Choosing SourcifyChina Factory for purchasing titanium versus steel from China is a smart decision. The factory ensures top-notch quality for both materials, meeting stringent industry standards. Titanium is lighter and stronger than steel, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. Meanwhile, steel’s robustness suits construction and automotive uses better.
SourcifyChina provides competitive pricing due to their efficient manufacturing processes and long-term supplier relationships. Whether you need titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio or steel’s durability, you can expect cost-effective solutions tailored to your needs.
Customer service at SourcifyChina is exceptional. Their experienced team offers personalized assistance, ensuring your specifications are met. From initial consultations to after-sales support, you can rely on their professional guidance throughout the purchasing process.
SourcifyChina’s state-of-the-art facilities guarantee precision and consistency in every product. With advanced machinery and a skilled workforce, the factory produces titanium and steel components that exceed expectations and adhere to international quality standards.
Timely delivery is another reason to choose SourcifyChina Factory. Their efficient logistics network ensures your order arrives on schedule, minimizing downtime and keeping your projects on track. Reliable lead times and transparent communication give you peace of mind.
SourcifyChina emphasizes sustainability. The factory adopts eco-friendly practices in its manufacturing processes, reducing environmental impact. By choosing SourcifyChina, you contribute to a more sustainable future without compromising on quality or performance.
In conclusion, SourcifyChina Factory stands out for its superior quality materials, competitive pricing, excellent customer service, and commitment to sustainability. Whether you need titanium’s unique properties or robust steel solutions, SourcifyChina offers reliable and efficient options. Ensure your projects benefit from the best materials and services by partnering with SourcifyChina for your procurement needs.
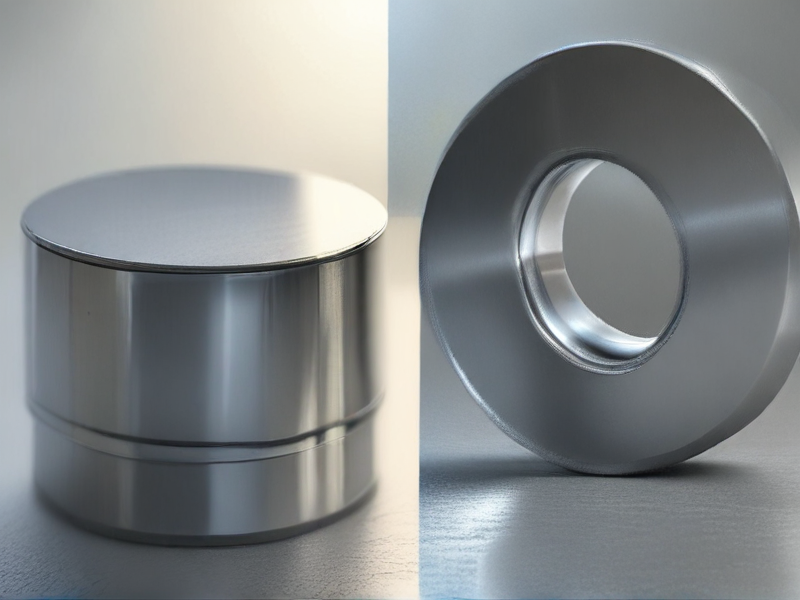
Titanium and steel are prominent materials in various industries. Titanium is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and biocompatible, making it ideal for aerospace and medical implants. Steel is durable, cost-effective, and versatile, suitable for construction and manufacturing.
Titanium:
– Weight: Lighter than steel
– Corrosion Resistance: Highly resistant
– Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Superior
– Biocompatibility: Excellent, used in medical implants
– Cost: Expensive
– Applications: Aerospace, medical, high-performance sports equipment
Types of Titanium:
– Grade 1-4: Pure titanium, varying in strength and ductility
– Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V): Most common alloy, excellent strength and corrosion resistance
– Grade 9: Moderate strength, used in chemical processing
– Grade 23 (Ti 6Al 4V ELI): Superior biocompatibility, used in medical implants
Steel:
– Weight: Heavier than titanium
– Durability: Highly durable and strong
– Corrosion Resistance: Varies; can be improved with treatments
– Cost: Generally lower than titanium
– Applications: Construction, automotive, infrastructure, appliances
Types of Steel:
– Carbon Steel: Varies in strength, hardness, and ductility
– Stainless Steel: High corrosion resistance, contains chromium
– Alloy Steel: Mixed with elements like nickel, chromium for enhanced properties
– Tool Steel: Hard and heat-resistant, used for cutting tools
Comparison Factors:
– Weight Considerations: Titanium for weight-sensitive applications
– Corrosion Resistance Needs: Titanium for harsh environments
– Cost Constraints: Steel for budget-friendly projects
– Strength and Durability Requirements: Select based on specific project needs – steel often preferred
– Biocompatibility: Titanium for medical uses
Conclusion:
Choosing between titanium and steel depends on the specific requirements of the project, including weight, corrosion resistance, cost, and application area. Each material offers unique advantages tailored to different industrial needs.
