Title: “SourcifyChina Factory Titanium vs. Stainless Steel: Comprehensive Comparison for Industrial Applications”
When choosing between titanium and stainless steel for industrial applications, it’s crucial to understand their distinct properties, uses, and costs. Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, superior corrosion resistance, and high biocompatibility, making it ideal for aerospace, medical implants, and marine environments. Conversely, stainless steel is valued for its overall strength, corrosion resistance, and affordability, commonly used in construction, kitchen appliances, and medical instruments.
Titanium offers a higher strength-to-weight ratio, being 50% less dense than stainless steel, which makes it ideal for weight-sensitive applications like aircraft components. It also resists corrosion better in extreme environments, such as saltwater or high temperatures, and is non-toxic and hypoallergenic, which is why it’s preferred for medical implants. However, titanium is more expensive and harder to machine compared to stainless steel.
Stainless steel, while heavier, provides excellent durability and resistance to rust and corrosion, especially in moist environments. It’s more cost-effective and easier to work with, making it a versatile choice for various applications from kitchen appliances to construction materials.
Ultimately, the choice between titanium and stainless steel depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as weight, cost, corrosion resistance, and application environment.
Why Choose “SourcifyChina” Factory for Buying Titanium Steel vs Stainless Steel from China?
Choosing “SourcifyChina” ensures access to high-quality titanium steel and stainless steel directly from reliable Chinese manufacturers. Their rigorous quality control processes guarantee superior product standards, meeting international specifications.
“SourcifyChina” offers competitive pricing for both titanium and stainless steel. By leveraging their strong relationships with manufacturers, buyers benefit from cost savings without compromising on quality, making it an economical choice.
The factory’s extensive industry experience ensures efficient handling of all purchasing requirements. Their team of experts provides comprehensive support, from product selection to shipment, ensuring a seamless buying experience.
“SourcifyChina” emphasizes sustainability and ethical manufacturing practices. Buyers can be confident that their products are sourced from factories that prioritize environmentally friendly processes and fair labor practices.
With a robust logistics network, “SourcifyChina” guarantees timely delivery of titanium and stainless steel products. Their reliable shipping solutions minimize delays and ensure that buyers receive their orders promptly and in excellent condition.
The factory’s commitment to innovation ensures that buyers receive cutting-edge materials that meet the latest industry standards. “SourcifyChina” continuously invests in research and development to stay ahead in the market.
Customer satisfaction is a top priority for “SourcifyChina.” Their dedicated customer service team is always available to address any concerns and provide tailored solutions, ensuring a positive purchasing experience.
In conclusion, “SourcifyChina” stands out as a trusted partner for purchasing titanium and stainless steel from China. Their quality assurance, competitive pricing, industry expertise, commitment to sustainability, reliable logistics, innovation, and excellent customer service make them the preferred choice for discerning buyers worldwide.

Titanium Steel vs Stainless Steel
Titanium steel and stainless steel are both popular materials used in various industries due to their unique properties. Titanium steel is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, while stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and versatility.
Titanium
Steel:
– Strength: Superior strength-to-weight ratio.
– Weight: Lightweight, ideal for aerospace and medical applications.
– Corrosion Resistance: Excellent, especially in seawater and acidic environments.
– Biocompatibility: Hypoallergenic, suitable for medical implants and jewelry.
– Durability: Extremely durable, resistant to fatigue and wear.
– Cost: Generally more expensive due to complex processing.
Stainless
Steel:
– Strength: Strong, but heavier than titanium steel.
– Weight: Heavier, used in construction and automotive industries.
– Corrosion Resistance: Good, especially with added elements like chromium and nickel.
– Variety: Available in multiple grades for different applications (e.g., 304, 316).
– Versatility: Used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, and architecture.
– Cost: More affordable and easier to work with than titanium steel.
Both materials have their specific advantages depending on the application, with titanium steel favored for high-performance needs and stainless steel for more general purposes.
Titanium steel and stainless steel have distinct properties that make them suitable for different applications. Titanium steel is known for its lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance, whereas stainless steel is favored for its durability, affordability, and resistance to rust and staining.
– Titanium Steel Applications:
– Aerospace industry: Aircraft components, structural parts
– Medical devices: Implants, surgical instruments
– Automotive industry: High-performance parts
– Sports equipment: Bicycle frames, golf clubs
– Marine industry: Ship components, offshore structures
– Stainless Steel Applications:
– Construction: Structural supports, building facades
– Food industry: Kitchen equipment, food processing machinery
– Automotive industry: Exhaust systems, decorative trims
– Household items: Cutlery, sinks, appliances
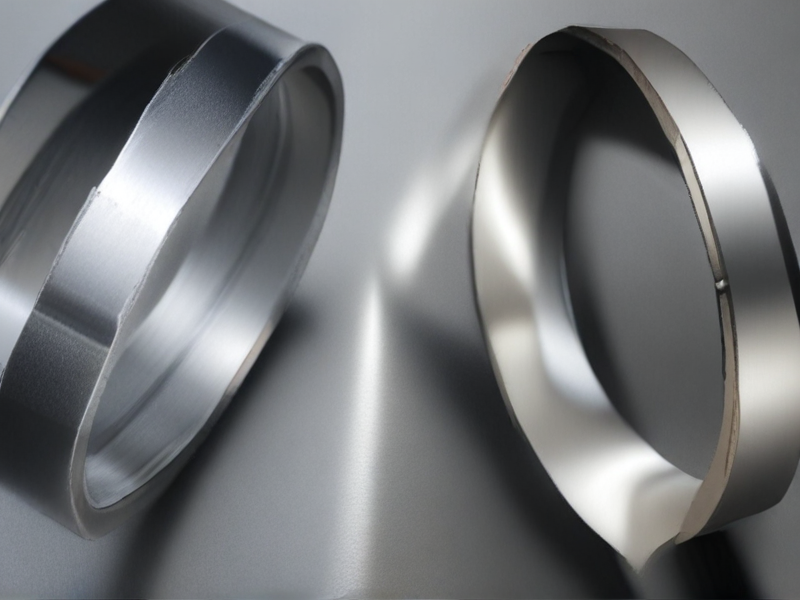

