Description
slotting machining Safety Certifications
Slotting machining, a precise and potentially hazardous operation, demands adherence to stringent safety standards and certifications to protect workers and ensure efficient production. Key safety certifications and standards include:
1. OSHA Compliance (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): OSHA sets and enforces standards to ensure safe and healthful working conditions. Compliance involves adhering to regulations on machine guarding, personal protective equipment (PPE), and training requirements specific to slotting machines.
2. ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems): This international standard specifies requirements for an occupational health and safety (OH&S) management system. It helps organizations create a safe working environment by preventing work-related injuries and illnesses, which is crucial for slotting operations.
3. ANSI B11.23 (American National Standards Institute): Part of the ANSI B11 series, this standard focuses on safety requirements for machining operations, including slotting machines. It covers machine controls, safeguarding, and safety procedures to mitigate hazards.
4. CE Marking (Conformité Européene): Required for machines sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), CE marking ensures that slotting machines meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. Compliance involves rigorous testing and documentation.
5. NFPA 79 (National Fire Protection Association): This electrical standard for industrial machinery outlines requirements to ensure electrical safety, which is vital for preventing electrical hazards in slotting machines.
6. ISO 12100 (Safety of Machinery – General Principles for Design): This standard provides a framework for designing safe machinery, including slotting machines, by identifying hazards and implementing protective measures.
Implementing these certifications and standards helps organizations ensure the safety of their slotting machining operations, minimize risks, and comply with legal requirements. Regular training, risk assessments, and maintenance checks are essential components of a comprehensive safety program.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “slotting machining”
Slotting machining is a precise and specialized process used to create slots, keyways, or other similar features in a workpiece. Here are the key technical parameters to consider:
1. Cutting Speed:
– Typically ranges between 20 to 40 meters per minute (m/min).
– Dependent on the material being machined and the type of slotting tool used.
2. Feed Rate:
– Measured in millimeters per minute (mm/min).
– Generally set between 0.05 to 0.2 mm/tooth.
– Influences the surface finish and tool life.
3. Depth of Cut:
– Determines the thickness of the material layer removed in one pass.
– Commonly ranges from 0.5 to 5 mm per pass, depending on the material hardness and machine rigidity.
4. Tool Material:
– High-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and sometimes coated carbide tools.
– Choice depends on the material being machined and the required precision.
5. Workpiece Material:
– Affects the selection of cutting parameters.
– Common materials include various steels, cast iron, aluminum, and non-ferrous metals.
6. Tool Geometry:
– Includes rake angle, clearance angle, and tool profile.
– Specific to the slotting tool design to achieve optimal cutting performance.
7. Coolant/Lubrication:
– Necessary to reduce tool wear, prevent overheating, and improve surface finish.
– Type and application method can vary (flood, mist, or dry machining).
8. Machine Specifications:
– Machine rigidity, power, and spindle speed capability.
– CNC slotting machines offer higher precision and repeatability compared to manual machines.
9. Surface Finish:
– Desired surface roughness will dictate the final passes and cutting parameters.
– Typically achieved by optimizing feed rate and tool sharpness.
10. Tolerances:
– Tight tolerances may require additional finishing operations or precise control of cutting parameters.
Understanding and optimizing these parameters is crucial for efficient slotting operations, achieving desired quality, and prolonging tool life.
List Product features of “slotting machining”
Slotting machining, also known as keyway broaching or slotting, is a machining process used to create slots, grooves, or keyways in a workpiece. Here are the primary features of slotting machining:
1. Precision Cutting:
– Slotting machines provide precise and accurate cuts, essential for creating specific slot dimensions and keyways that fit tightly with corresponding components.
2. Versatility:
– Suitable for a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
– Can produce various slot shapes, such as T-slots, dovetail slots, and straight slots.
3. Customization:
– Capable of producing custom slot profiles tailored to specific design requirements.
– Adjustable cutting tools allow for different slot widths and depths.
4. Tooling Flexibility:
– Utilizes a range of cutting tools, including single-point tools and multi-point broaches.
– Interchangeable tools cater to different slotting applications and material types.
5. High Efficiency:
– Automated slotting machines can handle high-volume production runs efficiently.
– Reduces manual labor and increases production speed with consistent quality.
6. Surface Finish:
– Produces high-quality surface finishes, reducing the need for additional finishing processes.
– Capable of achieving tight tolerances and smooth surfaces.
