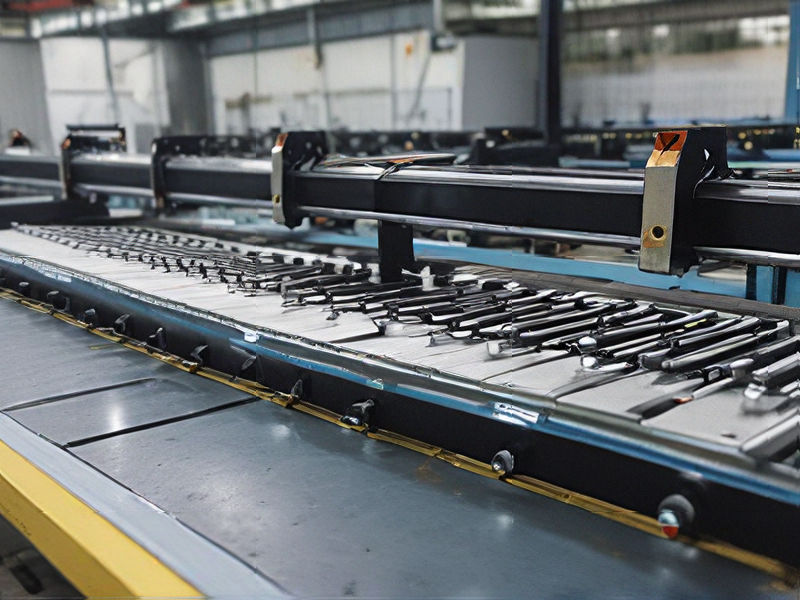
Technology and Applications of routers cnc
CNC routers (Computer Numerical Control routers) are advanced machining tools that automate the process of cutting, carving, and engraving various materials such as wood, plastic, metal, and composites. They utilize computer-aided design (CAD) software to guide the router in executing precise and complex shapes, making them invaluable in various industries, including woodworking, aerospace, automotive, and signage.
Technology:
CNC routers operate using a combination of hardware and software. The key components include a spindle or router bit, a motion control system (typically consisting of stepper or servo motors), and a computer interface. The CAD software creates the design, which is then converted into a Machine Control Language (MCL) file that instructs the router on how to perform the task. Controllers like the G-code facilitate the routing process by detailing the tool paths, speeds, and feed rates.
Applications:
1. Woodworking: CNC routers are extensively used for cabinetry, furniture making, and intricate wood carvings, thus enhancing productivity and precision.
2. Sign Making: They can cut and engrave signage quickly and accurately, allowing for customized designs.
3. Prototyping: CNC routers enable rapid prototyping in product development, allowing designers to test and refine concepts before mass production.
4. Aerospace and Automotive Industries: They help manufacture components with high tolerances and are often used in creating molds and tooling.
By combining precision and efficiency, CNC routers have revolutionized the way various materials are processed, providing significant benefits in terms of time, cost, and quality across multiple sectors.
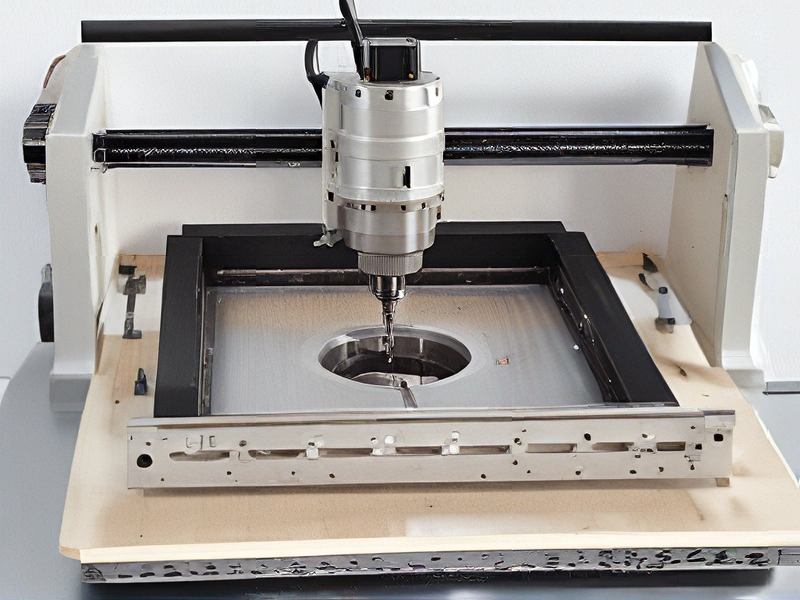
Quality Testing Methods for routers cnc and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for CNC routers are essential to ensure precision, reliability, and performance. Here are key methods and controls to implement:
1. Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the router for any physical defects, such as cracks, missing components, or misalignments. Check for proper assembly and finishing quality.