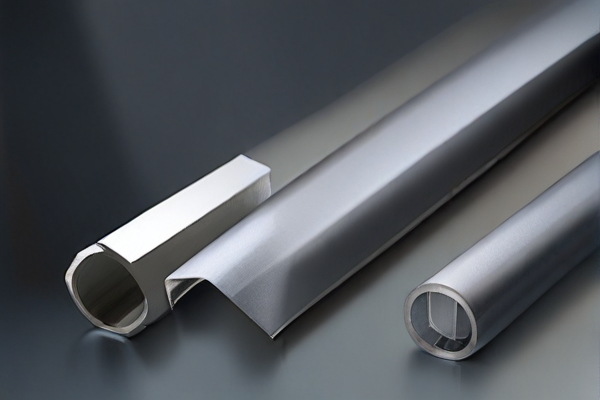
In the aerospace, defense, and marine sectors, the choice between titanium steel and stainless steel is crucial due to their distinct properties. Titanium steel is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, which is significantly higher than that of stainless steel. This makes titanium steel an ideal material for aerospace applications where reducing weight without compromising strength is paramount. Additionally, titanium steel exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against seawater and chlorine, making it suitable for marine applications and defense equipment exposed to harsh environments. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and its biocompatibility further enhance its utility in high-performance and specialized applications.
Conversely, stainless steel is prized for its durability, ease of fabrication, and cost-effectiveness. While it may not match the strength-to-weight ratio of titanium steel, stainless steel offers substantial resistance to corrosion and oxidation, which is critical in both marine and defense applications. Its versatility allows it to be used in a wide range of components, from structural parts to small fasteners. Stainless steel’s ability to maintain its properties at high temperatures makes it valuable in aerospace applications as well. Although heavier than titanium steel, its lower cost and robust performance often make stainless steel the material of choice for projects where budget constraints and comprehensive durability are key considerations.

In the automotive industry, the choice between titanium steel and stainless steel hinges on factors such as weight, strength, and corrosion resistance. Titanium steel is significantly lighter than stainless steel, offering a notable advantage in reducing overall vehicle weight, which in turn enhances fuel efficiency and performance. Additionally, titanium’s superior strength-to-weight ratio allows for the design of lighter and more durable components, such as exhaust systems and suspension parts. However, its higher cost and manufacturing complexity can be limiting factors. On the other hand, stainless steel is more cost-effective and easier to fabricate, making it a popular choice for a wide range of automotive applications, including body panels and structural components. Its excellent corrosion resistance ensures long-lasting durability, especially in harsh environments.
In the electronics sector, the properties of titanium steel and stainless steel play a crucial role in determining their suitability for various applications. Titanium steel’s lightweight nature and exceptional strength make it ideal for use in portable electronic devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and wearables, where durability and ease of handling are paramount. Moreover, its resistance to corrosion and biocompatibility also make it suitable for medical devices and implants. Stainless steel, while heavier, offers excellent electromagnetic shielding properties, which are beneficial in protecting sensitive electronic components from interference. Its ease of fabrication and lower cost also make it a preferred material for housings, frames, and other structural elements in electronic devices. Each material’s unique properties cater to different needs within the automotive and electronics industries, making the choice highly application-specific.

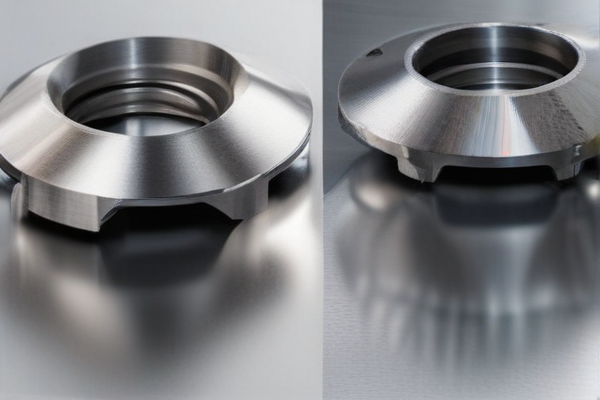
In the construction and energy sectors, titanium steel and stainless steel are both pivotal materials, each offering distinct advantages and trade-offs. Titanium steel is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction without compromising strength is crucial, such as in high-rise buildings, bridges, and offshore platforms. Its high corrosion resistance, even in harsh environments, extends the lifespan of structures exposed to marine or industrial atmospheres, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing safety. Furthermore, titanium steel’s non-magnetic properties make it suitable for energy infrastructure that requires minimal electromagnetic interference, such as in power plants and certain renewable energy installations.
On the other hand, stainless steel is celebrated for its versatility and cost-effectiveness. It offers excellent corrosion resistance, especially grades like 316 and 304, which are commonly used in construction for components like facades, roofing, and support structures. Stainless steel’s durability and aesthetic appeal are advantageous for both functional and decorative elements in buildings. In the energy sector, stainless steel is integral to the fabrication of pipelines, storage tanks, and various machinery components due to its ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. While stainless steel may not match titanium steel’s strength-to-weight ratio, its affordability and wide availability make it a practical choice for many construction and energy projects, balancing performance with cost considerations.