Titanium vs. Steel Applications
Titanium and steel are crucial in various industries due to their unique properties. Here’s a comparison of their applications:
– Aerospace Industry:
– Titanium’s strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for aircraft parts.
– Steel is used in components that demand high strength and durability.
– Medical Devices:
– Titanium is non-reactive and biocompatible, perfect for implants.
– Steel is often used for surgical instruments.
– Automotive Industry:
– Titanium is utilized in high-performance vehicle parts due to its lightweight nature.
– Steel is common in the construction of car bodies and frames because of its durability.
– Marine Applications:
– Titanium resists corrosion from seawater, suitable for submarine parts.
– Steel, when specially treated, is used in shipbuilding.
– Sports Equipment:
– Titanium is favored in premium sports gear for its strength and low weight.
– Steel is used in more durable, less expensive equipment.
– Architecture:
– Titanium’s aesthetic appeal and resistance to corrosion are used for unique building facades.
– Steel remains a staple in structural frameworks due to its robustness and flexibility.
– Industrial Applications:
– Titanium is indispensable in chemical plants for withstanding corrosive environments.
– Steel, known for its strength and cost-effectiveness, is used in a wide range of machinery and tools.
In summary, the choice between titanium and steel often comes down to specific needs in weight, strength, corrosion resistance, and cost.
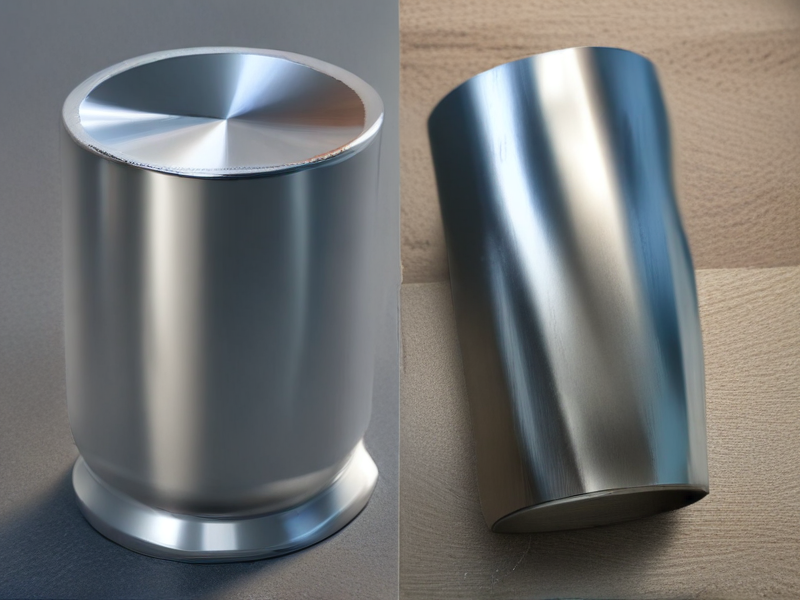


SourcifyChina offers both titanium and steel materials, each with unique properties. Titanium is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. It’s also highly resistant to corrosion and biocompatible, though it tends to be more expensive.
Steel, on the other hand, is widely known for its durability and cost-effectiveness. It’s easily machinable and weldable, making it a popular choice in construction, automotive, and general manufacturing. However, it is susceptible to rust if not properly treated or alloyed with other elements to improve its resistance.
When considering which material to choose, the application and specific needs are crucial. If weight and corrosion resistance are key factors, titanium is the better choice despite its higher cost. For applications requiring significant strength and cost-efficiency, steel is often the more practical option.
SourcifyChina specializes in sourcing high-quality materials to meet your project requirements. Whether you need titanium for its exceptional properties or steel for its practicality, they provide tailored solutions to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Ultimately, the decision between titanium and steel depends on balancing these factors to best suit your specific needs.