2. Calibration Checks: Regularly calibrate the CNC router using precision measuring tools (e.g., dial indicators, laser calibrators) to ensure the machine operates within specified tolerances. This step is crucial for maintaining accuracy.
3. Test Cuts: Conduct test cuts on various materials to evaluate the router’s performance. Assess the quality of the cuts for smoothness, precision, and adherence to specified dimensions. Use these test results to make necessary adjustments.
4. Mechanical Testing: Test the router’s mechanical components (spindles, drives, and belts) for wear and operational efficiency. This can include dynamic load tests and vibration analysis to identify potential issues.
5. Software Validation: Ensure that the CNC software is correctly configured and validated. Run diagnostic software to check for errors in G-code interpretations and verify tool paths.
6. Tolerances and Specifications: Define quality standards by setting acceptable tolerances for various operations. Regularly compare finished products against these specifications to ensure compliance.
7. Regular Maintenance and Documentation: Implement a routine maintenance schedule, documenting all maintenance and repairs. Maintain records of performance metrics and inspections to identify trends and areas for improvement.
8. Employee Training: Ensure operators are well-trained in both CNC operation and quality control practices, boosting overall productivity and reducing errors.
By combining these methods, manufacturers can maintain high-quality standards while minimizing defects in CNC router production.

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from routers cnc
When procuring CNC routers, several key considerations can guide your purchasing decision:
1. Identify Requirements: Clearly define what you need the CNC router for—materials, size, complexity of projects, and production volume. This helps narrow down models that meet your specific requirements.
2. Budget: Establish a budget that includes not just the initial purchase price, but also ongoing costs such as maintenance, software, and tooling. Consider the total cost of ownership.
3. Specifications Review: Evaluate machine specifications such as cutting area, spindle power, speed, and precision. Ensure that the router can handle the materials you plan to work with.
4. Supplier Reputation: Research and ensure you are buying from reputable suppliers or manufacturers. Check customer reviews, testimonials, and case studies to gauge reliability and service.
5. After-Sales Support: Investigate the support offered post-purchase, including warranty, technical support, and training. Good after-sales support is vital for long-term satisfaction.
6. Software Compatibility: Ensure the CNC router is compatible with the design software you use. Some machines come with proprietary software, which may limit your design capabilities.
7. Customization Options: Consider whether the router can be customized or upgraded in the future to accommodate your growing needs.
8. Hands-On Demos: If possible, request a demo or visit a facility where the router is in operation. This first-hand experience can provide valuable insights into performance and ease of use.
9. Local Regulations and Compliance: Verify that the CNC router complies with local regulations and safety standards.
Carefully considering these factors will help you make an informed decision and find the right CNC router for your needs.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from routers cnc in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing CNC Routers from China
1. What are CNC routers?
CNC routers are computer-controlled cutting machines used for various materials like wood, plastic, and metal, primarily for precision shaping and engraving.
2. Why source CNC routers from China?
China offers competitive pricing, diverse manufacturers, and a wide range of specifications. The country is a global hub for manufacturing and can provide cost-effective solutions.
3. How do I select the right manufacturer?
Research potential suppliers by checking online directories, trade shows, and industry referrals. Assess their certifications (e.g., ISO), production capacity, and reviews from previous clients.
4. What are the quality control processes?
Reputable manufacturers implement rigorous quality control measures including raw material inspections, in-process quality checks, and final product testing to meet international standards.
5. What are the shipping and import regulations?
Understand the customs regulations for your country regarding importing machinery. Check tariff classifications, duties, and any required documentation (e.g., invoices, bills of lading).
6. How do I protect my intellectual property?
Consider signing Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and ensuring that your designs are formally registered. Work with manufacturers that respect IP rights.
7. What about after-sales support?
Inquire about warranty periods, spare parts availability, and technical support. A reliable manufacturer will provide comprehensive after-sales service.
8. Are there language barriers?
While many manufacturers have English-speaking staff, communication might still pose challenges. It’s advisable to have clear, written specifications and to consider hiring a local agent if needed.
9. What is the typical lead time?
Lead times can vary from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of your order and the manufacturer’s workload.
By addressing these FAQs, potential buyers can navigate the sourcing process more effectively.