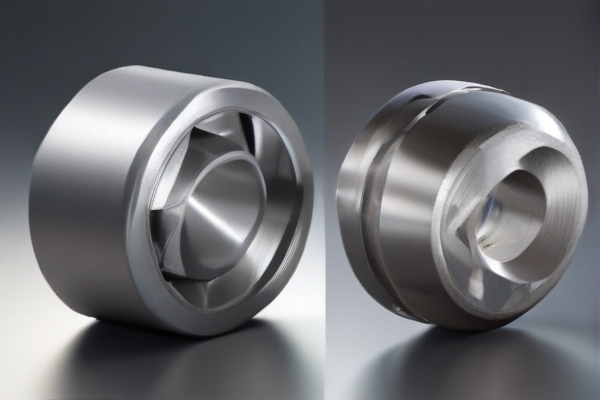
When comparing titanium steel and stainless steel for industrial equipment, it’s essential to consider their respective properties and applications. Titanium steel, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand extreme temperatures. This makes it an ideal choice for aerospace, marine, and chemical processing industries where both high performance and durability are paramount. Titanium’s low density and high tensile strength allow for the manufacturing of lighter yet more robust components, which can significantly enhance the efficiency and longevity of industrial equipment.
Stainless steel, on the other hand, is renowned for its versatility, excellent corrosion resistance, and overall durability. Composed primarily of iron, carbon, and chromium, stainless steel forms a passive layer of chromium oxide that protects against rust and corrosion. This material is widely used in food processing, medical equipment, and construction industries due to its hygienic properties and ease of maintenance. Stainless steel is also more cost-effective compared to titanium steel, making it a practical choice for applications where budget constraints are a factor. While both materials have their unique advantages, the selection between titanium steel and stainless steel ultimately depends on the specific demands of the industrial application, such as required strength, weight, environmental conditions, and cost considerations.

When comparing titanium steel to stainless steel in the context of medical devices, several key factors come into play, including biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties. Titanium steel, primarily composed of titanium and a small percentage of other elements such as aluminum or vanadium, is highly biocompatible, making it ideal for implants and other medical devices that need to integrate with human tissue. Its resistance to corrosion in bodily fluids is superior, reducing the risk of implant degradation over time. Additionally, titanium steel is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, providing durable yet lightweight solutions, essential for devices like joint replacements and bone plates.
On the other hand, stainless steel, often used in surgical instruments and certain types of implants, offers its own set of advantages. Composed mainly of iron, chromium, and nickel, stainless steel is known for its robust mechanical strength and relatively lower cost compared to titanium steel. Its corrosion resistance is also significant, though it may not match the superior levels of titanium steel in certain bodily environments. Stainless steel’s durability and ease of sterilization make it a preferred choice for reusable instruments. However, for long-term implants, concerns about nickel allergies and slightly lower biocompatibility can be limiting factors, making titanium steel a more favorable option in those scenarios.

In the realms of machining and manufacturing, titanium steel and stainless steel are prominent materials, each with distinct properties and applications. Titanium steel, an alloy predominantly composed of titanium with other elements such as aluminum and vanadium, is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. These characteristics make it particularly advantageous in aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance automotive parts, where durability and weight savings are critical. However, titanium steel poses significant machining challenges due to its low thermal conductivity and high chemical reactivity, which can cause tool wear and require specialized cutting techniques and tools, thus increasing production costs and complexity.
On the other hand, stainless steel, an alloy primarily composed of iron, chromium, and often nickel, is widely celebrated for its corrosion resistance and versatility across various industries. It is easier to machine compared to titanium steel, especially the austenitic grades like 304 and 316, which are commonly used due to their good machinability and balance of strength and corrosion resistance. Stainless steel is ubiquitous in applications ranging from kitchenware and construction to medical devices and chemical processing equipment. While it may not match titanium steel in terms of weight reduction or specific strength, its ease of fabrication, cost-effectiveness, and reliable performance make it a staple material in manufacturing, with well-established techniques and tools for efficient processing.