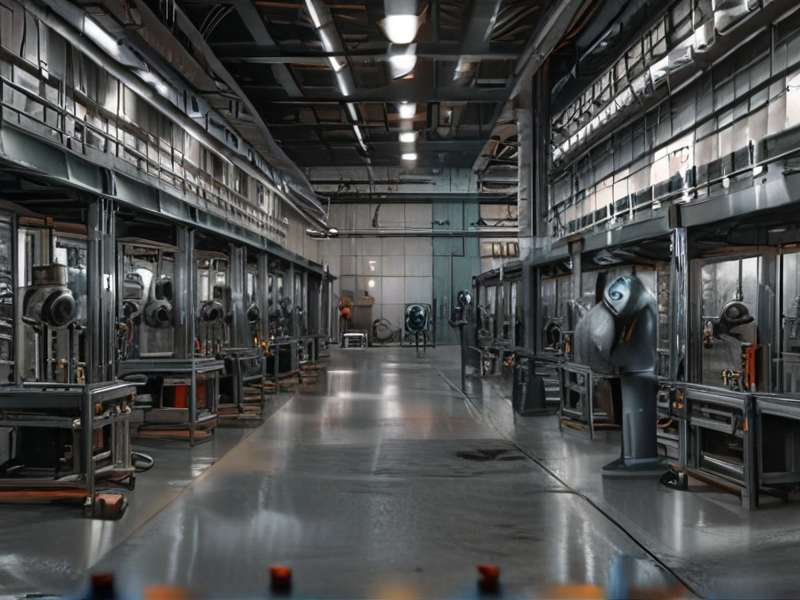
SourcifyChina specializes in rigorous quality control for titanium and steel products. Their manufacturing process starts by sourcing only top-grade titanium and steel materials. Quality checks begin right from the raw material procurement stage, ensuring the foundational integrity of each product.
Each stage of manufacturing—cutting, shaping, and final assembly—is closely monitored. Precision and attention to detail are paramount, with regular inspections conducted. State-of-the-art equipment and skilled technicians work in tandem to maintain consistent product quality across all batches.
Advanced machine tools are calibrated for specific tolerances. This ensures that both titanium and steel maintain their structural integrity and mechanical properties. SourcifyChina emphasizes ensuring that each product meets stringent international quality standards.
Final products undergo rigorous testing for strength, durability, and purity. Titanium is tested for lightweight strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Steel products are scrutinized for tensile strength, malleability, and resistance to wear and tear.
SourcifyChina employs additional advanced quality control techniques, including ultrasonic testing and x-ray analysis. This ensures that even the internal structure of the materials meets required specifications. Any defects, no matter how minute, are identified and addressed.
The company maintains thorough documentation during the entire process, making product traceability effortless. By doing so, they ensure every product can be tracked back to its origin, minimizing any risk of quality issues. SourcifyChina’s commitment to stringent quality control measures guarantees that their titanium and steel products consistently meet high standards of performance and reliability.
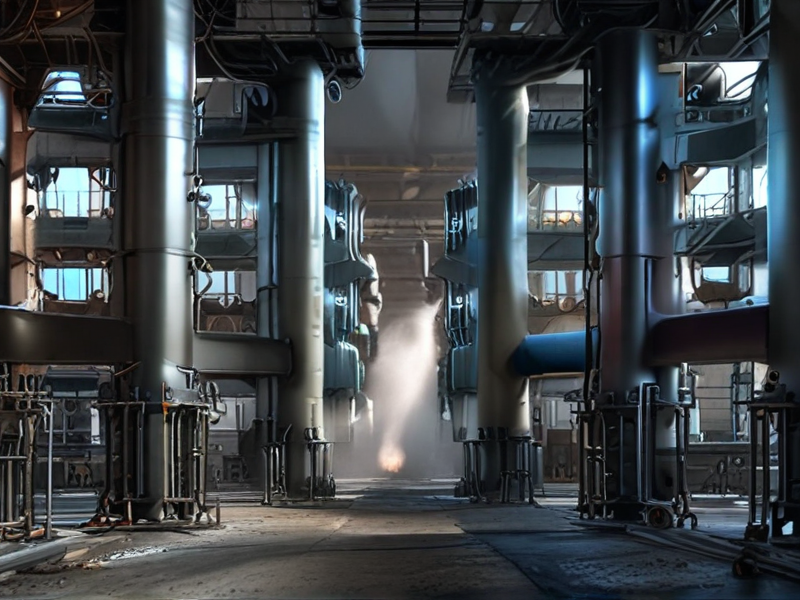



SourcifyChina offers a comprehensive range of titanium and steel products, catering to diverse industrial needs. Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace and biomedical applications. Steel, on the other hand, boasts superior tensile strength and versatility, suitable for construction, automotive, and various engineering projects.