7. Depth Control:
– Allows for precise control over slot depth, ensuring consistency across multiple workpieces.
– Depth adjustments can be easily made during the machining process.
8. Cost-Effective:
– Reduces production costs by minimizing waste and maximizing material usage.
– Long tool life and reduced need for frequent replacements lower operational costs.
9. Integration:
– Can be integrated with other machining processes, such as milling or drilling, for comprehensive manufacturing solutions.
– Often used in conjunction with CNC systems for enhanced control and automation.
10. Safety Features:
– Modern slotting machines are equipped with safety guards and emergency stop functions.
– Designed to minimize operator exposure to moving parts and cutting tools.
These features make slotting machining an essential process in manufacturing industries, especially for creating slots and keyways with high precision and efficiency.
List Application of “slotting machining”
Slotting machining is a precise manufacturing process used to create slots or grooves in a workpiece. This process is vital in various industrial applications, including:
1. Gear Manufacturing: Slotting is used to cut keyways and splines in gears, enabling them to fit accurately on shafts and transmit power efficiently.
2. Automotive Industry: Slotting machines are employed to produce keyways and other slots in engine components, transmission parts, and axles, ensuring proper assembly and operation.
3. Aerospace Industry: In the aerospace sector, slotting is used to create complex slots and keyways in turbine blades and other critical components, which require high precision and reliability.
4. Tool and Die Making: Slotting machines are used to manufacture dies, molds, and various cutting tools. The precision of slotting ensures the accurate formation of slots required for proper tool functionality.
5. Textile Machinery: Slotting is applied in producing parts of textile machinery, such as shafts and gears, that require specific slots for operational efficiency.
6. Electrical Components: Slotting is used to create slots in components like rotors and stators in electric motors, ensuring proper assembly and functionality.
7. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: Slotting machines produce slots in hydraulic valves and pneumatic actuators, which are crucial for controlling fluid and air flow in these systems.
8. Medical Devices: Precision slotting is essential in manufacturing components for medical devices, ensuring the devices’ functionality and safety.
9. Construction Equipment: Slotting is used in the production of parts for construction machinery, such as excavators and loaders, requiring robust and precise slots for assembly and operation.
10. Consumer Electronics: Slotting machines are employed in creating slots in various electronic components, ensuring proper fit and function in devices like smartphones and laptops.
Slotting machining’s versatility and precision make it indispensable across multiple industries, enhancing the performance and reliability of a wide range of products.
List Various Types of “slotting machining”
Slotting machining is a process used to create slots or grooves in a workpiece. Here are various types of slotting machining:
1. Vertical Slotting:
– Planer Type Slotting: Involves a vertical slotter with a single-point cutting tool that moves up and down to cut the slot.
– Shaper Type Slotting: Similar to planer slotting, but the tool reciprocates in a linear motion, typically used for internal keyways and slots.
2. Horizontal Slotting:
– Horizontal Milling: Utilizes a horizontal milling machine with a slotting cutter to create slots. It’s ideal for long slots with precision.
3. Broaching:
– Linear Broaching: A broach tool is pushed or pulled through the workpiece to cut the slot. This method is efficient for producing keyways and internal splines.
4. CNC Slotting:
– CNC Milling: Utilizes CNC machines to perform slotting with high precision and repeatability. Complex slotting patterns can be achieved using programmed tool paths.
– CNC Wire EDM: Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) uses a wire to cut precise slots, especially in hard materials.
5. Slot Drilling:
– End Milling: Uses an end mill cutter on a milling machine to cut slots. This is versatile for both horizontal and vertical slots.
– Slot Drills: Specially designed drills for creating slots in a single operation.
6. Laser Slotting:
– Laser Cutting: Uses a laser to cut slots with high precision and minimal material wastage. Suitable for intricate and delicate slotting tasks.
7. Punching:
– Turret Punching: Utilizes a punch press with a turret of tools to punch slots into sheet metal efficiently.
Each type of slotting machining has its specific applications, advantages, and limitations, making the choice of method dependent on the material, slot dimensions, and precision requirements.
slotting machining Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Slotting machining is a precise and versatile process used across various industries to create keyways, slots, and other intricate shapes. To enhance its efficiency and capability, several accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options are available.
Accessories
1. Indexable Slotting Cutters: These tools offer replaceable inserts that extend tool life and improve cutting performance.