SourcifyChina offers two popular materials: titanium steel and stainless steel. Titanium steel is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it incredibly durable and lightweight. This material is resistant to corrosion and can withstand extreme temperatures, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications.
Stainless steel, on the other hand, is known for its excellent resistance to rust and staining. It contains chromium, which forms a passive layer that prevents oxidation. This makes stainless steel a popular choice for kitchenware, construction, and automotive components due to its durability and ease of maintenance.
In terms of aesthetics, titanium steel often has a matte or slightly glossy finish, which can be anodized to produce various colors. Its unique appearance makes it favored in high-end jewelry and fashion accessories. Stainless steel typically has a shiny, mirror-like finish, which gives it a sleek and modern look, widely used in household appliances and industrial design.
Cost-wise, titanium steel is generally more expensive than stainless steel due to its complex extraction and processing methods. However, its superior strength and lightweight properties often justify the higher price in specialized applications. Stainless steel, being more affordable and versatile, is used extensively in everyday products where both durability and cost-effectiveness are important.
Ultimately, the choice between titanium steel and stainless steel from SourcifyChina depends on the specific needs of the application. Titanium steel offers unmatched strength and corrosion resistance for critical applications, while stainless steel provides a practical, cost-effective solution for a wide range of uses. Understanding the unique properties and advantages of each material can help in making an informed decision.
SourcifyChina’s titanium steel manufacturing involves rigorous quality control, ensuring high durability and resistance to corrosion. Each batch undergoes thorough testing for tensile strength, composition accuracy, and surface finish, guaranteeing top-tier products.
In contrast, their stainless steel production emphasizes precision in alloy composition and consistency in quality. Regular inspections and advanced metallurgical analysis ensure each piece meets stringent industry standards, providing reliable performance and longevity.
Both materials are subjected to detailed surface treatments, including polishing and coating, to enhance aesthetics and protective properties. This meticulous process results in visually appealing and robust products suited for various applications.
Quality control at SourcifyChina includes automated and manual inspections at multiple production stages. This dual approach helps identify and address potential defects early, maintaining high standards across titanium and stainless steel products.
Their commitment to quality extends to post-production, where random sampling and stress tests further validate product reliability. Continuous feedback loops from clients inform improvements, ensuring SourcifyChina’s manufacturing processes evolve to meet industry demands.
By integrating advanced technology and experienced craftsmanship, SourcifyChina ensures their titanium and stainless steel products not only meet but exceed market expectations. This holistic approach to quality control fosters customer trust and satisfaction.
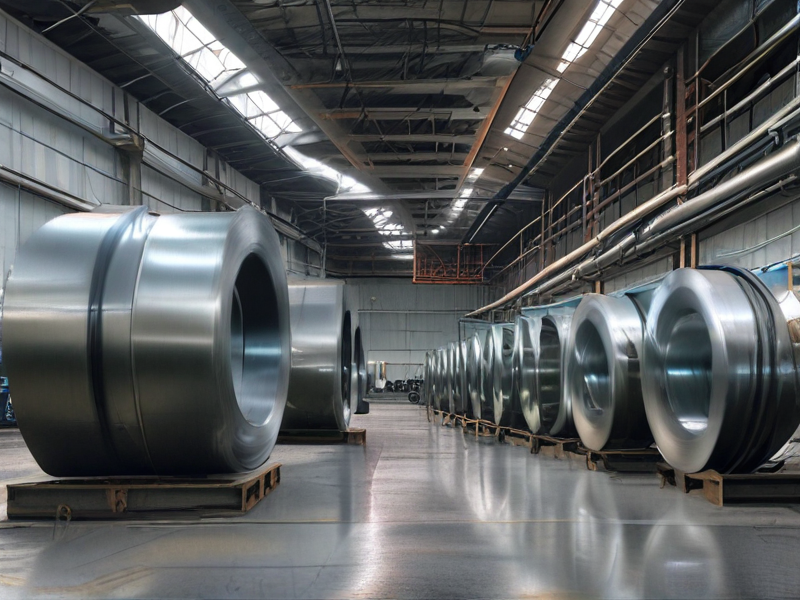
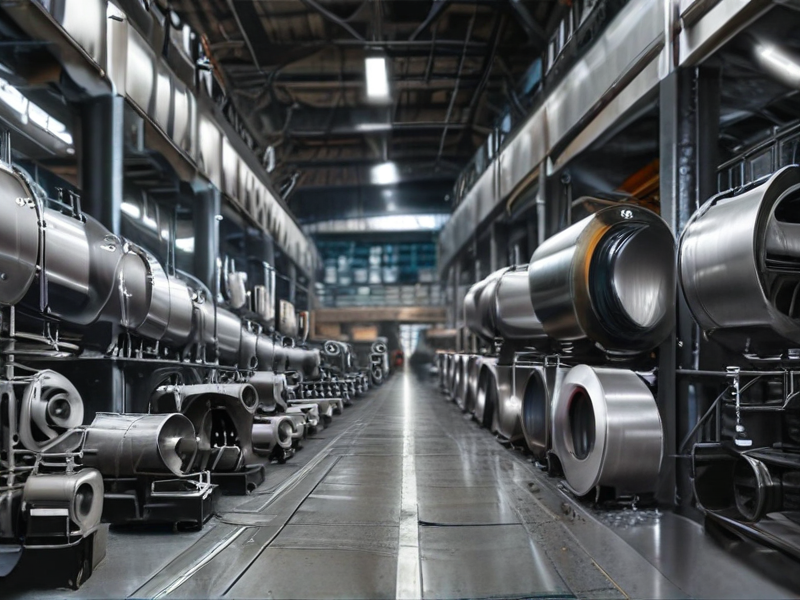
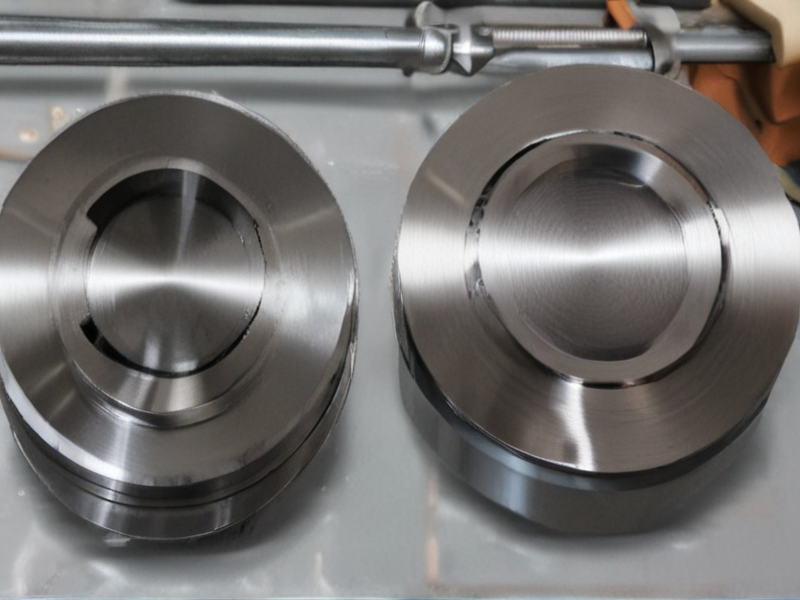