When considering weight, titanium outshines steel, being significantly lighter while maintaining similar strength levels. This makes it a preferred material for industries where weight reduction is crucial, such as the aerospace sector. Additionally, titanium’s biocompatibility makes it a favorite in medical implants and devices, offering enhanced compatibility with human tissues.
Steel’s notable advantage lies in its cost-effectiveness and widespread availability. It is easier to fabricate and weld, making it a go-to choice for large-scale infrastructure projects. Steel’s magnetic properties and durability further enhance its suitability for a wide range of standard and specialized applications.
Comparatively, titanium offers superior corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments, while steel needs protective coatings and treatments to prevent rust. This makes titanium an excellent choice for marine and chemical processing industries. However, the initial cost of titanium is generally higher than that of steel, influencing budget considerations for manufacturers.
In conclusion, SourcifyChina provides extensive options for both titanium and steel, ensuring that clients can select the material best suited to their specific requirements. Whether prioritizing weight and corrosion resistance with titanium or opting for the affordability and tensile strength of steel, SourcifyChina’s diverse offerings ensure tailored solutions for every industrial application.

When comparing titanium and steel, titanium offers several advantages that make it a superior choice for many applications, despite its higher cost.
– Lightweight: Titanium is about 45% lighter than steel, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment.
– Strength-to-Weight Ratio: It boasts an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, contributing to both strength and reduced bulk in structures.
– Corrosion Resistance: Titanium resists corrosion from seawater, chlorine, and other harsh environments better than steel.
– Biocompatibility: Widely used in medical implants, titanium is highly biocompatible and non-toxic to human tissue.
– Durability: Its exceptional fatigue and fracture resistance make it ideal for high-stress applications.
– Thermal Expansion: Titanium has a lower thermal expansion coefficient than steel, providing stability across temperature changes.
– Non-Magnetic: Ideal for use in environments where magnetism can be problematic, such as medical imaging and certain electronics.
– Longevity: Due to its resilience against wear and tear, titanium components often have a longer lifespan compared to steel.
In summary, while steel remains an excellent and cost-effective option for many uses, titanium’s unique properties make it preferable for specialized applications requiring high strength, low weight, and great durability.
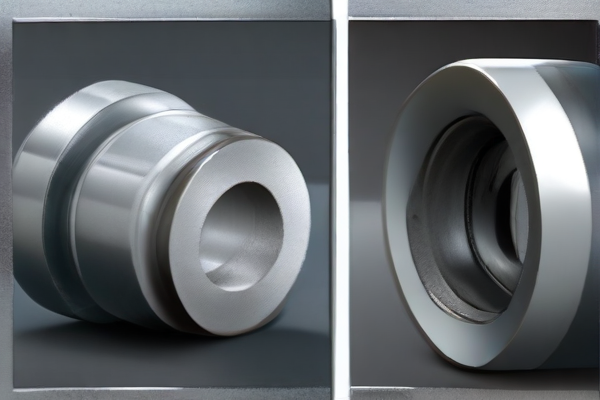
Titanium and steel are both strong, versatile metals, but they have distinct properties and applications. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right material.
– Weight: Titanium is about 45% lighter than steel, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios.
– Strength: While both metals are strong, titanium has a higher strength-to-weight ratio.
– Corrosion Resistance: Titanium offers superior resistance to corrosion and is often used in marine and chemical environments.
– Cost: Steel is generally more affordable than titanium, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications.
– Machinability: Steel is easier to machine and weld compared to titanium.
– Thermal Conductivity: Steel has better thermal conductivity, making it more suitable for heat-sensitive applications.
– Biocompatibility: Titanium is biocompatible and widely used in medical implants.
– Elastic Modulus: Titanium has a lower elastic modulus, meaning it is less rigid than steel.
– Fatigue Resistance: Titanium provides excellent fatigue resistance, which is beneficial in high-stress applications.