2. Adjustable Blade Holders: These holders allow for fine-tuning of the blade position, ensuring precise slot dimensions.
3. Coolant Systems: Essential for reducing heat and extending tool life, advanced coolant systems can be integrated to deliver high-pressure coolant directly to the cutting zone.
4. Workholding Fixtures: Custom fixtures improve stability and accuracy, essential for complex or high-tolerance projects.
Upgrades
1. CNC Integration: Upgrading to CNC-controlled slotting machines increases precision, repeatability, and allows for complex slot geometries.
2. Advanced Tooling Materials: High-speed steel (HSS) or carbide tools can be replaced with coated variants like titanium nitride (TiN) for enhanced durability and performance.
3. Digital Readouts (DRO): Installing DRO systems on manual machines improves accuracy by providing real-time positional feedback.
4. Automated Feeds and Speeds: Automation systems can optimize cutting parameters, improving efficiency and reducing operator error.
Custom Manufacturing Options
1. Tailored Slotting Blades: Custom blades can be manufactured to meet specific slot dimensions and material requirements.
2. Specialized Machine Configurations: Machines can be customized to accommodate unique workpieces, including extended stroke lengths or modified bed sizes.
3. Multi-Axis Slotting Machines: For complex parts, multi-axis slotting machines offer greater flexibility and capability to create intricate features.
4. Custom Software Solutions: Software tailored to specific machining tasks can streamline operations and integrate seamlessly with existing manufacturing systems.
Investing in these accessories, upgrades, and custom options can significantly enhance the productivity, precision, and versatility of slotting machining processes, ensuring high-quality results and efficient operations.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “slotting machining”
Quality Control in Slotting Machining
Quality control in slotting machining involves several key practices to ensure precision and consistency:
1. Inspection of Raw Materials: Ensuring the materials meet required specifications before starting the machining process.
2. Tool Calibration: Regular calibration of slotting tools to maintain accurate dimensions.
3. Process Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the slotting process using sensors and automated systems to detect any deviations.
4. In-process Inspection: Using techniques like Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) to inspect the workpiece during production.
5. Final Inspection: Thorough inspection of the finished product for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and tolerance adherence.
6. Documentation and Traceability: Keeping detailed records of the process parameters and inspection results for traceability.
The Manufacturing Process of Slotting Machining
1. Setup: The slotting machine is set up with the required tooling, workpiece, and fixtures. Tool paths and process parameters are programmed into the machine control unit.
2. Workpiece Clamping: The workpiece is securely clamped to prevent any movement during the machining process.
3. Tool Selection: Appropriate slotting tools, such as single-point tools or broaches, are selected based on the material and desired slot dimensions.
4. Slotting Operation: The tool moves in a reciprocating linear motion, gradually cutting the material to create the slot. The process involves multiple passes to achieve the desired depth and width.
5. Coolant Application: Coolant is applied to reduce heat and prevent tool wear, ensuring a better surface finish and prolonging tool life.
6. Monitoring and Adjustment: Continuous monitoring of the process is done to detect any anomalies. Adjustments are made as needed to maintain quality.
7. Finishing: After the slotting is completed, the workpiece may undergo secondary operations like deburring or surface treatment to achieve the final specifications.
8. Inspection: The finished slot is inspected for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and conformity to specifications.
By adhering to strict quality control measures and following a systematic manufacturing process, slotting machining ensures high precision and reliability in the production of slots.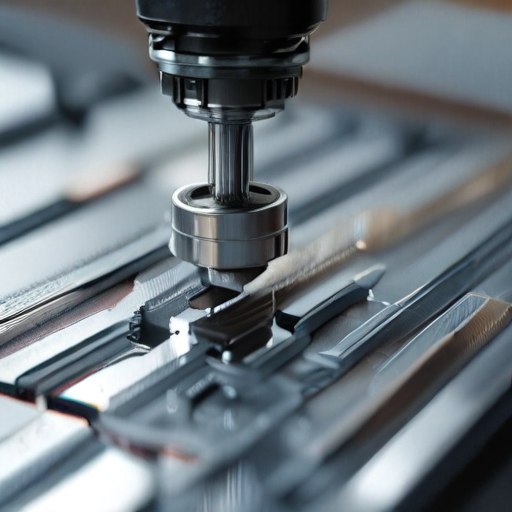
How to use “slotting machining”
Slotting machining is a process used to create vertical cuts or slots in a workpiece using a slotting machine or slotter. It is particularly useful for producing keyways, grooves, or internal gear teeth. Here’s how to use slotting machining effectively:
Equipment and Tools Needed:
– Slotting machine (vertical shaper)
– Appropriate slotting tool (single-point cutting tool)
– Workpiece
– Clamping devices or fixtures
– Measuring instruments (calipers, micrometers)
Steps to Use Slotting Machining:
1. Preparation:
– Select the Tool: Choose a cutting tool that matches the slot dimensions required. Ensure it is sharp and in good condition.