Titanium Steel vs Stainless Steel Capabilities by SourcifyChina
Strength and Durability
Titanium steel, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, excels in applications demanding robust performance under stress. Stainless steel, while strong, generally offers a lower strength-to-weight ratio but is highly durable and resistant to wear.
Corrosion Resistance
Titanium steel exhibits superior corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments like marine and chemical industries. Stainless steel also resists corrosion but may require specific grades and treatments to achieve optimal performance in extreme conditions.
Weight Considerations
Titanium steel is significantly lighter than stainless steel, making it ideal for industries where weight savings are crucial, such as aerospace and medical implants. Stainless steel’s heavier weight can be advantageous for structural stability in construction and heavy machinery.
Thermal Conductivity
Titanium steel has lower thermal conductivity compared to stainless steel, which can be beneficial in applications requiring thermal insulation. Stainless steel, with its higher thermal conductivity, is preferred in applications needing efficient heat transfer, such as cookware and heat exchangers.
Cost and Availability
Titanium steel tends to be more expensive due to its complex extraction and processing methods. Stainless steel is more cost-effective and widely available, making it the preferred choice for cost-sensitive projects and mass production.
Biocompatibility
Titanium steel is highly biocompatible, making it suitable for medical implants and devices. Stainless steel is also used in medical applications but may require specific grades to ensure biocompatibility and reduce allergic reactions.
Aesthetic and Finishing
Both materials offer excellent aesthetic appeal, but titanium steel is often preferred for its unique, sleek look and superior resistance to discoloration. Stainless steel is widely used for its classic appearance and versatility in finishes.
Application Versatility
Titanium steel’s unique properties make it suitable for high-performance and specialized applications, whereas stainless steel’s versatility and affordability allow for broader usage across various industries. SourcifyChina leverages these strengths to offer tailored solutions that meet diverse client needs. By understanding the distinct capabilities of titanium and stainless steel, SourcifyChina ensures optimal material selection for specific applications, enhancing product performance and longevity.
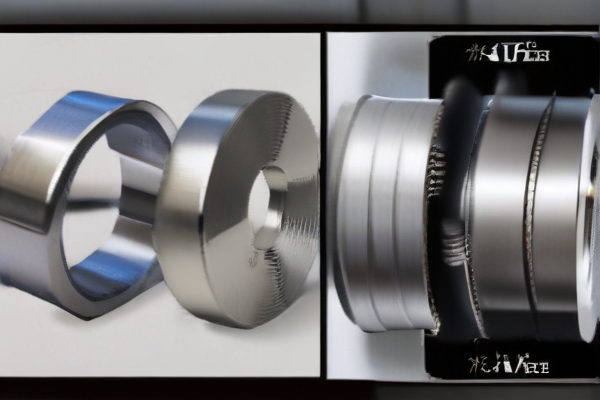

Titanium steel and stainless steel are both popular materials in various industries due to their unique properties and benefits. Understanding their advantages helps in choosing the right material for specific applications.
Titanium Steel:
– Lightweight: Significantly lighter than stainless steel, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive industries.
– Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Higher than stainless steel, offering superior performance in weight-sensitive applications.
– Corrosion Resistance: Exceptional resistance to corrosion, especially in saltwater environments.
– Biocompatibility: Non-toxic and suitable for medical implants and devices.
– Thermal Expansion: Low thermal expansion, beneficial in high-temperature applications.
Stainless Steel:
– Durability: Extremely durable and able to withstand harsh environments.
– Cost-Effective: Generally more affordable than titanium steel.
– Wide Availability: Readily available in various grades and forms.
– Ease of Fabrication: Easier to machine and weld compared to titanium steel.
– Aesthetic Appeal: Offers a polished and sleek appearance, popular in household and commercial applications.
Choosing between titanium steel and stainless steel depends on specific requirements such as weight, strength, corrosion resistance, and cost. Each material offers unique advantages tailored to different industries and uses.
Titanium Steel vs Stainless Steel
Titanium steel and stainless steel are two distinct materials known for their strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility. Each has unique properties and applications, making them suitable for different uses.
Titanium Steel:
– Lightweight: Approximately 45% lighter than stainless steel.
– High strength-to-weight ratio: Stronger relative to its weight.
– Corrosion resistance: Exceptional, even in harsh environments.
– Biocompatibility: Suitable for medical implants.
– High melting point: Suitable for high-temperature applications.
– Expensive: Generally more costly due to extraction and processing.
Stainless Steel:
– Durability: Highly durable and tough.
– Corrosion resistance: Good, but varies by alloy type.
– Versatility: Widely used in various industries.
– Cost-effective: Generally more affordable than titanium steel.
– Ease of fabrication: Easier to weld, cut, and machine.
– Aesthetic appeal: Often used for its shiny, polished look.