– Magnetism: Unlike most steels, titanium is non-magnetic.
Choosing between titanium and steel depends on specific application requirements, balancing factors like weight, cost, and environment.
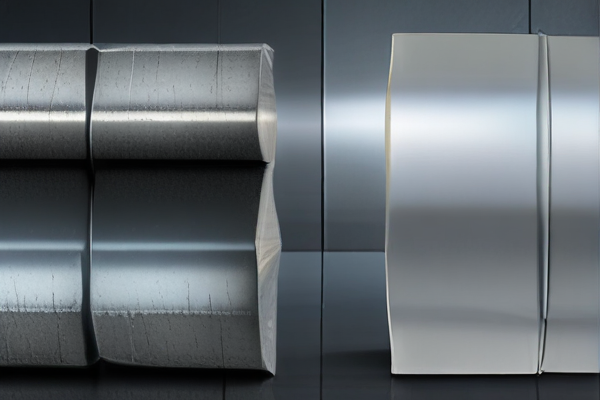
SourcifyChina offers high-quality titanium and steel custom products tailored for various industries. Their experienced team utilizes advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure precision and durability in their offerings.
Titanium products from SourcifyChina are known for their strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for aerospace, medical, and automotive applications. These products offer excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity in harsh environments.
Steel custom products provide robust, affordable solutions for construction, machinery, and infrastructure projects. Their high tensile strength and malleability make them versatile for a range of applications, offering both durability and cost-effectiveness.
SourcifyChina supports bespoke projects from conception to completion, ensuring customer specifications are met with precision. Their commitment to quality and innovation drives their ability to deliver tailored solutions that match unique project requirements.
For companies looking to leverage superior materials in their products and projects, SourcifyChina’s titanium and steel options present a compelling choice. Their extensive industry experience and focus on client satisfaction guarantee successful outcomes in any custom order.
SourcifyChina is a premier manufacturing and sourcing company that has carved a unique niche in the competitive market by offering tailored solutions in both titanium and steel products. Specializing in high-quality, cost-effective materials, SourcifyChina leverages advanced technology and a robust supply chain to deliver top-notch titanium and steel components, catering to diverse industrial needs such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and construction sectors. The company prides itself on its stringent quality control measures, ensuring that each product meets international standards and exceeds client expectations. Their proficient team of engineers and industry experts provides end-to-end support from product design and material selection to production and delivery, making SourcifyChina a one-stop solution for businesses seeking reliability and efficiency. While titanium offers unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, steel remains favored for its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and wide availability. By providing clients with a clear comparison of titanium and steel’s benefits and applications, SourcifyChina empowers them to make informed decisions that best suit their operational requirements and budget considerations.

Titanium and steel are both pivotal materials in aerospace, defense, and marine applications due to their distinct properties. In the aerospace industry, titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it a preferred choice for airframe and engine components. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and its resistance to corrosion significantly enhance the performance and longevity of aircraft. Conversely, steel, while heavier, exhibits exceptional durability and is often utilized in landing gear and other structural parts where weight is less critical but strength is paramount. Steel’s affordability and ease of fabrication also complement the engineering processes in aerospace manufacturing.
In the defense sector, titanium’s lightweight yet robust characteristics are valuable for advanced military hardware such as armor plating, missile systems, and aircraft. Its corrosion resistance ensures reliability in harsh environments, critical for maintaining operational readiness. Steel, renowned for its toughness and cost-effectiveness, is widely applied in the construction of tanks, artillery, and naval ships. In marine applications, titanium’s superior resistance to seawater corrosion and biofouling makes it the material of choice for submarine hulls, deep-sea exploration vehicles, and high-performance maritime components. Steel, however, remains indispensable in shipbuilding and offshore structures due to its strength and resilience under dynamic sea conditions. Both materials thus play specialized roles tailored to the rigorous demands of aerospace, defense, and marine industries.

Titanium and steel are two materials that play crucial roles in automotive and electronics applications, offering distinct advantages and challenges. In the automotive industry, titanium is celebrated for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. These properties make it ideal for high-performance parts such as engine components, exhaust systems, and suspension springs, where reducing weight is paramount for improving fuel efficiency and vehicle dynamics. However, the high cost and difficulty in machining titanium limit its widespread use. In contrast, steel remains the dominant material in automotive manufacturing due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of fabrication, and impressive strength. Advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) offer enhanced performance for safety-critical components like chassis and body structures, helping manufacturers meet stringent safety and emissions regulations while keeping costs manageable.
