrial use cost more.
4. What certifications should the machines have?
– Look for ISO, CE, and FDA certifications to ensure quality and safety standards. These certifications indicate compliance with international standards.
5. How reliable are Chinese manufacturers for laser cutting machines?
– Many Chinese manufacturers are reputable and produce high-quality machines. Check reviews, request references, and visit factories if possible to ensure reliability.
6. What is the average lead time for delivery?
– Lead times typically range from 30 to 60 days, depending on the manufacturer’s production schedule and the shipping method chosen.
7. What about after-sales service and technical support?
– Reputable manufacturers offer comprehensive after-sales service, including remote technical support, on-site training, and spare parts availability. Ensure this is included in the contract.
8. How do I handle customs and import regulations?
– Work with a freight forwarder experienced in handling laser cutting machines. They can assist with documentation, duties, and compliance with local regulations.
9. Can I get customization options for the machines?
– Many manufacturers offer customization based on specific requirements like power settings, software, and additional features. Discuss your needs with the supplier.
10. What payment terms are generally accepted?
– Common terms include a 30% deposit upon order and the remaining balance before shipment. Letters of credit (L/C) and telegraphic transfers (T/T) are commonly used.
By considering these FAQs, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing laser metal cutting machines from China.