SourcifyChina offers a range of custom products and projects using titanium steel and stainless steel. Titanium steel is known for its superior strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Stainless steel, on the other hand, is prized for its corrosion resistance and versatility. It is commonly used in various industries, from kitchenware to construction. Both materials provide unique advantages, depending on the project’s requirements.
For custom projects, SourcifyChina provides tailored solutions, ensuring that each product meets specific client needs. Their expertise in material properties ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Whether you need durable titanium steel for aerospace components or stylish stainless steel for architectural designs, SourcifyChina delivers high-quality results. Each project is executed with precision, reflecting the company’s commitment to excellence and innovation in custom manufacturing.
SourcifyChina specializes in sourcing and manufacturing high-quality titanium steel and stainless steel products. The company distinguishes itself through its commitment to delivering superior materials tailored to various industrial applications, ranging from aerospace to consumer goods. Titanium steel, known for its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, is a flagship offering of SourcifyChina, catering to industries requiring robust yet lightweight components. On the other hand, their stainless steel products are celebrated for their durability, resistance to rust, and aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for both structural and decorative uses. By leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques and stringent quality control processes, SourcifyChina ensures that each product meets international standards and client specifications. Their dedication to innovation and customer satisfaction positions them as a trusted partner for businesses seeking reliable and versatile metal solutions.

Titanium steel and stainless steel are both crucial materials in aerospace, defense, and marine applications due to their distinct properties. Titanium steel is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures, making it ideal for aerospace components such as airframes, landing gear, and engine parts. In defense, its strength and lightness are advantageous for armor plating and structural components in military vehicles and aircraft. The marine industry benefits from titanium steel’s resistance to seawater corrosion, using it in critical parts like propeller shafts, hulls, and fasteners that demand longevity and durability in harsh ocean environments.
Stainless steel, while heavier, offers significant advantages in terms of cost, availability, and ease of fabrication. In aerospace applications, it is often used where high strength and moderate corrosion resistance are necessary but weight is less of a critical factor, such as in fasteners, landing gear components, and various structural elements. In the defense sector, stainless steel is valued for its durability and resistance to both corrosion and impact, making it suitable for use in weapons, armor, and support structures. Marine applications of stainless steel include hulls, decks, and fittings, where its corrosion resistance, particularly in high-saline conditions, ensures longevity and reliability. While both materials are indispensable, the choice between titanium steel and stainless steel depends on specific application requirements, balancing factors such as weight, strength, cost, and environmental resistance.

Titanium steel and stainless steel both play pivotal roles in the automotive industry, each offering unique advantages that cater to different needs. Titanium steel is highly valued for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, which makes it ideal for applications where reducing weight without sacrificing durability is crucial. This characteristic makes titanium steel a popular choice for high-performance vehicles and motorsports, where components such as engine parts, exhaust systems, and suspension springs benefit from its lightweight and robust nature. Additionally, titanium’s resistance to corrosion and fatigue ensures longevity and reliability under the demanding conditions of automotive use. However, the high cost of titanium limits its widespread adoption to premium and specialized applications.
In contrast, stainless steel is widely used in the automotive sector due to its affordability, excellent corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication. Stainless steel components are common in exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and structural elements, providing a balance between cost-effectiveness and performance. Its durability and resistance to rust make it suitable for everyday vehicles exposed to various environmental conditions. Moreover, stainless steel’s ability to be readily welded and formed allows for versatile design options in car manufacturing. While stainless steel may not match the strength-to-weight ratio of titanium steel, its lower cost and ample performance characteristics make it a mainstay in mass-produced vehicles, highlighting its integral role in the industry.
In the electronics sector, titanium steel and stainless steel are utilized based on their distinct properties to meet specific needs. Titanium steel’s biocompatibility and non-magnetic nature make it ideal for medical devices and certain sensitive electronic applications. It is often used in the casings of high-end smartphones, laptops, and wearables, where its light weight, strength, and corrosion resistance enhance both durability and user experience. The aerospace industry also leverages titanium steel for critical components in electronics due to its high performance under extreme conditions.
Conversely, stainless steel’s versatility and cost-efficiency make it a common material in consumer electronics. It is frequently employed in the production of household appliances, computer components, and various electronic enclosures. The aesthetic appeal of stainless steel, combined with its resistance to staining and corrosion, makes it a preferred choice for products like kitchen appliances and personal gadgets. Its ability to be easily machined and finished into various forms also contributes to its widespread use in the electronics industry. Although it may not provide the same level of strength or lightness as titanium steel, stainless steel offers a practical balance of durability, aesthetics, and cost, making it a staple material in everyday electronic applications.

In the construction industry, both titanium steel and stainless steel are prized for their durability and resistance to corrosion. Titanium steel, known for its lightweight yet high-strength properties, is often utilized in projects requiring structural integrity without adding excessive weight. This makes it ideal for applications such as bridges, high-rise buildings, and other large structures where minimizing weight is crucial without compromising on strength. On the other hand, stainless steel, with its excellent resistance to rust and staining, is widely used in constructing buildings and infrastructure exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Stainless steel’s ability to withstand extreme weather and corrosive environments makes it a preferred choice for exterior cladding, roofing, and structural components in marine and coastal projects.
In the energy sector, titanium steel and stainless steel also play significant roles, particularly in scenarios requiring materials that can withstand extreme conditions. Titanium steel’s high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent resistance to corrosion and heat make it suitable for components in aerospace and power generation applications, such as turbine blades and heat exchangers. Its durability ensures long-term performance even under high stress and temperatures. Conversely, stainless steel is extensively used in the energy industry for its robustness and resistance to high temperatures and pressure, making it a material of choice for pipelines, storage tanks, and nuclear reactors. The material’s ability to endure the corrosive environments found in oil and gas exploration and production ensures reliability and longevity, essential for maintaining operational efficiency and safety in the energy sector.