In the realm of electronics, the choice between titanium and steel is often dictated by the need for thermal management, durability, and weight considerations. Titanium’s excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to electromagnetic interference make it advantageous for housing sensitive electronic components, especially in aerospace and high-performance computing applications. Additionally, its biocompatibility makes titanium suitable for medical devices and wearable technology. On the other hand, stainless steel is frequently used for electronic device casings due to its robustness, cost-effectiveness, and aesthetic appeal. It provides ample protection against physical damage and environmental factors, making it ideal for consumer electronics like smartphones, laptops, and household appliances. While steel is heavier than titanium, its prevalence is driven by the balance of performance, manufacturing ease, and affordability. Both materials, therefore, find tailored applications that maximize their unique properties within the electronics sector.

In the construction industry, titanium and steel are two prominent materials, each offering distinct advantages. Titanium is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, which permits the creation of sturdy but lighter structures. This property proves especially beneficial in seismic-prone areas, where reduced structural weight can result in less stress during an earthquake. Moreover, titanium’s superior corrosion resistance ensures durability in harsh environments, such as coastal areas or industrial settings with exposure to chemicals. However, the high cost of titanium often limits its application to specialized projects where its unique properties provide significant benefits over conventional materials. In contrast, steel dominates the construction sector due to its affordability, ease of fabrication, and vast availability. While not as corrosion-resistant as titanium, modern steel variants and protective coatings significantly enhance its longevity. Steel’s versatility and structural integrity make it a preferred choice for a plethora of construction endeavors, from skyscrapers to bridges.
In energy applications, the choice between titanium and steel hinges on factors like temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and material strength. Titanium excels in environments exposed to extreme temperatures and corrosive substances, making it a prime candidate for components in power plants, particularly those employing geothermal or nuclear energy. Its resistance to stress corrosion cracking and ability to withstand high pressures augment its utility in such demanding contexts. However, the high cost of titanium necessitates careful consideration of its usage. Conversely, steel, with its vast array of grades and treatments, remains a cornerstone of the energy sector. High-strength, low-alloy steels are integral in oil and gas pipelines, while stainless steel’s corrosion resistance finds widespread usage in various power generation systems. The economic viability and established supply chain of steel solidify its role in energy infrastructure, even though it may require more maintenance than titanium to combat corrosion and wear in aggressive environments.

In the industrial equipment sector, the choice between titanium and steel is critical due to the demanding applications and operating conditions these materials must endure. Titanium, renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, is particularly valuable in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and resist corrosive elements makes it indispensable in environments where longevity and reliability are paramount. For instance, in the aerospace industry, titanium components reduce aircraft weight, thereby improving fuel efficiency and performance. Similarly, in chemical processing, titanium’s resistance to corrosive substances ensures the durability of equipment, minimizing maintenance costs and downtime.
On the other hand, steel is a versatile and cost-effective material widely used across various industrial applications due to its high tensile strength and ease of manufacturing. While it lacks the lightweight properties of titanium, its affordability and robustness make it suitable for heavy-duty applications, such as construction machinery, shipbuilding, and structural components. Different grades of steel, including stainless and high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels, offer tailored solutions for specific requirements, balancing performance and cost. While steel may be prone to corrosion when exposed to harsh conditions, modern protective coatings and treatments can extend its lifespan significantly. In summary, the choice between titanium and steel hinges on specific application needs, balancing factors like weight, strength, resilience, and cost.

Titanium and steel are two pivotal materials utilized in the manufacture of medical devices, each offering distinct advantages and considerations. Titanium is renowned for its superior biocompatibility, making it a preferred choice for implants and devices that remain in contact with bodily tissues or fluids. Its ability to resist corrosion from bodily fluids ensures a longer lifespan and reduces the risk of device-related complications, such as infections. Additionally, titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio means that devices can be made lighter without sacrificing durability, which is particularly beneficial for implants like joint replacements and bone plates. The reduced weight translates into more comfort for patients and easier handling for medical personnel. Titanium’s non-magnetic property is another advantage—it ensures compatibility with imaging modalities such as MRI, widening its application in surgeries where precision is paramount.