– Set Up the Machine: Check the machine’s condition, ensuring it is properly lubricated and all moving parts function smoothly.
2. Workpiece Preparation:
– Mark the Slot: Clearly mark the area where the slot needs to be machined on the workpiece.
– Secure the Workpiece: Firmly clamp the workpiece to the machine table using suitable fixtures or clamping devices to prevent movement during machining.
3. Machine Adjustment:
– Tool Installation: Install the slotting tool in the machine’s ram. Ensure it is securely fastened.
– Set the Stroke Length: Adjust the stroke length of the slotter according to the depth of the slot required.
– Positioning: Align the tool with the marked slot location on the workpiece. Adjust the machine’s table to position the workpiece correctly.
4. Machining Process:
– Feed Rate: Set an appropriate feed rate. This will depend on the material of the workpiece and the depth of the cut.
– Start Machining: Begin the machining process by powering on the slotter. The ram will move the tool vertically, cutting into the workpiece to create the slot.
– Monitor the Process: Continuously monitor the machining process, making adjustments as necessary to ensure precision and quality.
5. Finishing:
– Inspect the Slot: After machining, inspect the slot for accuracy using measuring instruments.
– Deburring: Remove any burrs or rough edges from the slot using appropriate deburring tools.
By following these steps, you can effectively use slotting machining to create precise vertical slots in various materials.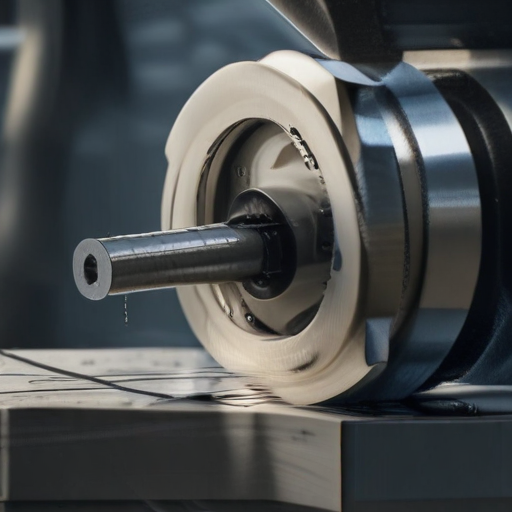
“slotting machining” Comparative Analysis
Slotting machining, often referred to as keyway broaching or slotting, is a versatile and precise machining process used to create slots or grooves in a workpiece. This process is vital in manufacturing industries for making keyways, splines, and other internal shapes. Here’s a comparative analysis of slotting machining, highlighting its advantages, disadvantages, and comparison with other machining processes:
Advantages of Slotting Machining
1. Precision: Slotting can produce highly accurate and precise slots, which are essential for fitting parts like keys or splines.
2. Versatility: It can handle various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
3. Complex Shapes: Slotting is capable of creating complex internal shapes that other machining processes may struggle with.
4. Tool Cost: Compared to other processes like broaching, slotting tools are generally less expensive.
Disadvantages of Slotting Machining
1. Speed: Slotting is typically slower than other machining processes like milling or broaching, which can impact production efficiency.
2. Tool Wear: The slotting tool can wear out faster, especially when working with harder materials, leading to higher maintenance costs.
3. Surface Finish: The surface finish of the slot may not be as smooth as those produced by processes like grinding or honing.
Comparison with Other Machining Processes
Milling:
– Speed: Milling is generally faster and more suitable for producing a variety of features in one setup.
– Versatility: Milling machines can perform a range of operations, including slotting, but may require multiple setups.
– Precision: While precise, milling might not achieve the same level of detail in internal shapes as slotting.
Broaching:
– Speed: Broaching is faster and more efficient for high-volume production of internal shapes.
– Precision and Finish: Broaching often produces superior surface finishes and precision compared to slotting.
– Cost: The initial cost of broaching tools and machines is higher, making it less economical for low-volume production.