In the industrial equipment industry, both titanium steel and stainless steel are prominent materials, each offering distinct advantages suited to different applications. Titanium steel, renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and high melting point, is ideal for environments that demand durability under extreme conditions. Its application is prevalent in industries such as aerospace, marine, and chemical processing, where equipment must withstand harsh environments and high temperatures. Titanium steel’s lightweight nature also reduces the overall weight of machinery and components, enhancing efficiency and performance, especially in dynamic and mobile applications.
Conversely, stainless steel is favored for its affordability, ease of fabrication, and excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in milder environments. It is commonly used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and general manufacturing where hygiene and aesthetic appeal are critical. Stainless steel’s versatility and wide availability make it suitable for a variety of equipment, from storage tanks and pipelines to machinery parts and tools. While it doesn’t match the strength-to-weight ratio of titanium steel, stainless steel offers a cost-effective solution for applications where the extreme conditions faced by titanium steel are not a primary concern. Both materials thus serve the industrial equipment industry by fulfilling specific requirements based on the operational environment and economic considerations.

Titanium and stainless steel are both extensively used in medical devices due to their exceptional properties, but they serve different applications based on their unique characteristics. Titanium is favored for its remarkable biocompatibility, which significantly reduces the risk of adverse body reactions, making it ideal for implants such as joint replacements, dental implants, and bone fixation devices. Its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion also contribute to its widespread use in these applications, ensuring durability and long-term functionality within the body. Additionally, titanium’s non-ferromagnetic nature is beneficial for patients undergoing MRI scans, as it does not interfere with imaging processes.
Stainless steel, on the other hand, is commonly used in surgical instruments and short-term implants due to its robustness and cost-effectiveness. Its high tensile strength and ability to withstand repeated sterilization processes make it suitable for instruments like scalpels, forceps, and retractors. In orthopedic surgery, stainless steel is often used for temporary fixation devices such as screws, plates, and nails, which can later be removed after healing. While stainless steel is less biocompatible than titanium, advancements in alloying techniques have improved its performance and reduced the risk of corrosion within the body. Thus, the choice between titanium and stainless steel in medical devices largely depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing factors such as biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and cost.

In the realm of machining and manufacturing, titanium steel and stainless steel each present distinct advantages and challenges. Titanium steel, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, is favored in aerospace, medical, and high-performance automotive industries. Its lightweight nature significantly reduces fuel consumption and enhances performance in aircraft and spacecraft. However, machining titanium steel can be challenging due to its hardness and low thermal conductivity, which can lead to tool wear and heat buildup. Specialized cutting tools and techniques, such as low cutting speeds and ample coolant usage, are often required to efficiently machine titanium steel, making the process more costly and time-consuming.
On the other hand, stainless steel, prized for its durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, is extensively used in construction, medical devices, kitchenware, and industrial applications. Machining stainless steel is generally more straightforward compared to titanium steel, though it still demands high-quality tools and careful handling to prevent work hardening and surface degradation. Its versatility and cost-effectiveness make stainless steel a preferred choice for mass production and consumer goods. Despite being heavier than titanium, stainless steel offers excellent formability and welding capabilities, which are advantageous in manufacturing complex components. Ultimately, the choice between titanium steel and stainless steel depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors like weight, strength, cost, and machinability.