On the other hand, steel, particularly stainless steel, remains a staple material for a variety of medical devices. Its affordability compared to titanium makes it a cost-effective choice for temporary devices or instruments that do not come into prolonged contact with the body. Stainless steel is also incredibly versatile and can be used to fabricate a wide range of devices, from surgical instruments to temporary orthopedic implants. Its mechanical strength and hardness stand up to repeated sterilization cycles, thereby extending the usability of these devices in a clinical setting. However, stainless steel is prone to corrosion over time when exposed to the harsh biological environment inside the human body, which limits its use for long-term implantation. Despite this, advances in coating technologies and alloy compositions seek to mitigate these issues, aiming to preserve the material’s benefits while enhancing its biocompatibility.

Machining and manufacturing applications involving titanium and steel present distinct challenges and advantages that dictate their usage in various industries. Titanium, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, is extensively used in aerospace, medical, and high-performance automotive applications. Machining titanium is, however, notably more difficult than machining steel due to its low thermal conductivity and high chemical reactivity, which can cause cutting tools to wear out quickly. This necessitates specialized tooling and techniques such as using sharp, high-quality carbide tools, slower cutting speeds, and ample coolant to dissipate heat, all of which increase the cost and complexity of the machining process.
On the other hand, steel, especially in its various alloy forms, remains a staple in the manufacturing industry due to its versatility, strength, and cost-effectiveness. Steel is easier and faster to machine compared to titanium, making it suitable for mass production in industries like automotive, construction, and heavy machinery. The wide range of steel grades available allows manufacturers to select materials tailored to specific mechanical properties and manufacturing needs, such as hardness, ductility, and tensile strength. While steel may lack the specialized advantages of titanium in certain high-end applications, its relative ease of machining and lower material costs make it an unparalleled choice for many traditional and contemporary manufacturing processes. Thus, the choice between titanium and steel in machining and manufacturing is often a balance of performance requirements, cost considerations, and processing capabilities.



Q: Which metal is more durable for industrial use: titanium or steel?
A: Titanium is generally more durable than steel due to its high resistance to corrosion and fatigue. It is ideal for extreme conditions and applications requiring long-term performance.
Q: How do the prices of titanium and steel compare?
A: Titanium is more expensive than steel, primarily due to its higher production costs. However, its longevity and reduced maintenance can offset the initial investment in many applications.
Q: Is titanium lighter than steel?
A: Yes, titanium is approximately 45% lighter than steel, making it preferable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as aerospace and automotive industries.
Q: Which material is better for high-temperature applications?
A: Titanium outperforms steel at high temperatures, maintaining its strength and structural integrity better than steel under such conditions.
Q: Can SourcifyChina factory work with both titanium and steel?
A: Yes, SourcifyChina factory is equipped to handle manufacturing processes involving both titanium and steel, ensuring high-quality output for various industrial requirements.
Q: How does machining titanium compare to machining steel?
A: Machining titanium is more challenging than machining steel due to its hardness and tendency to cause tool wear. Specialized equipment and techniques are often required.
Q: Which material is more corrosion-resistant?
A: Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to steel, especially in harsh environments such as marine or chemical processing applications.
Q: In terms of tensile strength, how do titanium and steel compare?
A: Steel generally has higher tensile strength than titanium, but titanium’s strength-to-weight ratio is much higher, making it a stronger choice for lightweight applications.
Q: Does SourcifyChina provide custom manufacturing solutions for both metals?
A: Yes, SourcifyChina provides tailored manufacturing solutions, offering expertise in custom designs and production processes for both titanium and steel.
Q: Which material should I choose for biomedical applications?
A: Titanium is the preferred choice for biomedical applications due to its biocompatibility and resistance to bodily fluids and tissues.
When considering titanium vs. steel manufacturing from SourcifyChina factory, it’s crucial to evaluate several key factors:
1. Strength and Weight:
– Titanium: Notably stronger and lighter than steel. Ideal for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as aerospace and medical devices.
– Steel: Heavier but offers good strength and durability at lower costs. It’s suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
2. Cost:
– Titanium: More expensive due to complex extraction and manufacturing processes. Costs involve raw material, machining, and potential waste management.
– Steel: Generally cheaper and more abundant, making it cost-effective for bulk manufacturing.
3. Corrosion Resistance:
– Titanium: Superior corrosion resistance, especially against seawater and chlorine environments. Preferred for marine and chemical applications.