Grinding:
– Surface Finish: Grinding provides an excellent surface finish, which is superior to slotting.
– Precision: Grinding can achieve very tight tolerances.
– Versatility: It is less versatile in creating internal shapes and is typically used for finishing rather than shaping.
In summary, slotting machining is a valuable process for producing precise internal slots and shapes, especially where versatility and cost are considerations. However, for higher speed, better surface finish, and efficiency in mass production, processes like broaching, milling, or grinding might be more appropriate. The choice of machining process depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired precision, surface finish, and production volume.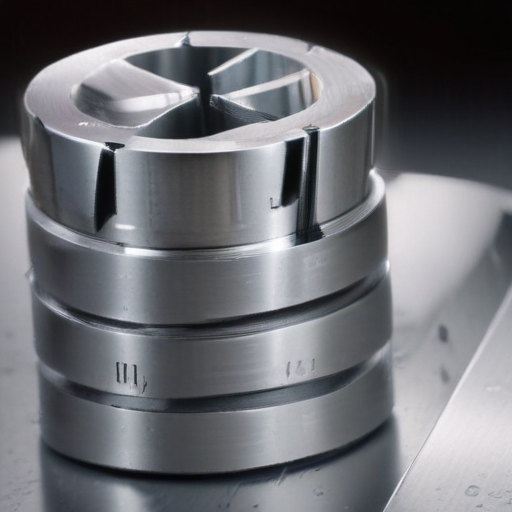
“slotting machining” Warranty and Support
Slotting Machining Warranty and Support
Warranty:
Slotting machines typically come with a manufacturer’s warranty that covers defects in materials and workmanship. The standard warranty period ranges from one to three years, depending on the manufacturer and the model. During this period, if any part of the machine fails due to manufacturing defects, the manufacturer will repair or replace the defective parts at no additional cost to the customer. It’s essential to register your machine with the manufacturer and retain proof of purchase to activate the warranty.
Extended Warranty:
Many manufacturers offer extended warranty plans that can be purchased separately. These plans extend the coverage beyond the standard warranty period and may include additional benefits such as periodic maintenance services, priority support, and replacement of wear-and-tear parts.
Support:
Manufacturers provide various support options to ensure smooth operation and minimal downtime. These typically include:
1. Technical Support:
– Hotline: Most manufacturers offer a dedicated hotline for technical support. Customers can call this number for immediate assistance with troubleshooting and operational issues.
– Email Support: For non-urgent inquiries, customers can reach out via email. This is useful for detailed technical questions or when sending diagnostic information.
2. On-site Support:
– Service Visits: In case of complex issues that cannot be resolved remotely, manufacturers can arrange for a technician to visit the site for diagnosis and repair.
– Maintenance Contracts: Some companies offer preventive maintenance contracts, ensuring regular check-ups and servicing to keep the machines running efficiently.
3. Online Resources:
– Documentation: Detailed user manuals, installation guides, and troubleshooting guides are often available on the manufacturer’s website.
– Video Tutorials: Many manufacturers provide video tutorials for common maintenance and operational tasks.
– Software Updates: For machines with digital controls, manufacturers may offer software updates that enhance functionality and performance.
By providing comprehensive warranty and support services, slotting machine manufacturers help ensure that their customers can rely on their equipment for precise and efficient machining operations.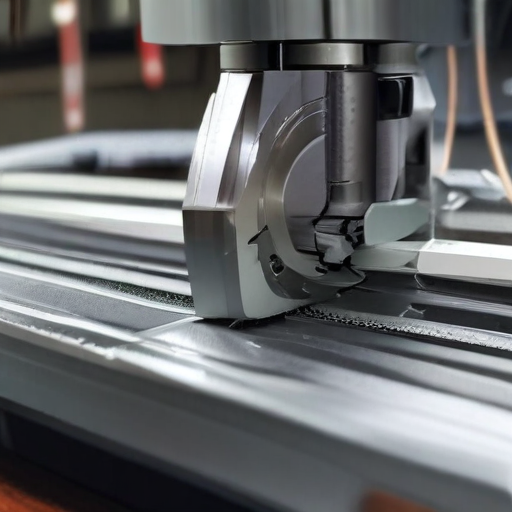
List “slotting machining” FAQ
Slotting Machining FAQ
What is slotting machining?