Q: What are the main differences between titanium steel and stainless steel?
A: Titanium steel is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, while stainless steel is appreciated for its durability, resistance to oxidation, and versatility in various applications.
Q: Which material is better for manufacturing high-quality products?
A: The choice depends on the application. Titanium steel is preferable for lightweight and high-strength requirements, such as aerospace and medical implants. Stainless steel is ideal for general industrial use, construction, and consumer products due to its robustness and cost-effectiveness.
Q: How does the cost of titanium steel compare to stainless steel?
A: Titanium steel is generally more expensive than stainless steel due to the complex extraction and refining process of titanium. However, the long-term benefits such as reduced maintenance and longevity can offset the initial cost.
Q: What are the advantages of using titanium steel in manufacturing?
A: Titanium steel offers superior strength, lightness, and exceptional resistance to corrosion and extreme temperatures, making it suitable for critical applications in aerospace, medical, and high-performance industries.
Q: Are there any disadvantages to using stainless steel?
A: While stainless steel is highly versatile and durable, it is heavier than titanium steel and may not offer the same level of corrosion resistance in extremely harsh environments.
Q: How does SourcifyChina ensure the quality of titanium steel and stainless steel products?
A: SourcifyChina adheres to strict quality control measures, including sourcing high-grade raw materials, utilizing advanced manufacturing technologies, and conducting rigorous testing to ensure product consistency and performance.
Q: Can SourcifyChina provide custom manufacturing solutions for both materials?
A: Yes, SourcifyChina offers customized manufacturing solutions tailored to specific requirements for both titanium steel and stainless steel, ensuring optimal performance and quality for various applications.
When comparing titanium steel and stainless steel for manufacturing, several key differences and considerations emerge, particularly relevant for sourcing from SourcifyChina factory.
Composition
and Properties:
– Titanium Steel: Primarily composed of titanium, it is lightweight yet extremely strong, offering an excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It boasts superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine and high-temperature environments. Titanium is also biocompatible, making it ideal for medical implants.
– Stainless Steel: An alloy primarily composed of iron, chromium, and nickel, stainless steel is known for its high resistance to rust and corrosion. It is highly durable and maintains structural integrity under various environmental conditions.
Manufacturing
Process:
– Titanium: The manufacturing process is complex and energy-intensive. Titanium’s high melting point and low thermal conductivity require specialized tools and techniques for machining and forming. This contributes to its higher cost and more challenging manufacturability compared to stainless steel.
– Stainless Steel: The process involves melting iron ore and other metals in a furnace, adding alloys like chromium and nickel, and then cooling and hardening in molds. The material is easier to machine, allowing for more straightforward manufacturing processes and lower costs.
Applications:
– Titanium: Its exceptional properties make it suitable for aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance sports equipment. It excels in applications requiring lightweight yet strong materials.
– Stainless Steel: Due to its corrosion resistance and ease of maintenance, stainless steel is widely used in kitchen appliances, medical instruments, automotive components, and construction. It is versatile and cost-effective for a wide range of applications.
Cost:
– Titanium: Generally more expensive due to its complex extraction and production process. The higher cost is justified in applications where performance benefits outweigh the expense.
– Stainless Steel: More affordable and readily available in various grades, making it suitable for projects with budget constraints.
Environmental
Impact:
– Titanium: The production process has a larger environmental footprint due to energy requirements.
– Stainless Steel: Highly recyclable, stainless steel is an environmentally friendly option, contributing to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Choosing between titanium and stainless steel depends on specific project requirements such as weight, strength, corrosion resistance, and budget. For applications demanding high performance in extreme environments, titanium is often preferred. However, for general use with cost considerations, stainless steel is typically the better choice.
Sources:
– YijinSolution
– UnionFab
– Qinghang Metal
– Rapid-Protos
FAQ:
Titanium Steel vs Stainless Steel from SourcifyChina Factory
1. What is the main difference between titanium steel and stainless steel?
Titanium steel is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. Stainless steel, while also resistant to corrosion, is heavier and is commonly used in construction, kitchenware, and automotive industries.
2. Which material is more durable?
Both materials are highly durable. However, titanium steel offers superior strength and resistance to extreme temperatures and chemicals, making it more durable in harsh environments compared to stainless steel.
3. How do the costs compare between titanium steel and stainless steel?
Titanium steel is generally more expensive than stainless steel due to its superior properties and more complex production process. Stainless steel is more affordable and widely used in various industries.
4. What applications are best suited for titanium steel?
Titanium steel is best suited for high-performance applications such as aerospace, medical implants, and high-end sporting goods due to its strength, light weight, and biocompatibility.
5. What are common uses for stainless steel?
Stainless steel is commonly used in construction, kitchen appliances, automotive parts, and medical instruments. Its versatility, affordability, and resistance to rust make it a popular choice across many industries.
6. How does SourcifyChina ensure the quality of these materials?
SourcifyChina employs stringent quality control measures, including material certification, rigorous testing, and adherence to international standards, ensuring that both titanium steel and stainless steel meet the highest quality requirements.
7. Can SourcifyChina provide customized products made from these materials?
Yes, SourcifyChina offers customization services to meet specific requirements. They can produce tailored components and products based on client specifications, ensuring optimal performance and satisfaction.
8. What is the lead time for orders of titanium steel and stainless steel from SourcifyChina?
Lead times vary depending on the order size and customization requirements. Generally, standard orders can be fulfilled within 2-4 weeks, while customized orders may take longer.
9. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for these materials?
Yes, MOQs may apply depending on the specific product and material requirements. It’s best to contact SourcifyChina directly for detailed information on MOQs.
10. How can I get a quote for titanium steel or stainless steel from SourcifyChina?
To get a quote, you can contact SourcifyChina through their website, providing details about your requirements, including material type, quantity, and any customization needs. They will respond promptly with pricing and delivery information.
When sourcing titanium steel versus stainless steel from a factory like SourcifyChina, consider the following tips to ensure quality and cost-efficiency:
1. Material Properties:
– Titanium Steel: Known for its high strength, lightweight, and excellent corrosion resistance. It is ideal for applications requiring durability and minimal weight.
– Stainless Steel: Offers good strength, corrosion resistance, and is generally more affordable. Suitable for a wide range of applications, including kitchenware, medical instruments, and construction.
2. Cost Comparison:
– Titanium steel is generally more expensive due to its superior properties and manufacturing complexities.
– Stainless steel is more cost-effective and widely available.
3. Application Needs:
– Assess the specific requirements of your project. For high-stress environments or where weight is a concern, titanium steel may be preferable.
– For more general purposes where budget constraints are significant, stainless steel is a practical choice.
4. Supplier Verification:
– Ensure SourcifyChina factory meets international quality standards (ISO, ASTM).
– Check past client reviews and request samples to verify material quality.
5. MOQ and Lead Times:
– Confirm the minimum order quantity (MOQ) and lead times for both materials. Titanium steel may have higher MOQs and longer lead times due to its production process.
6. Customization and Specifications:
– Clarify the specific grades of titanium or stainless steel required for your application.
– Discuss any custom alloy compositions or specific treatments needed.
7. Logistics and Compliance:
– Consider shipping costs and timeframes from China to your location.
– Ensure the materials comply with local regulatory standards.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision on whether titanium steel or stainless steel is the best choice for your needs when sourcing from SourcifyChina.

If you require packaging machine for your product, SourcifyChina should be your primary option. Please send us your detailed specifications and obtain an immediate quotation.
Copyright © 2024 SourcifyChina All Rights Reserved.