– Steel: Corrosion resistance varies by type (e.g., stainless, galvanized). Requires coatings or treatments for enhanced resistance, adding to the cost.
4. Machinability:
– Titanium: More challenging to machine, requiring specialized tools and techniques. Increases production time and cost.
– Steel: Easier to machine and weld, with more established processes and less wear on tools.
5. Applications:
– Titanium: Best for high-performance industries (aerospace, medical, military) due to its high strength, lightweight, and corrosion resistance.
– Steel: Versatile, used in construction, automotive, machinery, and general manufacturing due to its strength, durability, and lower cost.
6. Lead Time and Supply Chain:
– Titanium: Longer lead times due to complex procurement and processing.
– Steel: Usually shorter lead times with more accessible supply chains and established manufacturing processes.
In summary, the choice between titanium and steel largely depends on your specific application requirements, budget, and production capabilities. SourcifyChina offers expertise in both materials, providing tailored solutions to meet varied industrial needs.
Certainly! Below are some frequently asked questions (FAQ) with answers regarding sourcing titanium versus steel from the SourcifyChina factory:
1. What are the primary differences between titanium and steel?
Titanium is lighter and more resistant to corrosion compared to steel. However, steel is generally stronger, more affordable, and easier to process in manufacturing.
2. Which material is more cost-effective?
Steel is typically more cost-effective than titanium. Titanium’s high manufacturing and material costs make it less economical for projects with tight budgets.
3. How does the weight of titanium compare to that of steel?
Titanium is about 45% lighter than steel, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial without sacrificing strength.
4. Does SourcifyChina factory offer both materials?
Yes, SourcifyChina factory provides both titanium and steel, tailored to meet various industrial needs.
5. Which material is better for high-stress applications?
Steel generally offers superior performance in high-stress applications due to its higher tensile strength. However, specialized titanium alloys can also perform well under strenuous conditions.
6. How does corrosion resistance compare between titanium and steel?
Titanium is more resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for use in corrosive environments, while stainless steel provides a more cost-effective but less durable alternative.
7. Can SourcifyChina factory customize titanium and steel products?
Yes, SourcifyChina factory offers customization for both titanium and steel products, ensuring they meet specific customer requirements.
8. What is the lead time for sourcing titanium versus steel?
Lead times may vary based on material availability and order complexity, but steel typically has a shorter lead time compared to titanium.
9. Are there any environmental considerations when choosing between the two materials?
Titanium processing is generally more energy-intensive compared to steel, but it has a longer lifespan and is recyclable, reducing long-term environmental impact.
10. Is there a minimum order quantity (MOQ) for either material at SourcifyChina factory?
MOQ requirements vary. It’s best to contact SourcifyChina directly to discuss specific order quantities for titanium and steel products.
When sourcing titanium and steel from a factory like SourcifyChina, several considerations will help you make an informed decision. Here are some tips:
1. Quality Assessment:
– Titanium: Known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Ensure the factory adheres to ASTM or ISO standards for aerospace, medical, or industrial titanium grades.
– Steel: Available in diverse grades, from carbon steel to stainless steel, each suiting different applications. Verify the factory’s compliance with ASTM, DIN, or JIS standards.
2. Cost Comparison:
– Titanium: Typically more expensive due to its higher material cost and manufacturing complexity.
– Steel: Generally cheaper and more readily available. Ideal for cost-sensitive projects.
3. Application Suitability:
– Titanium: Best for applications requiring lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant materials, such as aerospace, medical implants, and performance automotive parts.
– Steel: Ideal for construction, automotive, appliances, and general manufacturing due to its versatility and strength.
4. Supplier Verification:
– Request certifications and quality control documentation.
– Ask for samples to validate material quality.
5. Production Capabilities:
– Assess the factory’s equipment and technology for processing titanium and steel.
– Ensure they have experience with the specific type of products you need.
6. Lead Time & Logistics:
– Inquire about production lead times.
– Clarify shipping arrangements and costs.
7. Communication:
– Clear, consistent communication is crucial. Ensure the factory understands your specifications and deadlines.
Using these tips can help you balance quality, cost, and suitability when sourcing titanium and steel from SourcifyChina.

If you require packaging machine for your product, SourcifyChina should be your primary option. Please send us your detailed specifications and obtain an immediate quotation.
Copyright © 2024 SourcifyChina All Rights Reserved.