Slotting machining is a manufacturing process used to create slots or grooves on a workpiece. It involves the use of a slotting machine, where a vertically reciprocating tool removes material from the workpiece to form the desired slot.
What are common applications of slotting machining?
Slotting machining is often used in creating keyways, splines, and internal gears. It’s also used for shaping intricate profiles and contours that are difficult to achieve with other machining processes.
What materials can be processed with slotting machining?
Slotting machining can handle a variety of materials, including metals like steel, aluminum, and brass, as well as non-metals such as plastics and composites.
What are the advantages of slotting machining?
– Precision: Slotting provides high precision and accuracy, especially for internal features.
– Versatility: It can create complex shapes and profiles.
– Surface Finish: Often results in a good surface finish with minimal secondary operations.
What are the limitations of slotting machining?
– Speed: Slotting is typically slower compared to other machining processes.
– Tool Wear: The reciprocating motion can cause rapid tool wear.
– Size Restrictions: Limited to smaller workpieces due to machine size constraints.
How does slotting machining compare to broaching?
Both slotting and broaching are used for internal shaping, but broaching is faster and more suitable for high-volume production. Slotting, however, is more versatile for lower volumes and intricate designs.
What types of slotting tools are used?
Common tools include single-point cutters, form tools, and specialized slotting cutters designed for specific applications.
How can one ensure the quality of slotting machining?
– Proper Tool Selection: Use the right tool for the material and desired slot.
– Machine Maintenance: Regular maintenance ensures machine precision.
– Process Monitoring: Continuously monitor the process for any deviations.
What safety precautions are necessary?
– Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
– Ensure proper machine guarding.
– Follow operational guidelines and training for machine use.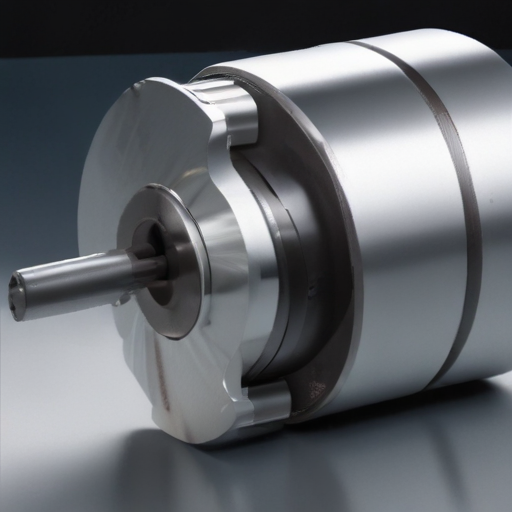
Top 10 FAQ with answer about slotting machining for Buyer Sourcing from China
Top 10 FAQ about Slotting Machining for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What is slotting machining?
Slotting machining is a process used to cut keyways, grooves, and slots into a workpiece using a vertically mounted tool that moves reciprocally.
2. What materials can be machined using slotting?
Slotting can be used on a variety of materials including steel, aluminum, brass, and plastics, making it versatile for different industrial needs.
3. Why should I source slotting machining from China?
China offers competitive pricing, a wide range of manufacturers, advanced machinery, and high production capacity, making it cost-effective for buyers.
4. How can I ensure the quality of slotting machining from China?
Conduct thorough research on suppliers, request samples, check certifications (like ISO), and consider third-party inspections to ensure quality standards.
5. What is the typical lead time for slotting machining orders?
Lead times vary based on order size and complexity but typically range from 2 to 8 weeks. Confirm with the supplier for specific timelines.
6. What are the common tolerances for slotting machining?
Typical tolerances for slotting machining are within ±0.02 mm, but this can vary depending on the precision required and the capabilities of the supplier.
7. How do I handle communication and language barriers?
Choose suppliers with proficient English-speaking representatives, use clear and concise communication, and consider hiring a local agent if necessary.
8. What payment terms are common with Chinese suppliers?
Common payment terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and sometimes, secure online payment methods. Initial deposits are typically 30%, with the balance due before shipment.
9. How do I manage shipping and logistics for my orders?
Coordinate with suppliers who offer FOB (Free on Board) terms, use reputable freight forwarders, and track shipments using logistics services to ensure timely delivery.
10. What should I include in my RFQ (Request for Quotation)?
Include detailed specifications, material requirements, tolerances, quantity, lead time expectations, and any special processing or finishing requirements to get accurate quotes.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, buyers can effectively source slotting machining services from China, ensuring quality and efficiency.
